 Loading...
Loading...

LCK
Cancer-related genes, Disease related genes, Enzymes, FDA approved drug targets, Human disease related genes, Metabolic proteins
Intracellular
Group enriched (NK-cells, T-cells, dendritic cells)
Group enriched (T-reg, naive CD4 T-cell, memory CD8 T-cell, naive CD8 T-cell, memory CD4 T-cell, gdT-cell, MAIT T-cell, NK-cell)
Group enriched (JURKAT, MOLT-4, U-698)
Binds to the cytoplasmic domain of cell surface receptors, such as AXL, CD2, CD4, CD5, CD8, CD44, CD45 and CD122. Also binds to effector molecules, such as PI4K, VAV1, RASA1, FYB1 and to other protein kinases including CDK1, RAF1, ZAP70 and SYK. Binds to phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase (PI3K) from T-lymphocytes through its SH3 domain and to the tyrosine phosphorylated form of KHDRBS1/p70 through its SH2 domain. This interaction inhibits its tyrosine-kinase activity. Interacts with SQSTM1. Interacts with phosphorylated LIME1. Interacts with CBLB and PTPRH. Interacts with RUNX3. Forms a signaling complex with EPHA1, PTK2B AND PI3-KINASE; upon activation by EFNA1 which may regulate T-lymphocyte migration. Associates with ZAP70 and RHOH; these interactions allow LCK-mediated RHOH and CD3 subunit phosphorylation in the presence of functional ZAP70. Interacts with UNC119; this interaction plays a crucial role in activation of LCK. Interacts with CEACAM1 (via cytoplasmic domain); mediates CEACAM1 phosphorylation resulting in PTPN6 recruitment that dephosphorylates TCR stimulation-induced CD247 and ZAP70 (PubMed:18424730). Interacts with CD160. Interacts with CD48 (PubMed:12007789). (Microbial infection) Interacts with herpes simplex virus 1 UL46; this interaction activates LCK. (Microbial infection) Interacts with HIV-1 Nef through its SH3 domain.
