High-Yield Monomeric IgA Purification Service
Background Service Highlights FAQs Contact
High-Yield Monomeric IgA Purification: Advancing Research and Therapeutic Development
Immunoglobulin A (IgA) stands as the predominant antibody isotype in mucosal secretions, constituting the first line of defense against a myriad of pathogens at epithelial barriers. It also circulates in serum, primarily in a monomeric form, where it contributes to systemic immunity. Structurally, IgA in secretions is typically a dimer (or larger polymer) complexed with a J-chain and a secretory component (SC), forming secretory IgA (sIgA). Serum IgA is mostly monomeric, although a notable fraction (around 10-15% in healthy adults, and potentially higher in certain conditions or age groups, as highlighted by studies like those showing a high proportion of polymeric IgA in young infants' sera) exists as polymers.
The dual structural nature and diverse functional roles of IgA-ranging from pathogen neutralization and agglutination to interaction with various Fc receptors like FcαRI (CD89) for triggering effector functions-make it a molecule of intense research interest. Its applications span diagnostics, vaccine development (particularly for mucosal vaccines), and therapeutics, including engineered IgA antibodies for oncology and infectious diseases.
A critical requirement for advancing these applications is the availability of highly pure, well-characterized IgA, especially in its monomeric form for many systemic applications and specific research assays. The inherent heterogeneity of IgA preparations (due to glycosylation, oligomerization, and potential degradation) poses significant purification challenges. Developing robust, scalable, and reproducible methods for high-yield monomeric IgA purification is therefore paramount.
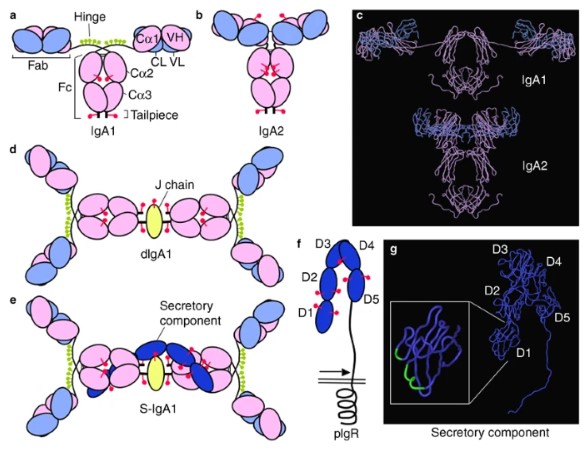 Fig.1 Schematic structure of human IgA.1
Fig.1 Schematic structure of human IgA.1
High-Yield Monomeric IgA Purification Service at Creative Biolabs
Creative Biolabs offers a specialized High-Yield Monomeric IgA Purification service designed to provide researchers and biopharmaceutical developers with top-quality monomeric IgA tailored to their specific needs. Recognizing the complexities associated with IgA, particularly its tendency to form polymers and aggregates, our service leverages state-of-the-art chromatographic techniques and optimized protocols to isolate monomeric IgA with exceptional purity and yield from diverse sources.
Service Content: A Step-by-Step Approach to Pure Monomeric IgA
Our High-Yield Monomeric IgA Purification service at Creative Biolabs is a comprehensive, multi-stage process meticulously designed to maximize recovery and purity.
Consultation and Strategy Development
Every project begins with an in-depth consultation to understand the client's specific requirements: the source of IgA (e.g., hybridoma supernatant, ascites, serum, recombinant expression systems like CHO or HEK293 cells), the IgA isotype and subclass (e.g., human IgA1, IgA2, murine IgA), desired yield, target purity (especially monomeric content), buffer specifications, and intended downstream applications.
Based on this, a customized purification strategy is developed, outlining the proposed chromatographic steps and quality control parameters.
Starting Material Preparation
Upon receipt, the starting material undergoes necessary pre-processing. This may include clarification (centrifugation and/or filtration to remove cells and debris), buffer exchange to ensure compatibility with the initial chromatography step, and sometimes initial concentration if the starting volume is large and IgA concentration is low.
