Glembatumumab Overview
Introduction of Glembatumumab
Glembatumumab (CR011) is a fully human IgG2 monoclonal antibody (mAb) that targets cancer cells expressing transmembrane glycoprotein NMB (GPNMB, or osteoactivin). It was designed to linke to monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE) via a valine-citrulline enzyme-cleavable linker to act as an antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) termed glembatumumab vedotin (also known as CDX-011 and CR011-vcMMAE) for the treatment of advanced, refractory, or resistant GPNMB-expressing breast cancer.
Mechanism of Action of Glembatumumab Vedotin
gpNMB shows homology closest to pMEL-17, a melanocyte-specific marker that is differentially expressed in melanoma cells. Both are intracellular transmembrane proteins that transit the cell surface, representing a new class of targets for ADCs. gpNMB is expressed in subcellular compartments and on the cell surface on multiple cell types, including epithelial cells, osteoclasts, osteoblasts, macrophages, and dendritic cells (DCs). A number of tumors, including those of melanoma, breast cancer, and glioblastoma, overexpress gpNMB relative to normal tissue. Overexpression of gpNMB promotes invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma, glioma, and breast cancer cells, decreases tumor cell apoptosis, and promotes angiogenesis in preclinical models. As an ADC, glembatumumab vedotin consists of a human anti-GPNMB antibody conjugated to the anti-mitotic agent MMAE, it binds to GPNMB on the surface of cancer cells, followed by internalization of the conjugate by endocytosis and release of its cytotoxic payload MMAE after lysosomal degradation. MMAE is a synthetic antineoplastic agent. Because of its toxicity, it cannot be used as a drug itself; instead, it is usually linked to a mAb which directs it to the cancer cells. MMAE disrupts microtubules and induces apoptosis of the tumor cell. In addition to the direct cytotoxic effect of MMAE at the cellular level, the antitumor effect of enfortumab vedotin can be mediated through additional mechanisms involving signal transduction inhibition from direct binding, antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) and complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC).
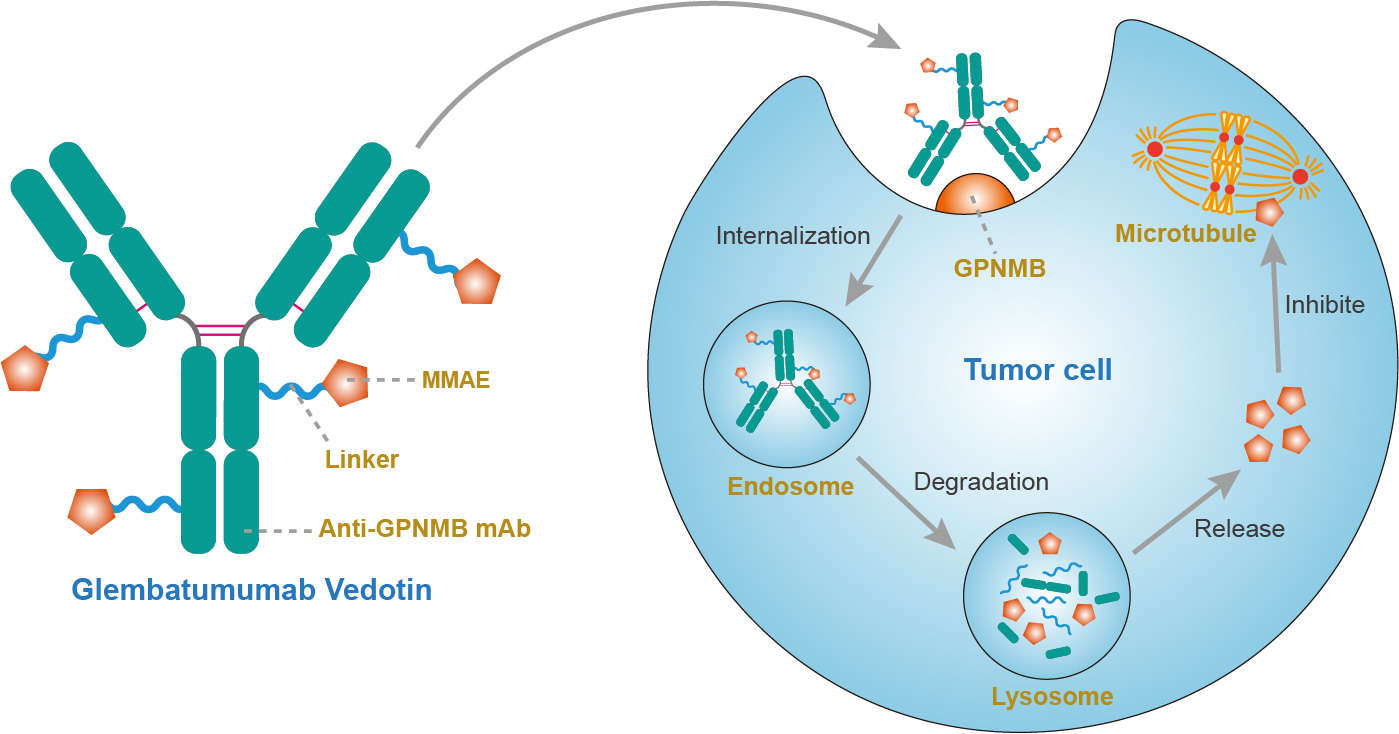 Fig.1 Mechanism of action of glembatumumab vedotin
Fig.1 Mechanism of action of glembatumumab vedotin
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.



