Anti-CASP1 Recombinant Antibody Products
 Loading...
Loading...Anti-Casp1 Products
 Loading...
Loading...- Mouse Anti-CASP1 Recombinant Antibody (clone B0-6) (MRO-0236-CN)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: WB, IF, IHC
- Rabbit Anti-CASP1 Recombinant Antibody (clone CBACN-086) (MRO-0237-CN)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IHC, FC
- Rabbit Anti-CASP1 Polyclonal Antibody (MRO-1718-CN) (MRO-1718-CN)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IHC
- Rabbit Anti-CASP1 Polyclonal Antibody (MRO-1719-CN) (MRO-1719-CN)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: IF, IHC, FC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IHC, FC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IP
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1, κ
- Application: WB, IF, IHC, IP
- Mouse Anti-CASP1 Recombinant Antibody (clone EML275) (MOB-0323CT)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG2a
- Application: IHC-P, WB
- Recombinant Anti-Mouse Casp1 VHH Single Domain Antibody (NAB-209-sdAb)
-
- Species Reactivity: Mouse
- Type: Llama VHH
- Application: FA, FC, ICC, ELISA
-
- Derivation: Phage display library screening
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, ELISA, IHC-P, IHC-Fr, FC, ICC, IF
- Anti-CASP1 Immunohistochemistry Kit (VS-0525-XY993)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Target: CASP1
- Application: IHC
Can't find the products you're looking for? Try to filter in the left sidebar.Filter By Tag
Our customer service representatives are available 24 hours a day, from Monday to Sunday. Contact Us
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.
Creative Biolabs has you covered when it comes to immunology and inflammation research! We can provide highly specific and validated anti-CASP1 recombinant antibodies to suit your needs. Caspase-1 (CASP1) is a prototypical inflammatory caspase and the motor of the inflammasome, the master initiator of the innate immune response. Our premium antibodies can help you study pyroptosis, the processing of critical cytokines, and the development of novel anti-inflammatory therapeutics.
CASP1: The Inflammasome's Executioner Enzyme
Caspase-1, also called Interleukin-1 Converting Enzyme (ICE), is a cysteine protease that is a key initiator of inflammation. It is expressed as an inactive proenzyme called pro-caspase-1. In response to pathogen and/or cellular danger signals that are detected by intracellular sensor proteins like NLRP3, large protein platforms known as inflammasomes are formed. Inflammasomes act to recruit and activate pro-caspase-1, which is then activated through dimerization due to proximity with auto-cleavage. Active caspase-1 then performs two critical functions. It cleaves the inflammatory cytokines pro-IL-1beta and pro-IL-18, producing mature, secreted IL-1beta and IL-18. Caspase-1 also cleaves Gasdermin D, which initiates a fiery, lytic form of cell death known as pyroptosis.
Alternative Names
Caspase 1; Caspase 1, Apoptosis-Related Cysteine Peptidase; Interleukin 1, Beta, Convertase; IL-1 Beta-Converting Enzyme; EC 3.4.22.36; Caspase-1; IL1BC; P45; ICE; Caspase 1, Apoptosis-Related Cysteine Peptidase (Interleukin 1, Beta, Convertase); Caspase 1, Apoptosis-Related Cysteine Protease (Interleukin 1, Beta, Convertase);
Background
Enables cysteine-type endopeptidase activity. Involved in several processes, including AIM2 inflammasome complex assembly; positive regulation of canonical NF-kappaB signal transduction; and positive regulation of interleukin-1 beta production. Acts upstream of or within several processes, including membrane hyperpolarization; mitochondrial depolarization; and positive regulation of cytokine production. Located in extracellular region. Part of IPAF inflammasome complex. Is active in cytosol. Is expressed in several structures, including forelimb mesenchyme; knee joint; oocyte; small intestine; and telencephalon. Orthologous to human CASP1 (caspase 1).
Enzymes, Plasma proteins
Intracellular
Cell type enriched (Neutrophils)
Group enriched (neutrophil, monocyte, eosinophil)
Cell line enhanced (THP-1, U-937, ACHN, HeLa, MOLT-4)
Cysteine peptidase, Aspartate peptidase, Hydrolase
Anti-CASP1 rAb Products
Creative Biolabs' anti-CASP1 recombinant antibodies are validated to be highly specific and performant. We have carefully tested these antibodies to make sure that they detect both the pro-form of caspase-1 as well as the cleaved, active p20/p10 subunits. We have optimized these antibodies for Western Blot applications to track inflammasome activation, and they have become a gold standard for the field of inflammation research, giving you clear and unambiguous results.
Table 1. Featured anti-CASP1 recombinant antibody products at Creative Biolabs.
