cAMP Signaling Pathway
About cAMP Pathway
Cyclic adenosine 3’,5’-monophosphate (cAMP) was the first identified second messenger that involved in many hormones and neurotransmitters regulate in cell. The intracellular levels of cAMP are regulated by the balance between adenylyl cyclase (AC) and the cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (PDE), which are regulated positively and negatively by numerous other signaling pathways such as calmodulin, G protein-coupled receptors and so on. Protein kinase A (PKA), the GTP-exchange protein EPAC and the cyclic-nucleotide-gated ion channels are three well-known main efforts of cAMP.
The PKA is consist in two regulatory (R) subunits and two catalytic (C) subunits, and actives when cAMP binding to R subunits. Once activated, R subunits would dissociate from the C subunits, and the C subunits will phosphorylate and activate many downstream target proteins, resulting in cascade signal transmission. PKA can directly phosphorylate transcription factors such as cAMP-response element-binding protein (CREB), cAMP-responsive modulator (CREM), and ATF1, regulating transcription. In addition, PKA also phosphorylates NF-κB and regulates NF-κB signals.
EPAC, a specific GTP exchange-protein for the small GTPase Rap1, is another important target of cAMP. When binding to cAMP, EPAC is activated and mediated the signal transduction of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway. Some studies suggest that it may work by binding and activating B-Raf and/or inhibiting Ras-Raf pathway. But the detailed mechanism needs more research.
Finally, cAMP also modulate intracellular pathway through cyclic-nucleotide-gated ion channels. This ion channel can conduct ca2+ to stimulate CaM and CaM-dependent kinases, which influence the activities of AC and PDE, and modulate the production of cAMP finally. Besides, sodium and potassium are also permeable to this channel to alter the membrane potential in electrically active cells.
In general, cAMP is a key secondary massager that regulates multiple pivotal physiologic processes including metabolism, secretion, calcium homeostasis, muscle contraction, cell fate, and gene transcription.
Related Pathways
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.


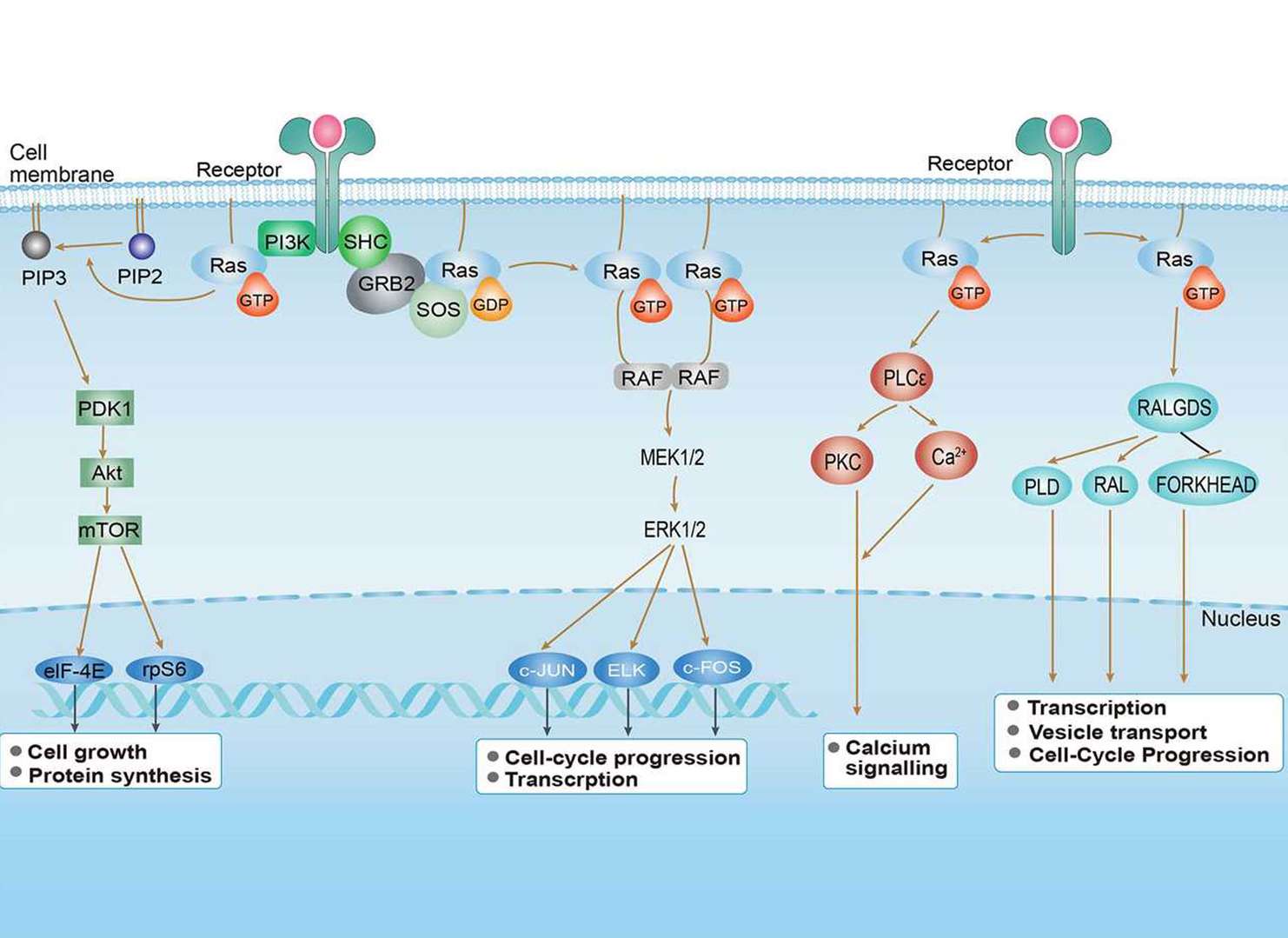 Ras Signaling Pathway
Ras Signaling Pathway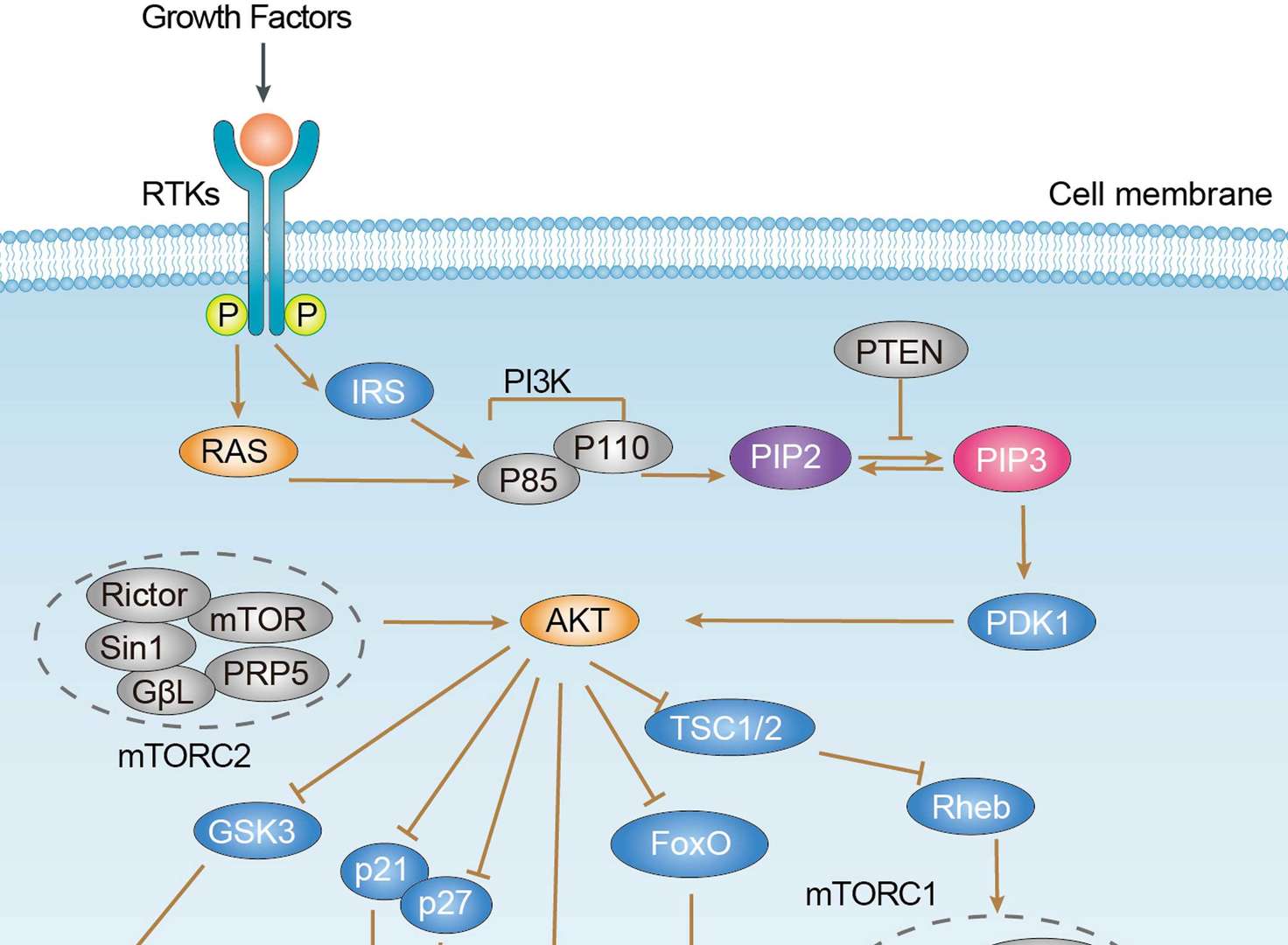 PI3K-Akt Pathway
PI3K-Akt Pathway
