 Loading...
Loading...

ITCH
Disease related genes, Enzymes, Human disease related genes, Metabolic proteins, Potential drug targets
Intracellular
Cell type enhanced (Oligodendrocytes, Late spermatids)
Low immune cell specificity
Low cell line specificity
Monomer. Interacts (via WW domains) with OCNL (By similarity). Interacts (via WW domains) with NOTCH1 (By similarity). Interacts (via WW domains) with JUN (By similarity). Interacts with JUNB; the interaction promotes ITCH-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of JUNB (PubMed:16387660). Interacts with FYN; the interaction phosphorylates ITCH on Tyr-420 decreasing binding of JUNB (PubMed:16387660). Interacts (via WW domain 2) with N4BP1; the interaction inhibits the E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase activity (By similarity). Interacts with NDFIP1 and NDFIP2; this interaction activates the E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase and may induce its recruitment to exosomes (By similarity). Interacts with ARHGEF7 (PubMed:17652093). Interacts with RNF11 (PubMed:14559117, PubMed:19131965). Interacts (via the WW 1 domain) with NFE2 (via the PXY motif 1); the interaction promotes 'Lys-63'-linked ubiquitination of NFE2, retains it in the cytoplasm and prevents its transactivation activity (PubMed:11318614, PubMed:18718448). Interacts (via WW domains) with CXCR4 (via C-terminus); the interaction depends on CXCR4 phosphorylation (PubMed:19116316). Found in a complex with E3 ligase DTX3L and ESCRT-0 components HGS and STAM (PubMed:24790097). Interacts with DTX3L (via C-terminus); the interaction is increased upon CXCL12 stimulation and inhibits ITCH catalytic activity (the interaction is direct) (PubMed:24790097). Interacts with HGS (PubMed:14602072). Interacts (via WW domains) with PCBP2 within a complex containing ITCH, MAVS and PCBP2 (PubMed:19881509). Interacts (via WW domains) with TXNIP (via C-terminus) (PubMed:20068034). Interacts with p15 BID (PubMed:20392206). Interacts with ERBB4 (PubMed:20858735). Interacts with DTX1 (PubMed:17028573). Interacts with SPART (PubMed:19580544). Interacts with SNX9 and SNX18 (PubMed:20491914). Interacts (via its WW domains) with ATN1 (PubMed:9647693). Interacts (via WW domains) with SGK3 (PubMed:16888620). Interacts with CBLC (PubMed:12226085). Interacts with OTUD7B (PubMed:22179831). Interacts (via WW domain 1,2 and 3) with PI4K2A; the interaction inhibits PI4K2A catalytic activity and promotes ITCH catalytic activity (PubMed:23146885). Interacts with ARRDC4 (PubMed:23236378). Part of a complex containing ITCH, NDFIP1 and MAP3K7 (By similarity). Interacts with UBE2L3; the interaction is mediated by NDFIP1 (PubMed:25632008). Interacts with MAPK8/JNK1 (By similarity). Interacts (via WW domains) with ARRDC1 (via PPxY motifs); the interaction is direct and participates in the recruitment of the ubiquitin-protein ligase ITCH to the NOTCH1 receptor (PubMed:21191027, PubMed:23886940). Interacts (via WW domains) with ARRDC2 (PubMed:21191027). Interacts (via WW domains) with ARRDC3 (PubMed:21191027, PubMed:23886940). Interacts directly with LDLRAD3; this interaction promotes ITCH auto-ubiquitination leading to its degradation (PubMed:26854353). (Microbial infection) Interacts with Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A. (Microbial infection) Interacts with Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) protein UL42; this interaction induces ubiquitination and degradation of ITCH. (Microbial infection) Interacts with herpesvirus 1 (HHV-1) UL56 protein; this interaction induces ubiquitination and probably degradation of ITCH. (Microbial infection) Interacts with herpesvirus 2 (HHV-2) UL56 protein. (Microbial infection) Interacts with varicella-zoster virus (VZV) Orf0 protein. (Microbial infection) Interacts with herpesvirus 6A (HHV-6A) U24 protein. (Microbial infection) Interacts with ebola virus protein VP40; this interaction is required for efficient viral egress from the infected cell. (Microbial infection) Interacts with influenza A virus matrix protein 1.