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Target Species | Host Species | Applications |
| MRO-0236-CN | Mouse Anti-CASP1 Recombinant Antibody (clone B0-6) | Human, Mouse, Rat | Mouse IgG1 | WB, IF, IHC |
| MRO-0237-CN | Rabbit Anti-CASP1 Recombinant Antibody (clone CBACN-086) | Human, Mouse, Rat | Rabbit IgG | WB, IHC, FC |
| MOB-3801z | Mouse Anti-CASP1 Recombinant Antibody (clone 12G12) | Human | Mouse IgG1, κ | WB, IF, IHC, IP |
Customer Reviews

Mouse Anti-CASP1 Recombinant Antibody (clone B0-6)
rAb Production
Creative Biolabs is proud to provide tools that support the specialized field of immunology with its state-of-the-art antibody production platforms. We express our anti-CASP1 recombinant antibodies in an optimized system to make sure that the antibody can recognize the various forms of the enzyme in question to give you a specific and active tool for your research.
Featured Anti-CASP1 Recombinant Antibody Production Platforms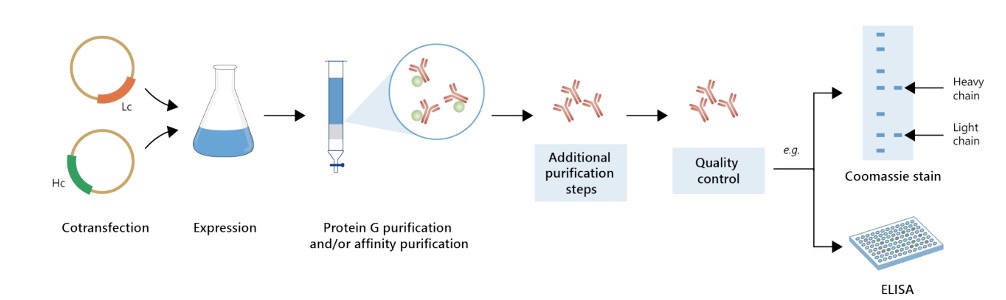
Fig.1 Milligram-scale anti-CASP1 recombinant antibody production.
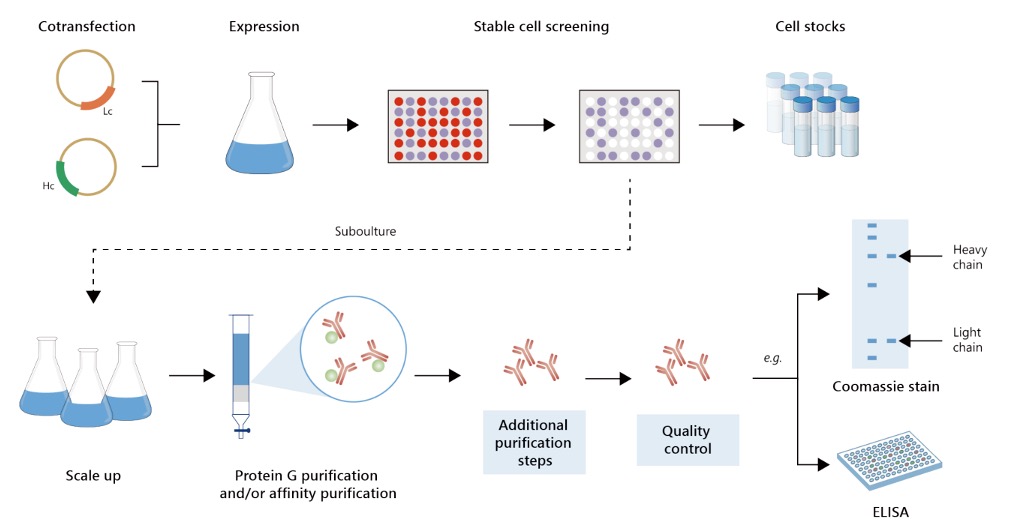 Fig.2 Gram-scale anti-CASP1 recombinant antibody production.
Fig.2 Gram-scale anti-CASP1 recombinant antibody production.
rAb Modalities
Creative Biolabs is committed to facilitating scientific discovery by providing antibody solutions that allow for flexibility. Our anti-CASP1 recombinant antibodies are offered in several formats so that researchers around the world can study this critical inflammatory enzyme in their specific systems.
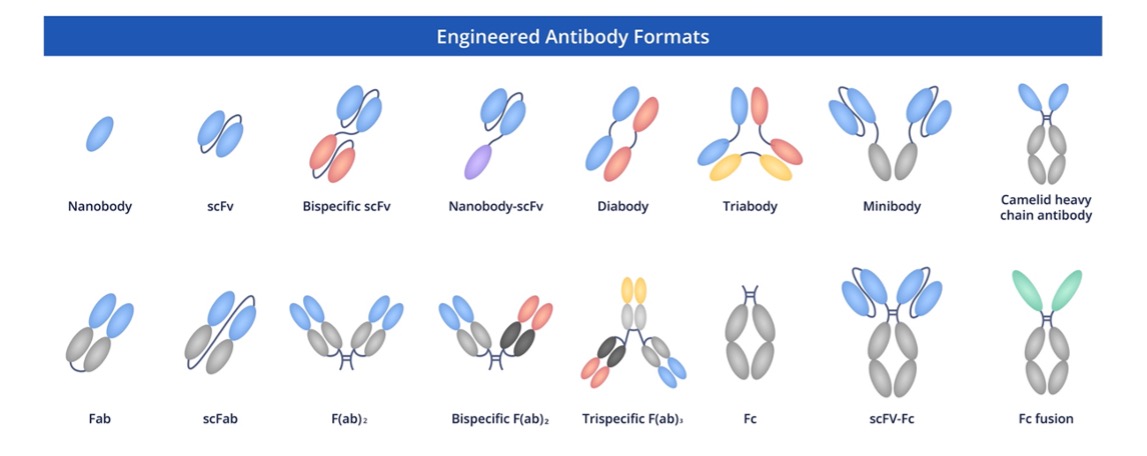 Fig.3 Full-length anti-CASP1 recombinant antibody production and modalities.
