 Loading...
Loading...

FMOD
Fibromodulin belongs to the family of small interstitial proteoglycans. The encoded protein possesses a central region containing leucine-rich repeats with 4 keratan sulfate chains, flanked by terminal domains containing disulphide bonds. Owing to the interaction with type I and type II collagen fibrils and in vitro inhibition of fibrillogenesis, the encoded protein may play a role in the assembly of extracellular matrix. It may also regulate TGF-beta activities by sequestering TGF-beta into the extracellular matrix. Sequence variations in this gene may be associated with the pathogenesis of high myopia. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants.
Predicted location
Intracellular, Secreted (different isoforms)
Single cell type specificity
Cell type enhanced (Intestinal goblet cells, Fibroblasts, Peritubular cells, Leydig cells, Breast myoepithelial cells)
Immune cell specificity
Not detected in immune cells
Cell line specificity
Cell line enhanced (ASC diff, CACO-2, HHSteC, HSkMC, OE19)
Interaction
Binds to type I and type II collagen.
More Types Infomation
-
- Class: Class I
- Antigen: Fibromodulin
- Antigen Species: Human
- Peptide: YMEHNNVYTV
- Conjugate: Unlabeled, Biotin, R-PE, APC
-
- Class: Class I
- Antigen: Fibromodulin
- Antigen Species: Human
- Peptide: YLQHNEIQEV
- Conjugate: Unlabeled, Biotin, R-PE, APC
-
- Class: Class I
- Antigen: Fibromodulin
- Antigen Species: Human
- Peptide: YLLDLSTNHL
- Conjugate: Unlabeled, Biotin, R-PE, APC
-
- Class: Class I
- Antigen: Fibromodulin
- Antigen Species: Human
- Peptide: LLLAGLFSL
- Conjugate: Unlabeled, Biotin, R-PE, APC
Our customer service representatives are available 24 hours a day, from Monday to Sunday. Contact Us
Can't find the products you're looking for? Try to filter in the left sidebar.Filter By Tag
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.

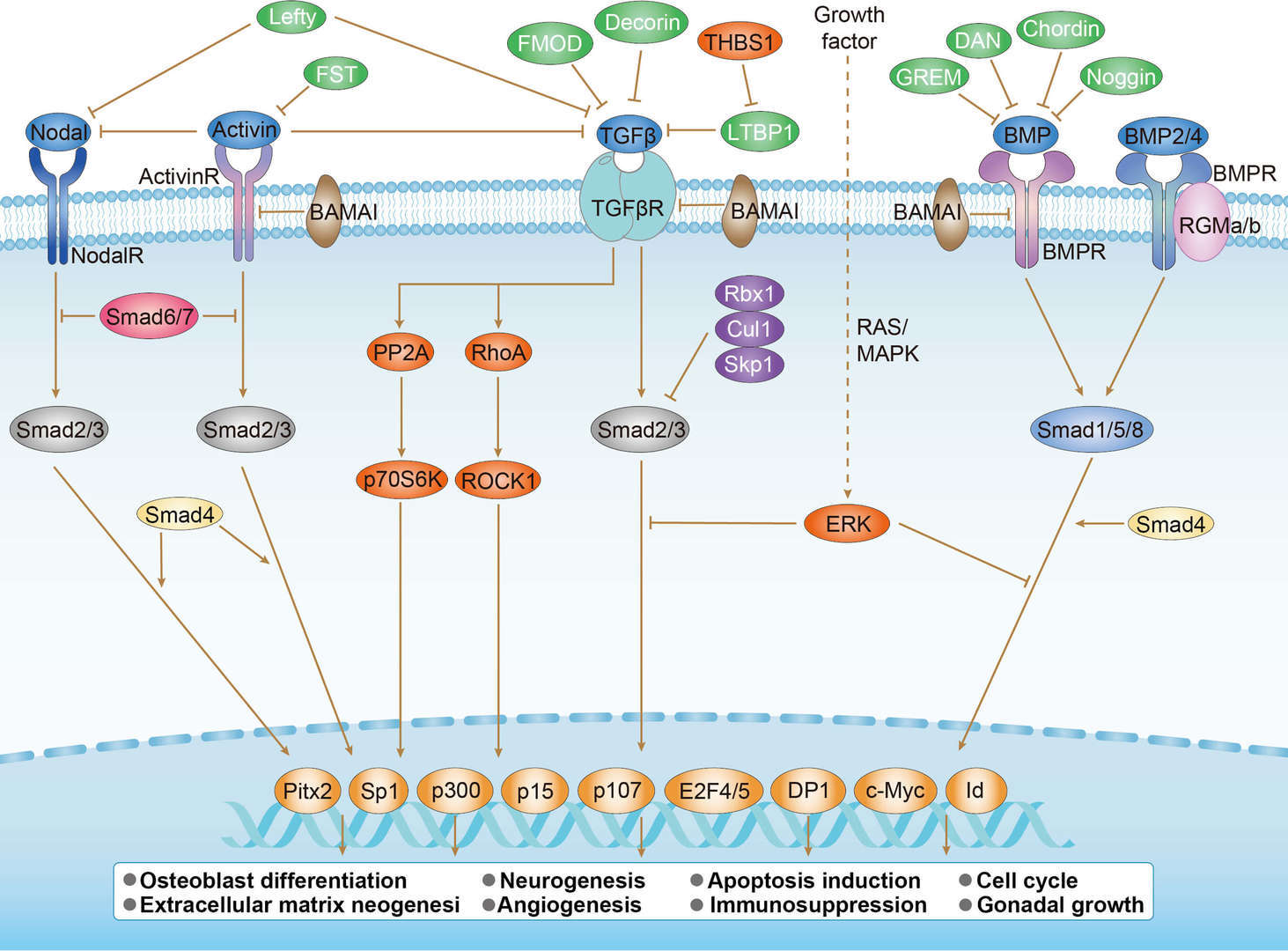 TGF-β Signaling Pathway
TGF-β Signaling Pathway