 Loading...
Loading...

SMAD3
Cancer-related genes, Disease related genes, Human disease related genes, Transcription factors
Intracellular
Cell type enhanced (Urothelial cells, Granulosa cells, Prostatic glandular cells)
Low immune cell specificity
Low cell line specificity
Monomer; in the absence of TGF-beta (PubMed:9670020). Homooligomer; in the presence of TGF-beta (PubMed:9670020). Heterotrimer; forms a heterotrimer in the presence of TGF-beta consisting of two molecules of C-terminally phosphorylated SMAD2 or SMAD3 and one of SMAD4 to form the transcriptionally active SMAD2/SMAD3-SMAD4 complex (PubMed:9670020, PubMed:11224571, PubMed:15799969, PubMed:15350224). Part of a complex consisting of AIP1, ACVR2A, ACVR1B and SMAD3 (PubMed:9892009). Forms a complex with SMAD2 and TRIM33 upon addition of TGF-beta (PubMed:16751102). Found in a complex composed of SMAD3, RAN and XPO4; within the complex interacts directly with XPO4 (PubMed:16449645). Component of the multimeric complex SMAD3/SMAD4/JUN/FOS which forms at the AP1 promoter site; required for synergistic transcriptional activity in response to TGF-beta (PubMed:9732876, PubMed:10995748). Interacts (via an N-terminal domain) with JUN (via its basic DNA binding and leucine zipper domains); this interaction is essential for DNA binding and cooperative transcriptional activity in response to TGF-beta (PubMed:9732876, PubMed:10995748). Identified in a complex that contains at least ZNF451, SMAD2, SMAD3 and SMAD4 (PubMed:24324267). Interacts with PPM1A; the interaction dephosphorylates SMAD3 in the C-terminal SXS motif leading to disruption of the SMAD2/3-SMAD4 complex, nuclear export and termination of TGF-beta signaling (PubMed:16751101). Interacts (via MH2 domain) with ZMIZ1 (via SP-RING-type domain); in the TGF-beta signaling pathway increases the activity of the SMAD3/SMAD4 transcriptional complex (PubMed:16777850). Interacts (when phosphorylated) with RNF111; RNF111 acts as an enhancer of the transcriptional responses by mediating ubiquitination and degradation of SMAD3 inhibitors (PubMed:9311995). Interacts (dephosphorylated form via the MH1 and MH2 domains) with RANBP3 (via its C-terminal R domain); the interaction results in the export of dephosphorylated SMAD3 out of the nucleus and termination of the TGF-beta signaling (PubMed:19289081). Interacts (via MH2 domain) with LEMD3; the interaction represses SMAD3 transcriptional activity through preventing the formation of the heteromeric complex with SMAD4 and translocation to the nucleus (PubMed:15601644, PubMed:15647271). Interacts (via the linker region) with EP300 (C-terminal); the interaction promotes SMAD3 acetylation and is enhanced by TGF-beta phosphorylation in the C-terminal of SMAD3 (PubMed:9843571, PubMed:15588252). This interaction can be blocked by competitive binding of adenovirus oncoprotein E1A to the same C-terminal site on EP300, which then results in partially inhibited SMAD3/SMAD4 transcriptional activity (PubMed:9843571, PubMed:15588252). Interacts with TGFBR1 (PubMed:9311995). Interacts with TGFB1I1 (PubMed:15561701). Interacts with PRDM16 (PubMed:19049980). Interacts with SNW1 (PubMed:11278756). Interacts (via MH2 domain) with ZFYVE9 (PubMed:9865696, PubMed:12154125). Interacts with HDAC1 (PubMed:19049980). Interacts with TGIF2 (PubMed:11427533). Interacts with SKOR1 (PubMed:17292623). Interacts with SKOR2 (PubMed:16200078). Interacts with DACH1; the interaction inhibits the TGF-beta signaling (PubMed:14525983). Interacts with RBPMS (PubMed:17099224). Interacts (via MH2 domain) with MECOM (PubMed:9665135, PubMed:15897867). Interacts with WWTR1 (via its coiled-coil domain) (PubMed:18568018). Interacts with SKI; the interaction represses SMAD3 transcriptional activity (PubMed:19049980). Interacts with MEN1 (PubMed:11274402). Interacts with IL1F7 (PubMed:20935647). Interaction