Kinase, Transferase, Tyrosine-protein kinase
- Mouse Anti-LCK Recombinant Antibody (clone 25C4) (MOB-1482z)
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: WB, FC, ICC, IHC, IP
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Application: ELISA, WB
-
- Derivation: Phage display library screening
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: IgG
- Application: FC, ICC, IHC-P, IP, WB
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IHC-Fr, IHC-P, ICC, IF, IP
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: WB
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: WB, ELISA
- Mouse Anti-LCK Recombinant Antibody (VS3-CJ434) (VS3-CJ434)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: WB, ICC, IHC, FC
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG2a
- Application: WB, IHC, ICC, FC, ELISA
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: WB
Our customer service representatives are available 24 hours a day, from Monday to Sunday. Contact Us
Can't find the products you're looking for? Try to filter in the left sidebar.Filter By Tag
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.

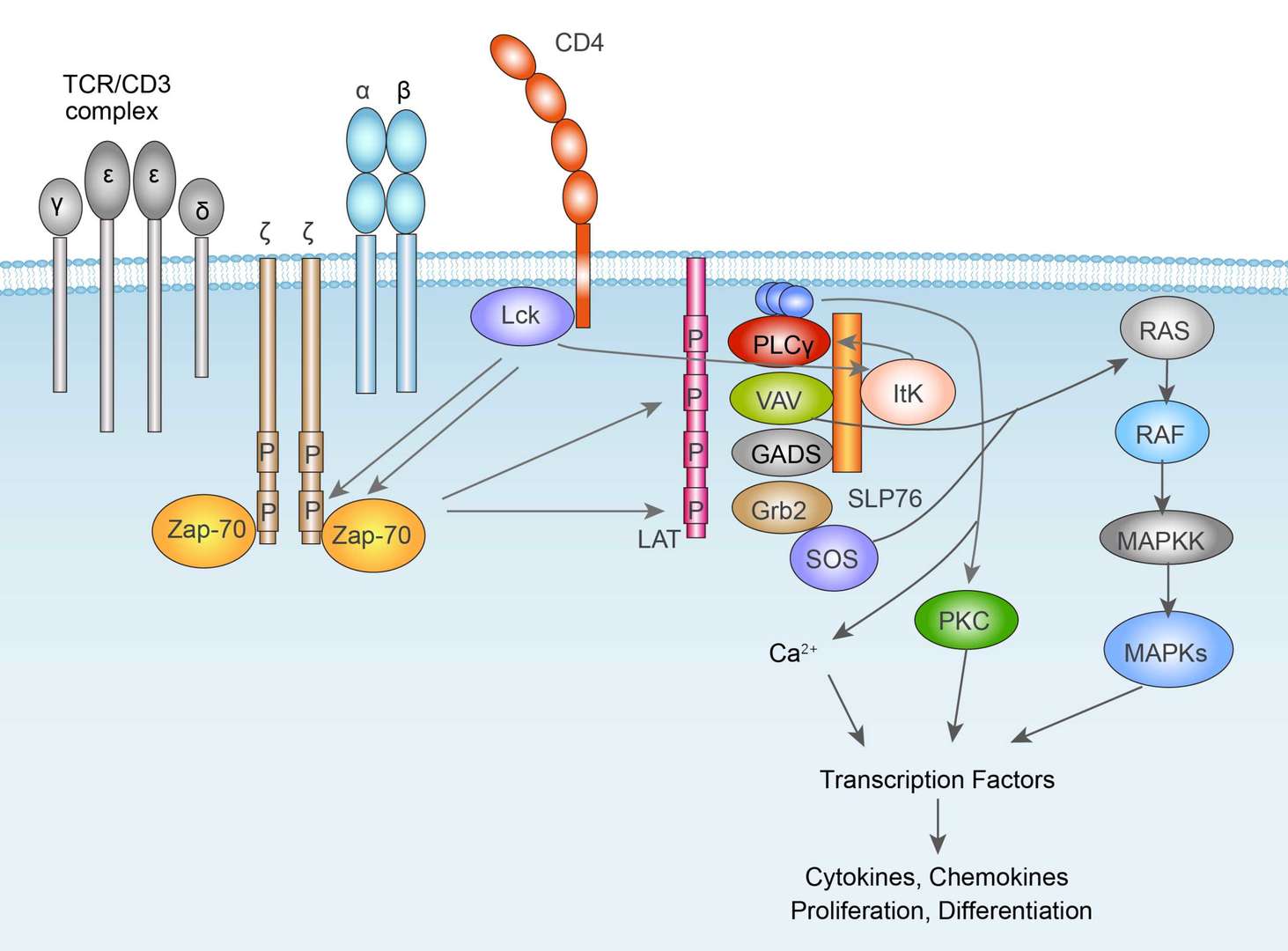 TCR Signaling Pathway
TCR Signaling Pathway
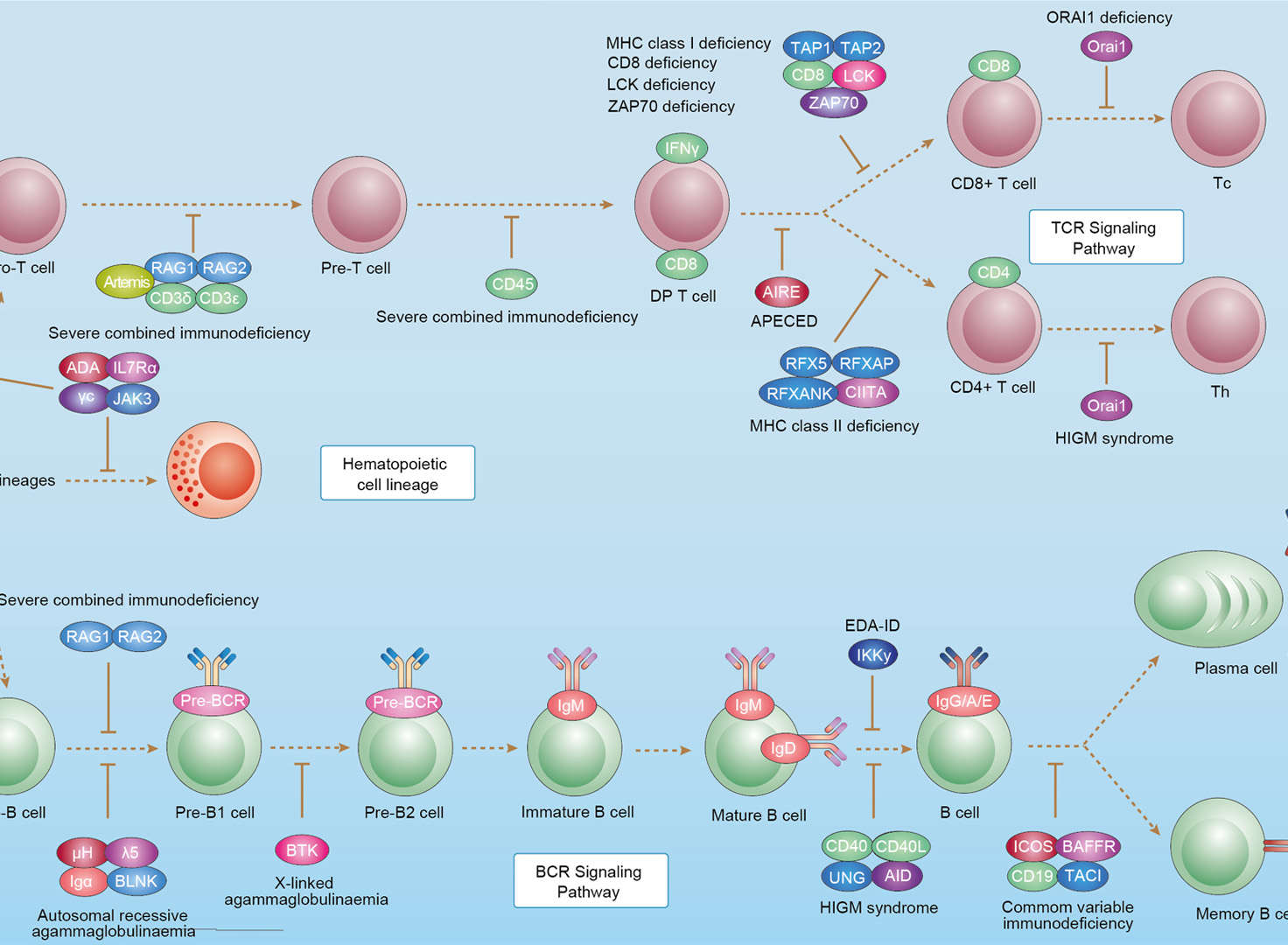 Primary Immunodeficiency
Primary Immunodeficiency