Fig.3 Full-length anti-CASP1 recombinant antibody production and modalities.
Gain a clearer understanding of inflammasome activation with Creative Biolabs' anti-CASP1 recombinant antibodies. We offer the validation and lot-to-lot consistency required for studying this highly therapeutically relevant target in inflammatory disease. Let us lay the groundwork for your research; contact our scientific team today.


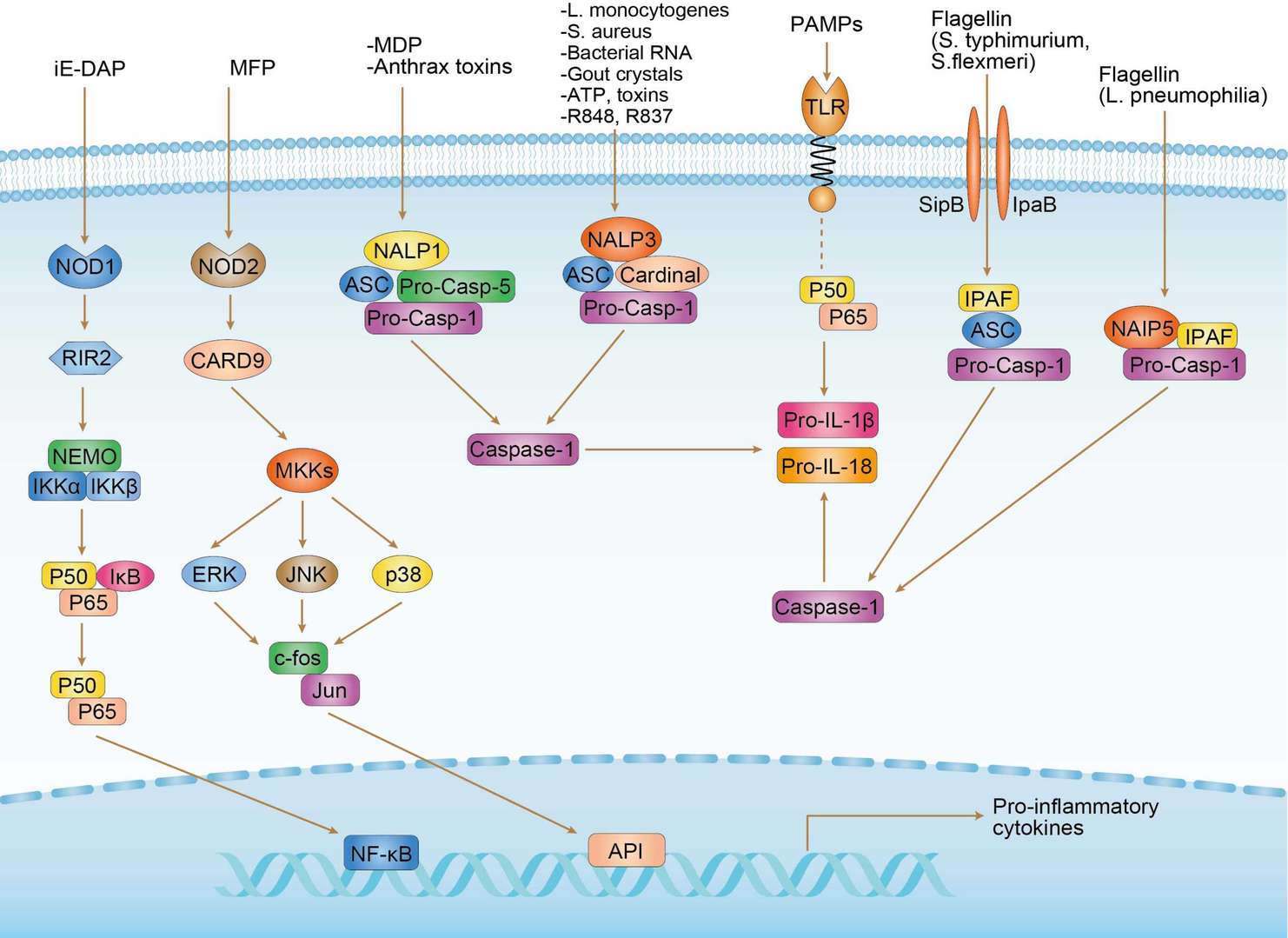 NLR Signaling Pathway
NLR Signaling Pathway