with CSNK1G2 (PubMed:18794808). Interacts with PDPK1 (via PH domain) (PubMed:17327236). Interacts with DAB2; the interactions are enhanced upon TGF-beta stimulation (PubMed:11387212). Interacts with USP15 (PubMed:21947082). Interacts with PPP5C; the interaction decreases SMAD3 phosphorylation and protein levels (PubMed:22781750). Interacts with LDLRAD4 (via the SMAD interaction motif) (PubMed:24627487). Interacts with PMEPA1 (PubMed:20129061). Interacts with ZNF451 (PubMed:24324267). Interacts with ZFHX3 (PubMed:25105025). Interacts weakly with ZNF8 (PubMed:12370310). Interacts with STUB1, HSPA1A, HSPA1B, HSP90AA1 and HSP90AB1 (PubMed:24613385). Interacts with YAP1 (when phosphorylated at 'Ser-127') (By similarity). Interacts with AIP1 (By similarity). Interacts (via MH2 domain) with CITED2 (via C-terminus) (By similarity). Interacts with HGS (By similarity). Interacts with WWP1 (By similarity). Interacts with TTRAP (By similarity). Interacts with FOXL2 (By similarity). Interacts with PML (By similarity). Interacts with NEDD4L; the interaction requires TGF-beta stimulation (By similarity). Interacts with ZC3H3 (By similarity). Interacts with TGIF. Interacts with CREBBP. Interacts with ATF2. (Microbial infection) Interacts with SARS-CoV nucleoprotein.
DNA-binding
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Rat, Mouse
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: WB, IHC-P, IF
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Rat, Mouse
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: IHC-P, IF
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: IHC-P, IF
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IF, IHC, FC
- Rabbit Anti-SMAD3 Polyclonal Antibody (MRO-2193-CN) (MRO-2193-CN)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: IF, IHC, FC
- Rabbit Anti-SMAD3 Polyclonal Antibody (MRO-2192-CN) (MRO-2192-CN)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat, Zebrafish
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: IF, IHC, FC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IF, IHC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Application: IHC-P, WB
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: IHC-P, IF
- Rabbit Anti-SMAD3 Recombinant Antibody (clone AFY0023) (MOR-0052-FY)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ICC, IHC-P, WB
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Rat, Mouse
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: WB, IHC-P, IF
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1, κ
- Application: WB, ELISA, IHC
-
- Derivation: Phage display library screening
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: IgG
- Application: WB, ICC, IHC-P, IP, sELISA
- Mouse Anti-SMAD3 Recombinant Antibody (clone 5G11) (VS3-XY1434)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: ELISA, WB, ICC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: WB, ELISA, IF
- Rabbit Anti-SMAD3 Polyclonal Antibody (VS3-WK1563)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, ELISA
- Mouse Anti-SMAD3 Recombinant Antibody (clone 8E1) (VS3-QX1027)
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: WB, IP, IF, IHC
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human, Rat, Mouse
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: WB, IHC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat, Hamster
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IP
- Mouse Anti-SMAD3 Recombinant Antibody (VS3-WK1363) (VS3-WK1363)
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human, Rat, Mouse
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: IHC-P, WB
Our customer service representatives are available 24 hours a day, from Monday to Sunday. Contact Us
Can't find the products you're looking for? Try to filter in the left sidebar.Filter By Tag
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.

