Canakinumab Overview
Introduction of Canakinumab
Canakinumab (previously ACZ885) is a human monoclonal antibody (mAb) targeting interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β). It has no cross-reactivity with other members of the interleukin-1 family, including interleukin-1 alpha (IL-1α). It was developed for the treatment of cryopyrin-associated periodic syndromes (CAPS). CAPS is a spectrum of autoinflammatory syndromes including familial cold autoinflammatory syndrome, Muckle–Wells syndrome, and neonatal-onset multisystem inflammatory disease. In September 2016, FDA approved the use of canakinumab on 3 additional rare and serious auto-inflammatory diseases: Tumor necrosis factor receptor associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS), Hyperimmunoglobulin D syndrome (HIDS)/Mevalonate kinase deficiency (MKD) and Familial Mediterranean fever (FMF).
Mechanism of Action of Canakinumab
Interleukin-1 (IL-1) consists of a group of cytokines that activate the expression of several pro-inflammatory genes. The 11 members of the IL-1 family of genes include IL-1β, as well as the anti-inflammatory interleukin-1-receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) that acts as a regulator of IL-1β signaling. Numerous studies suggest that the severity of inflammation is influenced by the relative amounts of IL-1 and IL-1Ra. IL-1β is a pro-inflammatory cytokine that acts as mediator of the peripheral immune response during infection and inflammation, but is also implicated in acute and chronic autoimmune diseases, diabetes, pain and neurological disorders. And IL-1β is a more potent mediator of inflammation than IL-1α, it is initially synthesized in the form of a precursor peptide (pro-IL-1β) that is cleaved in the inflammasome complex by caspase-1, and secreted into the extracellular space. There are two IL-1 receptors, IL-1RI and IL-1RII; IL-1β exerts its action on target cells through the receptor IL-1RI. IL-1β can be released by various cell types, including macrophages, keratinocytes, fibroblasts, microglia and astrocytes, as well as mast, endothelial, neuronal and Schwann cells. Dysregulated IL-1β activity is characteristic of autoimmune diseases and may occur due to either abnormally increased levels of the cytokine, or qualitative or quantitative deficiency of IL-1RI endogenous antagonist. IL-1β is specifically implicated in several autoinflammatory diseases. Canakinumab is a human IgG1κ mAb targeting IL-1β. Its mode of action is based on the neutralization of 1β signaling, resulting in suppression of inflammation in patients with disorders of autoimmune origin.
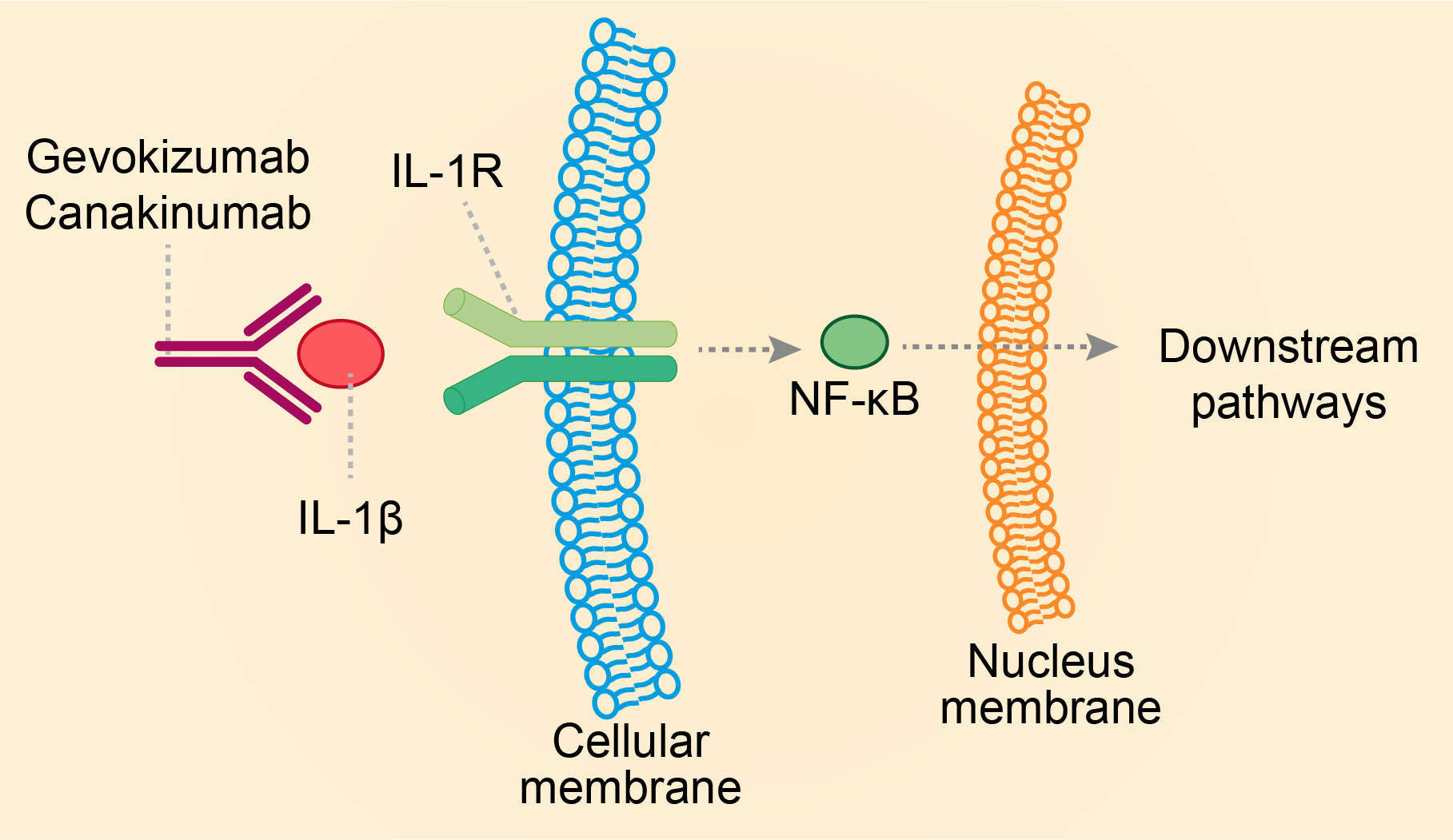 Fig.1 Mechanism of action of canakinumab
Fig.1 Mechanism of action of canakinumab
What We Provide
Therapeutic Antibody
Canakinumab
We provide high-quality Canakinumab for use in WB, FC, IP, ELISA, Neut, FuncS, IF and most other immunological methods. For lab research use only, not for diagnostic, therapeutic or any in vivo human use.
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.