Initial Capture and Enrichment
The primary capture step typically involves affinity chromatography. Depending on the IgA type and source, various ligands can be employed:
-
Protein L: Effective for many kappa light chain-containing IgAs.
-
Jacalin: A lectin that binds to the O-linked glycans typically found on the hinge region of human IgA1.
-
Peptide M: A synthetic ligand with high affinity for human IgA.
-
Anti-IgA specific antibodies: For highly selective capture.
This step aims to significantly enrich the IgA fraction and remove the bulk of non-IgA proteins. Elution conditions are carefully optimized to preserve IgA integrity.
Intermediate Purification (Optional)
Following the capture step, an intermediate purification step, such as ion-exchange chromatography (IEX) or hydrophobic interaction chromatography (HIC), may be incorporated.
IEX separates proteins based on net surface charge differences, effective for removing remaining host cell proteins or other IgA variants.
HIC separates based on hydrophobicity and can be useful for further polishing.
The choice of method and conditions is tailored to the specific impurities present.
High-Resolution Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC)
This is the crucial step for separating monomeric IgA from dimers, higher-order polymers, and aggregates. Creative Biolabs utilizes advanced SEC resins and columns that provide excellent resolution based on hydrodynamic volume.
Fractions corresponding to the monomeric IgA peak are carefully collected. The efficiency of this step is critical for achieving high monomeric purity (often >95% or >98%).
Final Formulation and Quality Control
The purified monomeric IgA is buffer exchanged into a client-specified formulation suitable for its intended use and long-term stability.
Rigorous quality control (QC) is performed, including:
-
Concentration determination: (e.g., A280 nm, BCA assay).
-
Purity assessment: SDS-PAGE (reducing and non-reducing conditions) to visualize protein bands and estimate purity.
-
Monomeric content verification: Analytical SEC-HPLC to precisely quantify the percentage of monomer, dimer, and aggregates.
-
Optional tests: Endotoxin testing (LAL assay), specific binding activity assays (e.g., ELISA, SPR), or other client-requested analyses.
A comprehensive purification report and Certificate of Analysis (CoA) are provided with the final product.
Why Choose Us
Creative Biolabs stands out as a preferred partner for High-Yield Monomeric IgA Purification due to several key advantages:
-
Customization and Flexibility:
-
State-of-the-Art Technology
-
Commitment to Quality
Proven Track Record
FAQs
Q1: What is the typical yield and purity of monomeric IgA I can expect from Creative Biolabs' service?
A: Yield is highly dependent on the expression level in the starting material. However, our optimized processes aim to maximize recovery. We routinely achieve >95% monomeric purity as determined by SEC-HPLC, and can often reach >98% or higher based on project requirements. We will discuss achievable targets during the initial consultation.
Q2: How does Creative Biolabs ensure the biological activity of the purified monomeric IgA is preserved?
A: We prioritize maintaining biological activity by using mild purification conditions, avoiding harsh chemicals or extreme pH where possible, performing procedures at controlled temperatures (typically 4°C), and using buffers that promote stability. If you have a specific activity assay, we can discuss incorporating it into our QC.
Q3: What starting material and quantity are typically required?
A: This varies greatly depending on the IgA concentration in your sample and your desired final yield. We can work with a wide range, from milligrams to grams of starting IgA. Please contact us with details about your specific material (e.g., cell culture supernatant volume and estimated titer, ascites volume, serum volume).
Contact Us
Creative Biolabs is dedicated to providing exceptional protein science solutions. If you are seeking high-quality, pure, and functional monomeric IgA, our team of experts is ready to assist you. Let us help you accelerate your research and therapeutic development with our specialized purification services.
For inquiries, detailed discussions about your project, or to request a quote, please contact Creative Biolabs today.
Reference
-
Woof, J. M., and M. W. Russell. "Structure and function relationships in IgA." Mucosal immunology 4.6 (2011): 590-597. Distributed under Open Access License CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.


 Fig.1 Schematic structure of human IgA.1
Fig.1 Schematic structure of human IgA.1