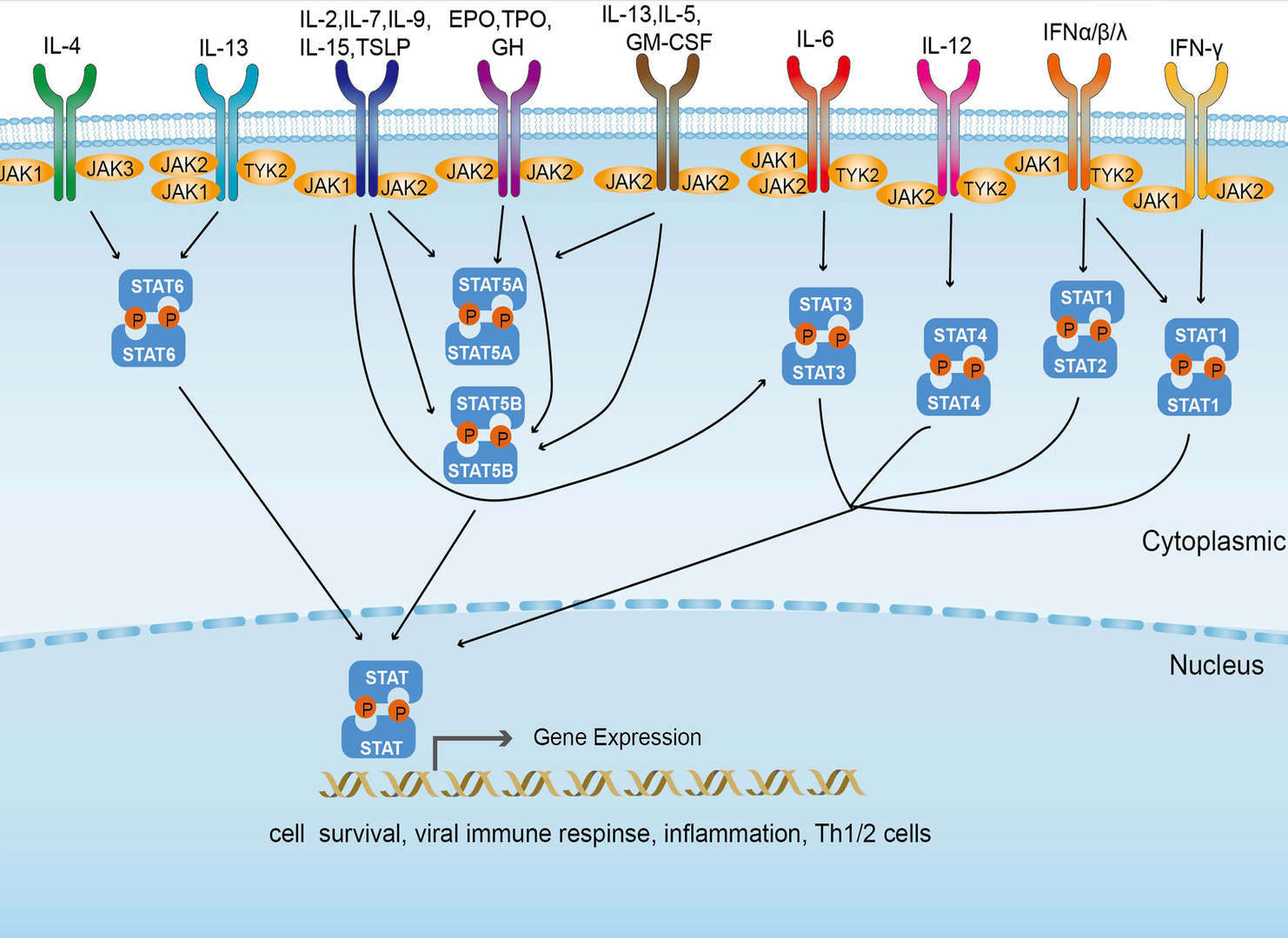 JAK-STAT Signaling Pathway
JAK-STAT Signaling Pathway
