 Loading...
Loading...

HNF4A
Disease related genes, Human disease related genes, Nuclear receptors, Transcription factors
Intracellular
Cell type enhanced (Distal enterocytes, Hepatocytes, Proximal tubular cells, Proximal enterocytes, Undifferentiated cells, Paneth cells, Intestinal goblet cells)
Not detected in immune cells
Group enriched (CACO-2, Hep G2, OE19)
Homodimerization is required for HNF4-alpha to bind to its recognition site (PubMed:14982928). Interacts with CLOCK, ARNTL, CRY1, CRY2, PER1 and PER2 (PubMed:30530698). Interacts with NR0B2/SHP; the resulting heterodimer is transcriptionnally inactive (PubMed:28128295). Interacts with DDX3X; this interaction disrupts the interaction between HNF4 and NR0B2 that forms inactive heterodimers and enhances the formation of active HNF4 homodimers (PubMed:28128295).
Activator, DNA-binding, Receptor, Repressor
- Rabbit Anti-HNF4A Recombinant Antibody (clone CBACN-280) (MRO-0757-CN)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IF, IHC, FC
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1, κ
- Application: WB, ELISA, IF, IHC, IP
- Recombinant Mouse Anti-Human HNF4A Antibody (MOB-2375MZ)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse antibody
- Application: ICC/IF, WB
-
- Derivation: Phage display library
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: FC, ICC, IHC-P, IP, WB
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, ICC, IF, IHC, FC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: WB, ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Mouse
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IHC-Fr, IHC-P, ICC, IF
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IP, ChIP
-
- Type: Mouse IgG2b
- Application: ELISA, IHC, FC
Our customer service representatives are available 24 hours a day, from Monday to Sunday. Contact Us
Can't find the products you're looking for? Try to filter in the left sidebar.Filter By Tag
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.

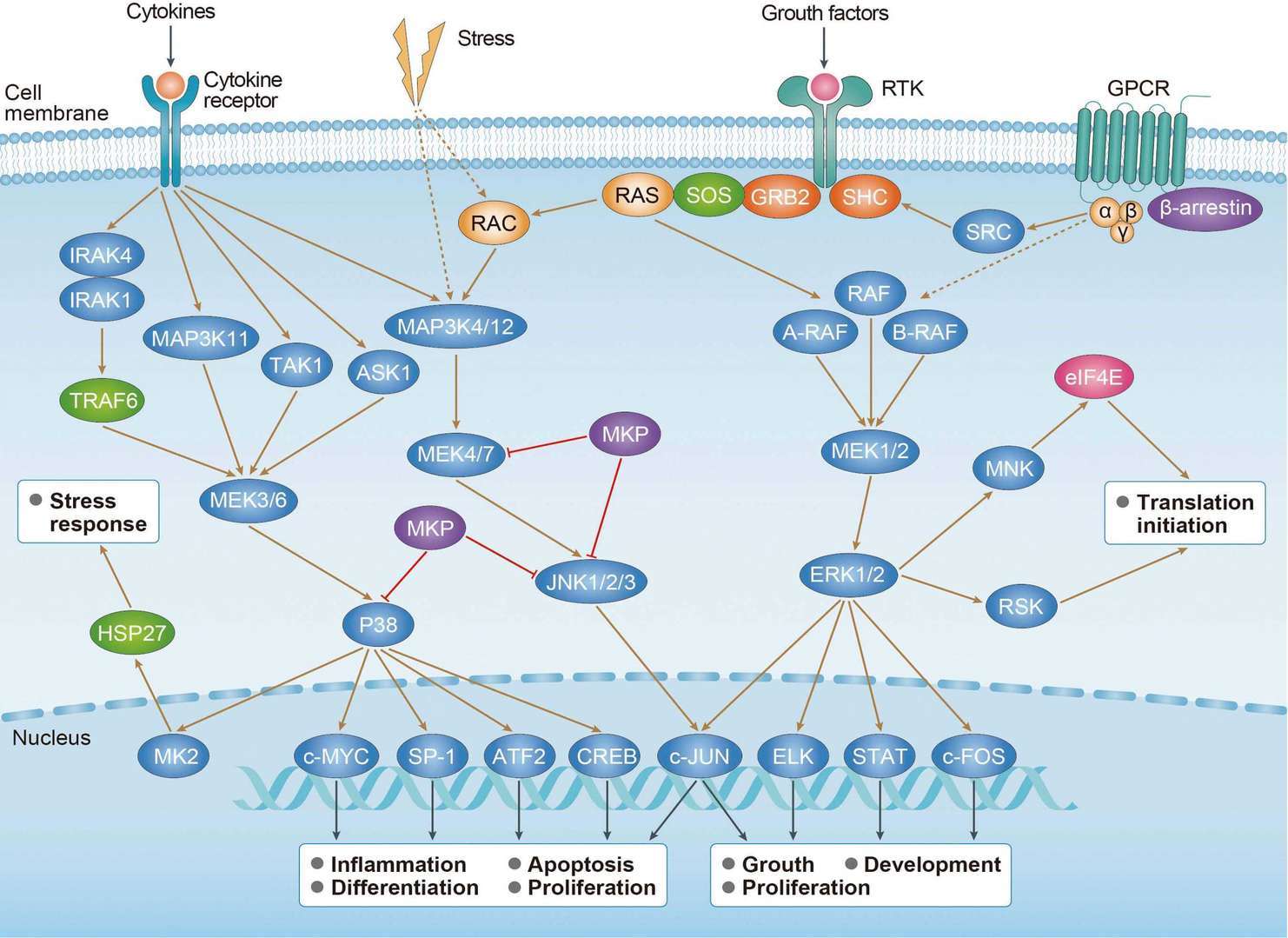 cAMP Signaling Pathway
cAMP Signaling Pathway
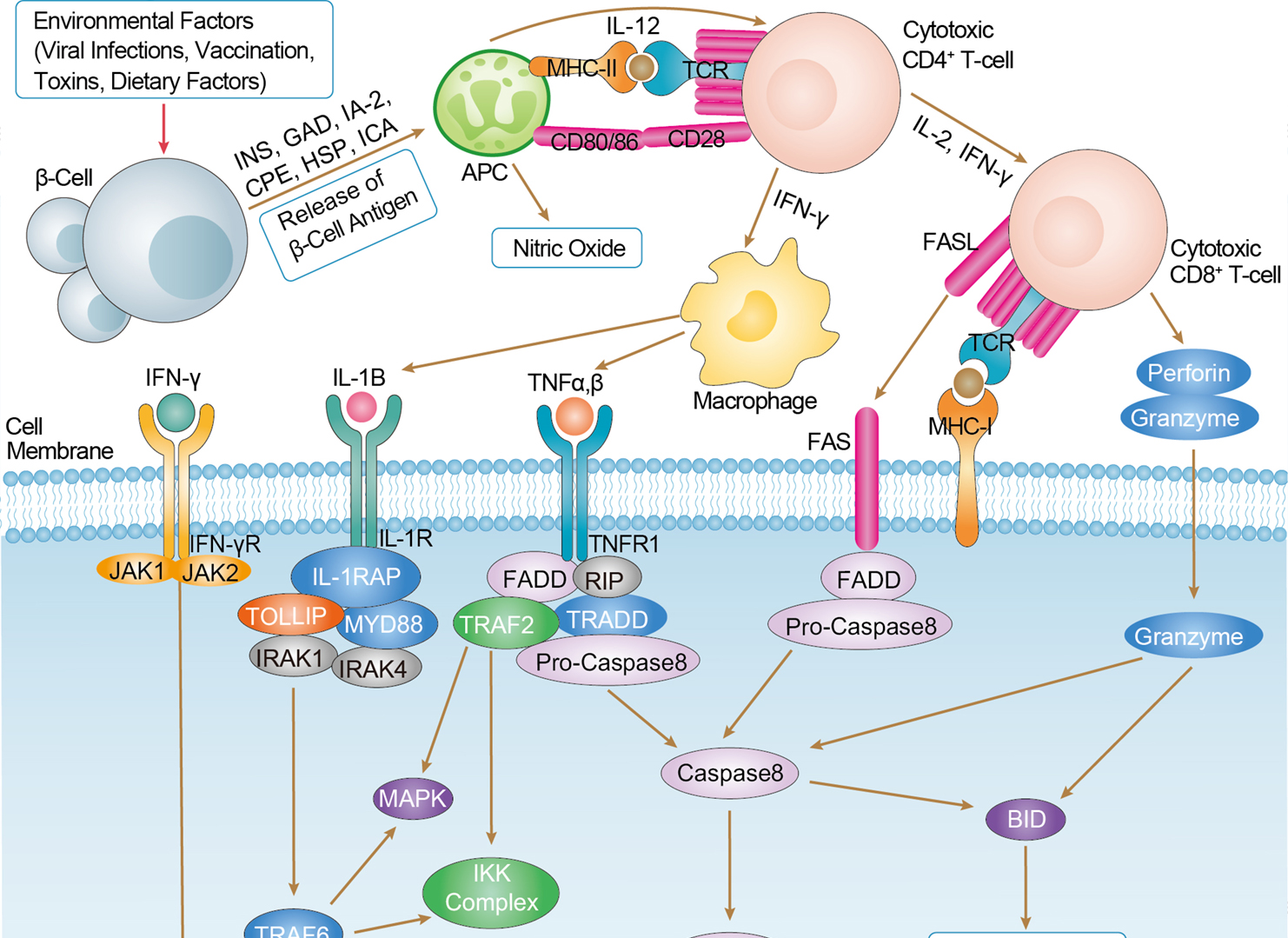 Type I Diabetes Mellitus
Type I Diabetes Mellitus