

Etrolizumab Overview
Introduction of Etrolizumab
Etrolizumab (rhuMAb Beta7) is the first dual-action anti-integrin antibody in Phase III trials designed to selectively control disease in the gut of patients with two major forms of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), ulcerative colitis (UC) and Crohn’s disease (CD). It is a humanized monoclonal antibody against the β7 subunit of integrins α4β7 and αEβ7. Etrolizumab was developed by Genentech by engineering the FIB504 antibody to include human IgG1-heavy chain and κ-light chain frameworks; it is manufactured in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells. As of 2016 it was in phase Ⅲ studies for induction and maintenance therapy in people with UC and CD.
Mechanism of Action of Etrolizumab
To maintain a healthy mucosa, a balance is maintained between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines. The inflammation in the colon in UC patients reflects the outcome of a genetic alteration in the innate immune system as well as the amplified responses of adaptive immunity. The α4β7 integrin is a glycoprotein on the surface of circulating T-lymphocytes which is involved in their recruitment to the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. The α4β7 integrin is activated on the lymphocyte surface and it binds with its counter receptor, a glycosaminoglycan ligand on the endothelial surface membrane, the mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule-1 (MAdCAM-1). It is selectively expressed on the endothelium of intestinal vasculature. MAdCAM-1 binds the lymphocytes from the endothelial lumen as part of the rolling process. These bound lymphocytes then migrate to the lamina propria and tissue. Abnormal retention in these cells forms a critical part of the inflammatory process. The α4β7 integrin facilitates the intrusion of the GI tract by memory T-cells and the MAdCAM-1. The αEβ7 integrin is a heterodimeric integrin found on intraepithelial T-cells and facilitates their adhesion to the epithelial cells. This αEβ7 integrin is also found on dendritic cells (DC) which mediate gut homing and induce regulatory T-cell development.
Etrolizumab is a humanized monoclonal IgG1 antibody against the β7 subunit of the heterodimeric integrins α4β7 and αEβ7. The α4β7 integrin is a critical mediator of leucocyte infiltration into the gastrointestinal tract through its interactions with mucosal addressin cell adhesion molecule-1 (MAdCAM-1) on the endothelium of mucosal tissue vessels. On the other hand, αEβ7 integrin binds selectively to E-cadherin and has been shown to facilitate the adhesion of intraepithelial T cells to epithelial cells. It can, potentially, also reduce the generation of gut-tropic T-cells by interacting with the mesenteric lymph nodes (MLN) DCs. More than 95% of intraepithelial lymphocytes and 40% of lymphocytes in the human intestinal lamina propria express αEβ7 integrin whereas it is expressed in only 2% of the resting peripheral blood lymphocytes. This suggests an important role of this integrin in physiology of immune response in the mucosa. Data also shows that αEβ7 and E-cadherin are up-regulated on the activated lymphocytes and the inflamed mucosa in UC and CD.
Etrolizumab with its dual mechanism of action can inhibit leucocyte trafficking to the gut (by blocking of α4β7- MAdCAM-1 interactions) and inhibit retention of leucocytes in the intraepithelial lining of the gut (by blocking αEβ7- E-cadherin interactions). This can potentially improve the efficacy and specificity for the treatment of UC. Etrolizumab does not inhibit adhesion of α4β1+ α4β7- Ramos cell line to vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) at very high concentrations providing evidence of the selectivity of the molecule. Consistent with this data, preclinical studies in mice have demonstrated that blockade of β7 integrin inhibited homing of T cells to the inflamed colon in a mouse model of IBD while having no effect on lymphocyte homing to the brain in a mouse model of multiple sclerosis. These findings contribute to the understanding of the mechanism of action of etrolizumab: blockade of leukocyte homing and decreased inflammation in the colon.
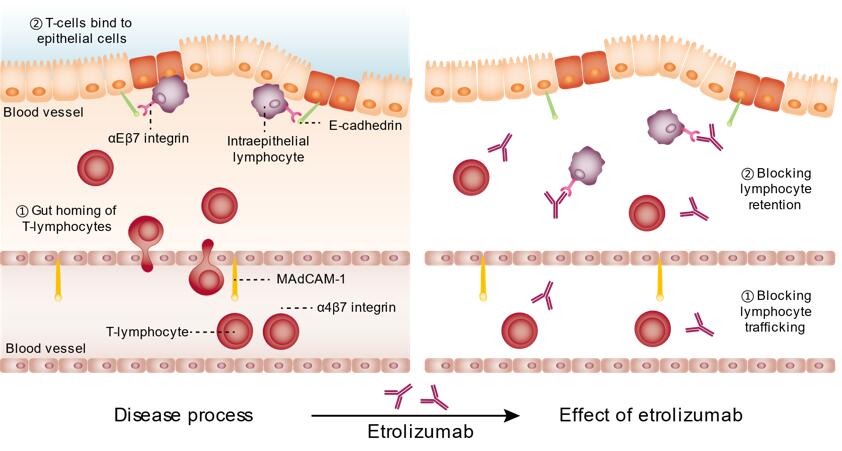 Fig.1 Mechanism of action of etrolizumab
Fig.1 Mechanism of action of etrolizumab
Clinical Projects of Etrolizumab*
| NCT ID | Status | Conditions | Lead Sponsor | Update Time |
| NCT02118584 | Recruiting | Ulcerative Colitis | Hoffmann-La Roche | April 21, 2014 |
| NCT02403323 | Recruiting | Crohn Disease | Hoffmann-La Roche | March 31, 2015 |
| NCT02394028 | Recruiting | Crohn Disease | Hoffmann-La Roche | March 20, 2015 |
| NCT03478956 | Recruiting | Ulcerative Colitis | Hoffmann-La Roche | March 27, 2018 |
| NCT02100696 | Recruiting | Ulcerative Colitis | Hoffmann-La Roche | April 1, 2014 |
| NCT02136069 | Recruiting | Ulcerative Colitis | Hoffmann-La Roche | May 12, 2014 |
| NCT02165215 | Recruiting | Colitis, Ulcerative | Hoffmann-La Roche | June 17, 2014 |
| NCT02171429 | Recruiting | Ulcerative Colitis | Hoffmann-La Roche | June 24, 2014 |
| NCT02163759 | Recruiting | Ulcerative Colitis | Hoffmann-La Roche | June 16, 2014 |
What We Provide
Therapeutic Antibody
Etrolizumab
We provide high-quality Etrolizumab for use in WB, FC, IP, ELISA, Neut, FuncS, IF and most other immunological methods. For lab research use only, not for diagnostic, therapeutic or any in vivo human use.
* The table was excerpted from the following website
https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?cond=&term=Etrolizumab
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