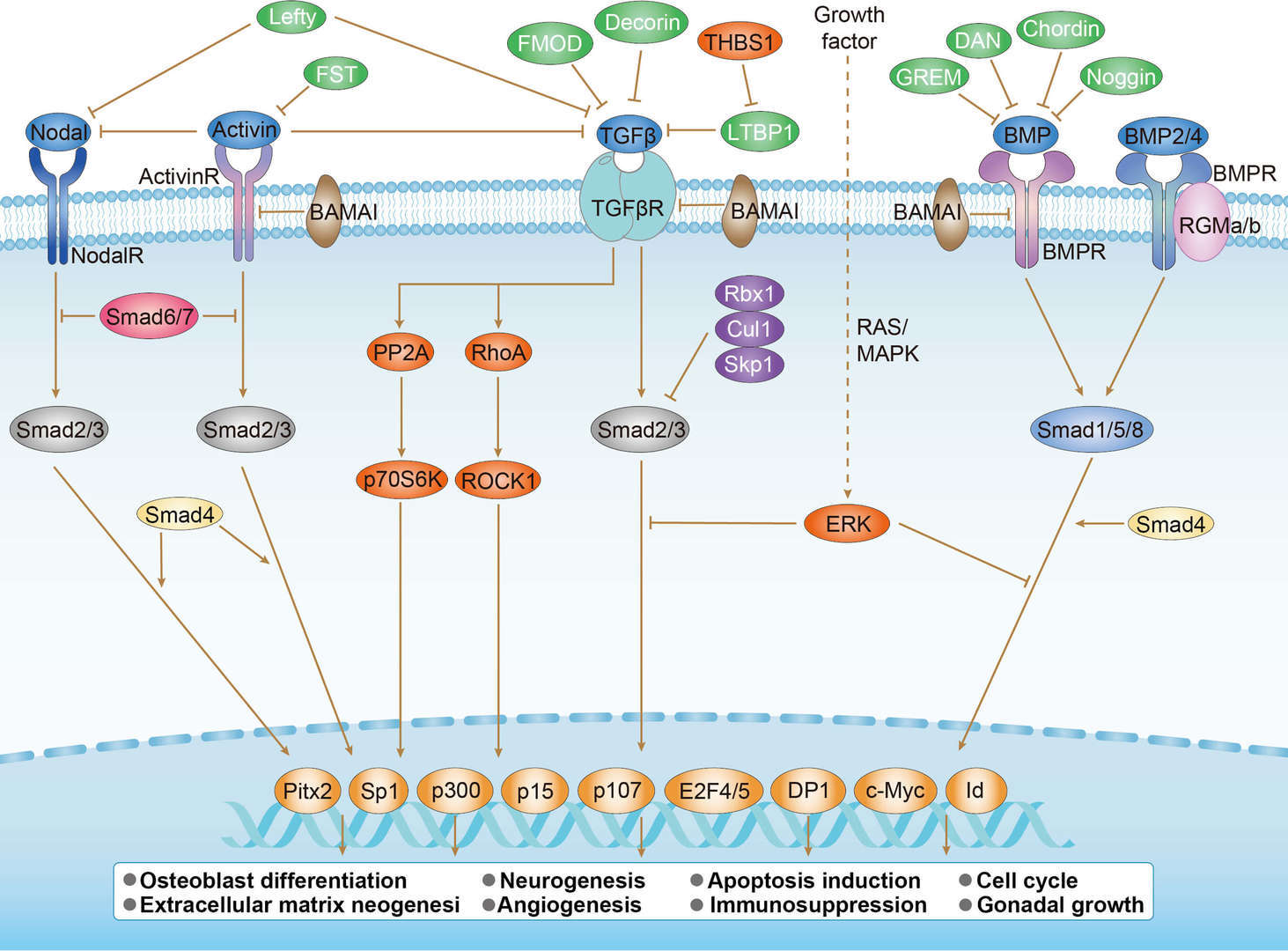 TGF-β Signaling Pathway
TGF-β Signaling Pathway
