Simtuzumab Overview
Introduction of Simtuzumab
Simtuzumab (formerly GS-6624) is a humanized IgG4 monoclonal antibody (mAb) that specifically binds and inhibits lysyl oxidase homolog 2 (LOXL2) and acts as an immunomodulator. It was designed by Gilead Sciences for the treatment of fibrosis. Simtuzumab binds to LOXL2, was shown to have a role in suppressing bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in a murine model. Therefore, simtuzumab was a logical choice as a potentially effective pharmacological treatment for treatment of IPF, and screening for a phase 2 randomised clinical trial began in 2013. In January 2016, Gilead Sciences terminated its Phase 2 clinical study in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) due to lack of efficacy.
Mechanism of Action of Simtuzumab
Collagen crosslinking is an essential process for fibrotic matrix stabilisation, which contributes to fibrosis progression and limits reversibility of liver fibrosis. Thus, inhibition of collagen crosslinking is considered to be a promising therapeutic strategy in fibrotic diseases. At least two types of crosslinking enzymes, tissue transglutaminase (TG2) and the lysyl oxidase (LOX) family, are overexpressed in hepatic fibrosis. LOX family enzymes are secreted, copper-dependent amine oxidases that oxidise and deamidate the side chain of peptidyl lysine, which produces α-aminoadipic-δ-semialdehyde residues that react with the amino group of peptidyl lysine on a second collagen (or elastin) chain to form a covalent interchain crosslink. The LOX family is comprised of five isoforms, LOX and the LOX-like enzymes LOXL, with overlapping but distinct functions and expression patterns in normal and diseased tissues. The prototypic member of the family is essential to the biogenesis of connective tissue, encoding an extracellular copper-dependent amine oxidase that catalyses the first step in the formation of crosslinks in collagens and elastin. A highly conserved amino acid sequence at the C-terminus end appears to be sufficient for amine oxidase activity. The N-terminus is poorly conserved and may impart additional roles in developmental regulation, senescence, tumor suppression, cell growth control, and chemotaxis to each member of the family. LOX and LOXL2, both belong to the LOX family, have been reported to be overexpressed in Wilson's disease and murine liver fibrosis. Only recently, proof-of-concept experiments using the non-selective LOX inhibitor b-aminopropionitrile (BAPN) confirmed that overall LOX activity functionally contributes to fibrotic matrix crosslinking and stabilisation, and retards reversal of CCl4-induced liver fibrosis. However, it is currently unclear which specific enzyme(s) within the LOX family are most relevant for collagen stabilisation, and whether functions other than collagen crosslinking mediate their putative profibrotic effects. Simtuzumab was designed to specifically target and block the LOXL2 which has been assigned to an important role in fibrosis.
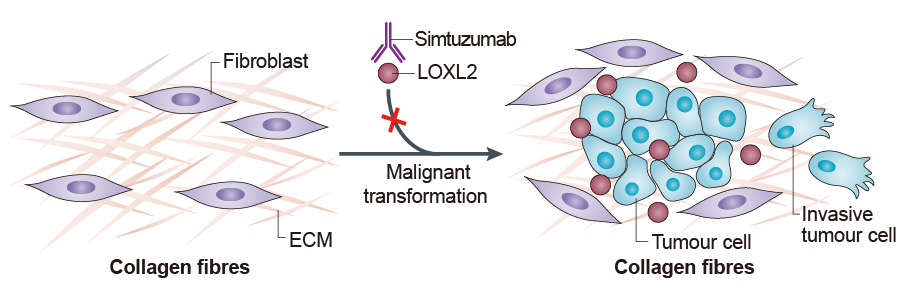 Fig.1 Mechanism of action of Simtuzumab
Fig.1 Mechanism of action of Simtuzumab
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

