Immunoradiometric Assay Protocol & Troubleshooting
Immunoradiometric assay (IRMA) is an immunoassay that uses radiolabeled antibodies to bind sample antigens. In this assay, the antibody is labeled using a radioisotope. The radiolabeled antibody binds to the antigen to form an antigen-antibody complex. Finally, the antigen-bound portion is radiometrically determined.
Based on the principles of immunoradiometric assays, we describe experimental protocols for the quantification of compound concentrations using radiolabeled specific antibodies. We provide IRMA-related methods and troubleshooting to provide standardization and accuracy for your actual measurements.
Solutions and Reagents
| Stages | Solutions and Reagents |
| Preparation | Standards, dilution buffer |
| Antigen-antibody reaction | Solid-phase carrier materials, capture antibody, labeled antibody, dilution buffer, blocking agent, isolating agent, washing buffer |
Immunoradiometric Assay Procedure
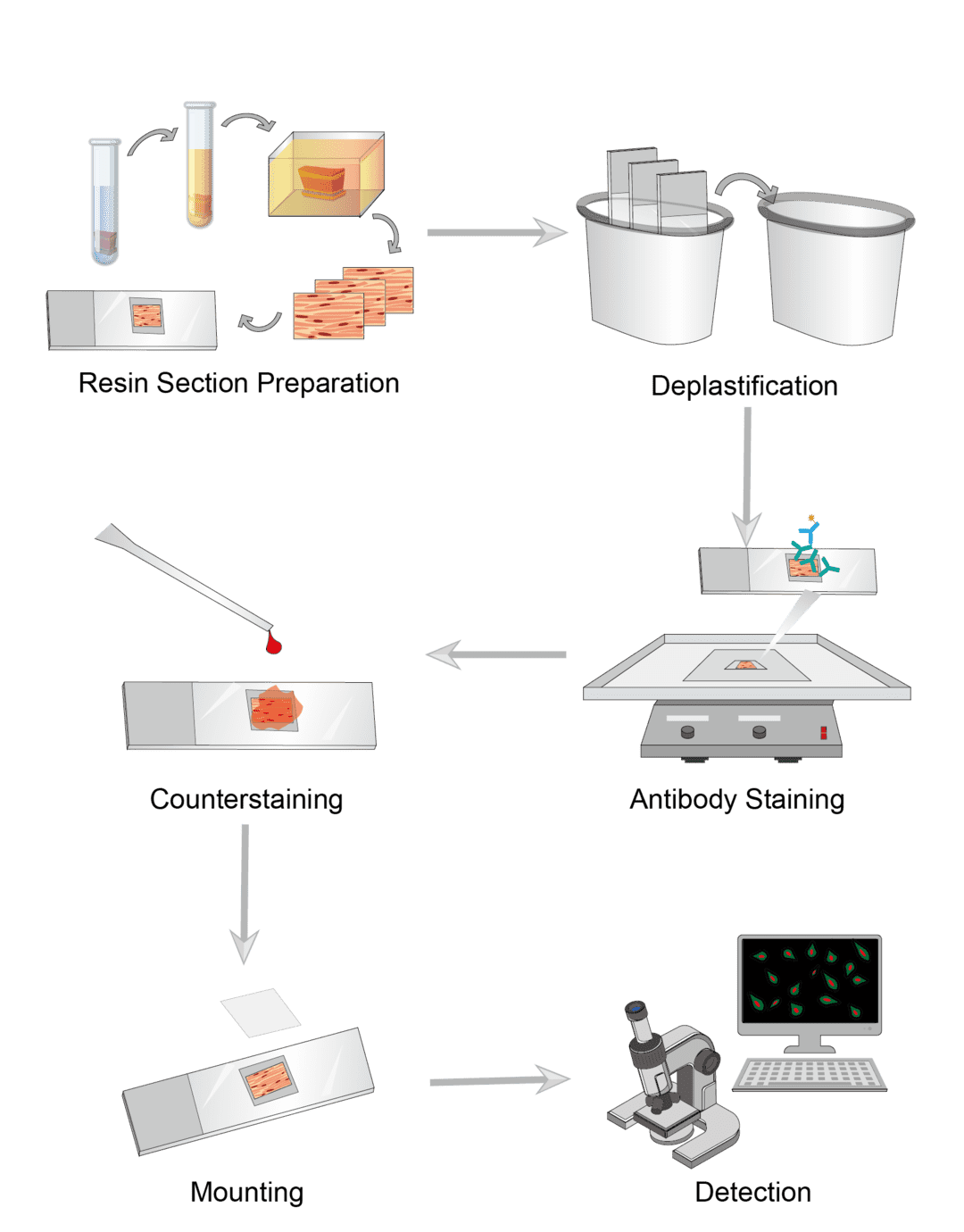
First prepare the sample to be tested and the standard. Dilute the sample appropriately using dilution buffer. Select the assay range to design the concentration of the standard solution and perform a gradient dilution.
First, absorb the antibody onto the surface of the solid phase carrier to make a capture agent. The commonly used solid phase carriers are polystyrene, which can be made into microtubes, discs and microspheres. The specific style is designed according to the needs of the experiment. Then incubate the capture antibody with the sample. The antigen in the sample reacts immunologically with the antibody on the solid phase carrier.
Add radioisotope-labeled antibody and incubate. Since the antigen has multiple binding sites, it can bind to the labeled antibody and eventually form an antibody-antigen-labeled antibody immune complex on the surface of the solid phase carrier. Finally, wash with buffer to remove the free labeled antibodies.
Determine the count rate of radioactivity carried by the solid phase. Plot the curve according to the standards and calculate the sample antigen concentration.
Troubleshooting
High background
- Contamination causes. We recommend the appropriate use of a well sealer to avoid cross-well contamination. And use a multichannel pipette to pipette without touching the reagents in the plate.
- Washing causes. It may be the cause of insufficient washing. You need to increase the number of washes.
Low signal
- Sample causes. Antigens may not be present in the sample or may be present in smaller amounts. You can increase the sample volume or replace it with a sample that has a high concentration of antigen. It is also important to use a precision pipette to add samples accurately and avoid contamination.
- Incubation causes. The temperature and time of incubation should be ensured to be suitable. You should incubate for the time required by the reagent instructions, which can be extended as appropriate. The temperature should be kept as consistent as possible without much error.
- Antibody causes. Add sufficient amount of antibody solution. Ensure adequate reaction of the antigen antibody and adequate binding of the antigen antibody complex with the secondary antibody.
Measurement error
- Instrument causes. The accuracy, stability, and contamination of equipment can introduce errors, including radioactivity measurement instruments, sample containers, pipettes, and a host of other instruments used. We recommend checking the accuracy and stability of the equipment before starting the test to minimize this error.
- Reagent causes. The purity, quality, and stability of reagents are also important factors in causing errors, such as antibodies, buffer solutions, blocking agents, and other reagents. Similarly, check the purity and stability of the reagents used before starting the test.
- Sample causes. Sample collection, storage, removal, and possible contamination and denaturation can all contribute to measurement errors. Check the quality of the sample to ensure it is ready for testing.
You can refer to our IRMA protocols and troubleshooting for your measurements. As well as our IRMA services include custom radiolabeling services. If you are interested in our services, please contact us.
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