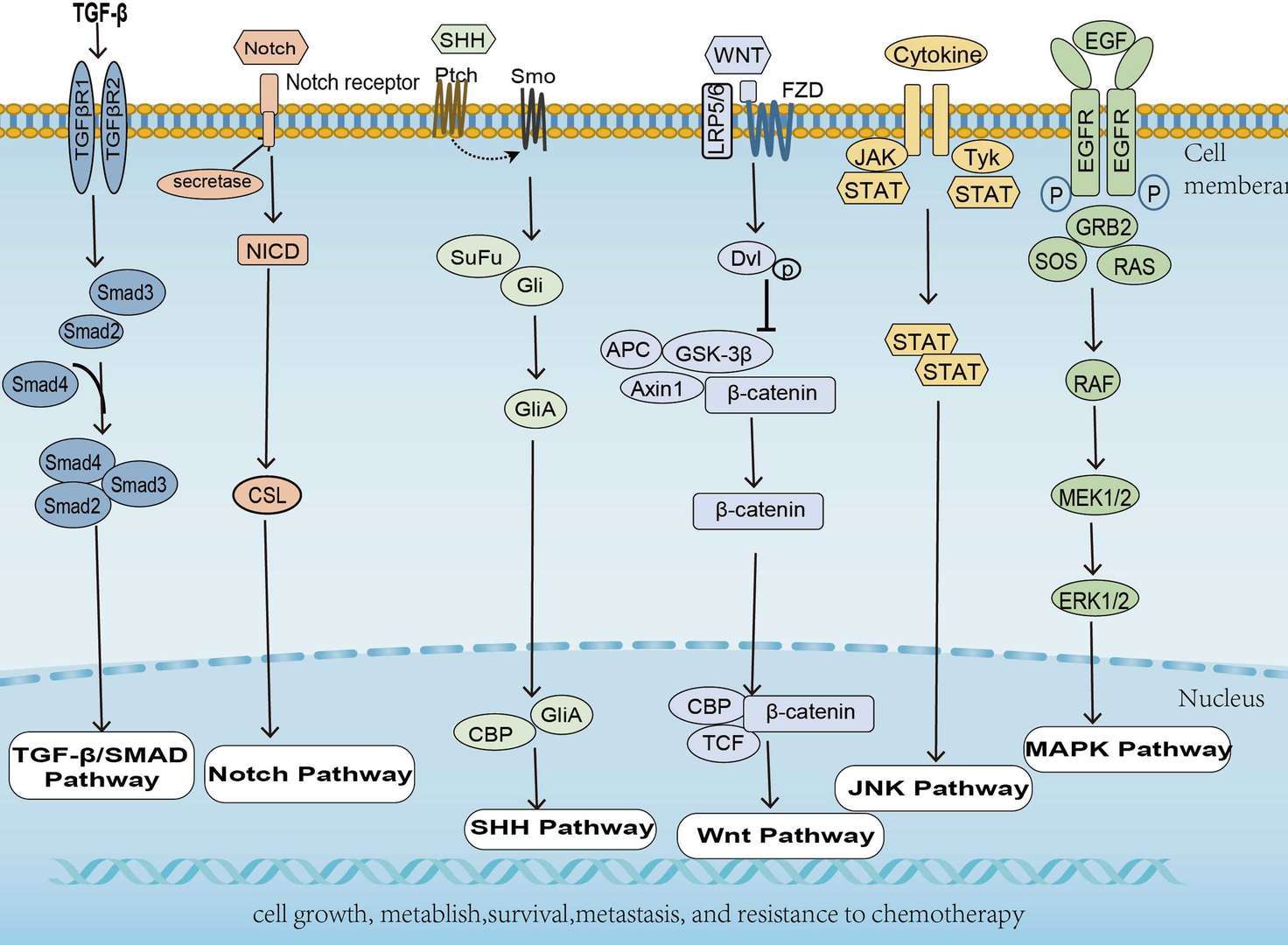 Pancreatic Cancer
Pancreatic Cancer
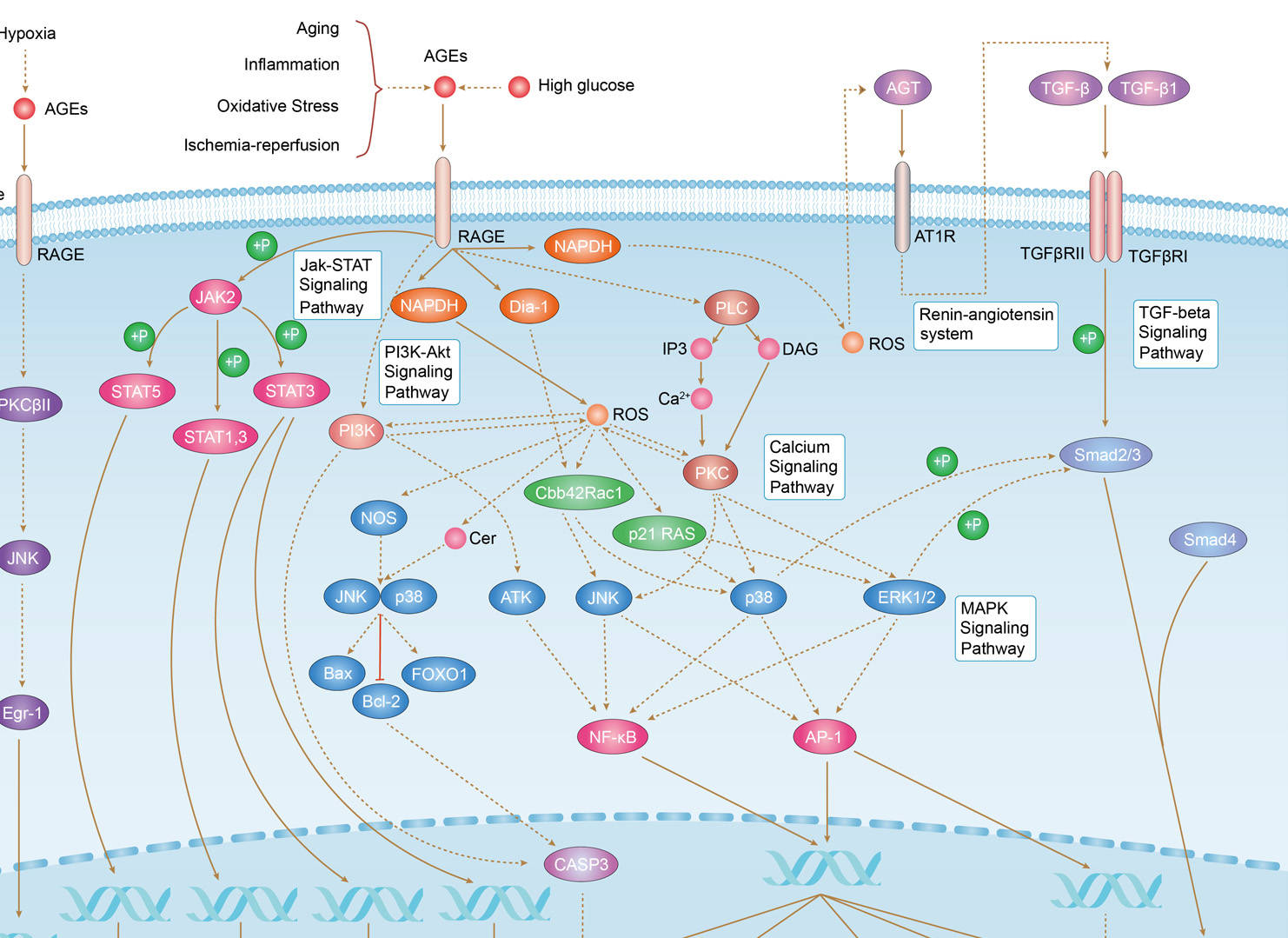 AGE-RAGE Signaling Pathway in Diabetic Complications
AGE-RAGE Signaling Pathway in Diabetic Complications