Transferase
-
- Derivation: Phage display library screening
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: IgG
- Application: WB
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA, WB
Our customer service representatives are available 24 hours a day, from Monday to Sunday. Contact Us
Can't find the products you're looking for? Try to filter in the left sidebar.Filter By Tag
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.

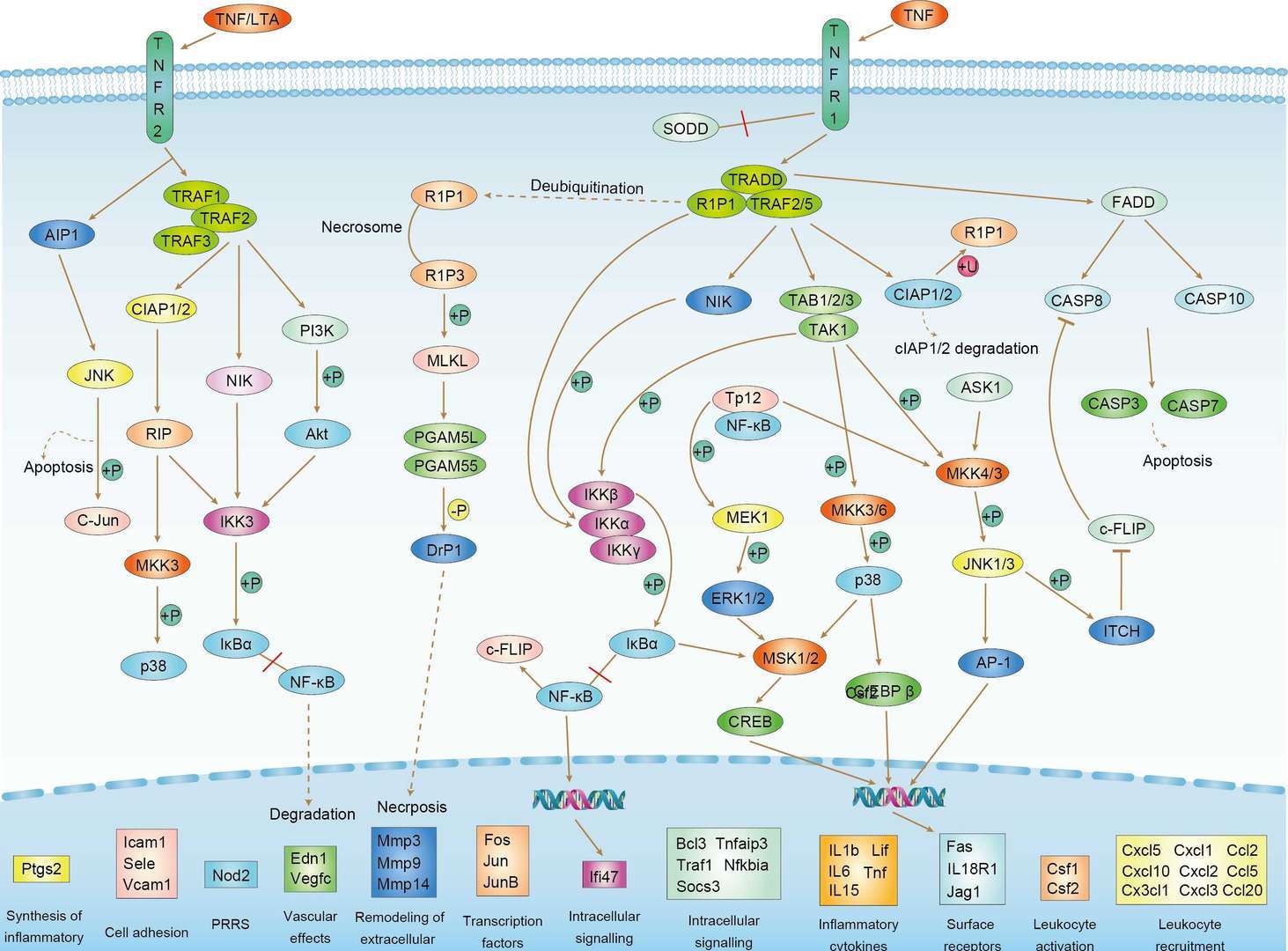 TNF Signaling Pathway
TNF Signaling Pathway