

Hedgehog Signaling Pathway
About Hedgehog Pathway
Hedgehog (Hh) is a local protein ligand secreted by signaling cells, with a small range of action, generally no more than 20 cells. In many developmental processes of the spine and invertebrates, the Hedgehog signaling pathway controls cell fate, proliferation and differentiation. When this signaling pathway is abnormally activated, it will cause the occurrence and development of tumors. The signal protein induces different cell fates depending on the concentration of the Hh signal molecule. Like other morphogens, its production is strictly controlled in time and space. Hedgehog is synthesized and secreted in the form of a precursor inside the cell, and then undergoes autocatalytic degradation outside the cell, and then undergoes cholesterolation and palmitoylation at different amino acid residue positions at the N-terminal, thereby restrict its diffusion and increase its affinity with plasma membrane.
Hh signal pathway is mainly composed of three kinds of ligands (Sonic hedgehog, Desert hedgehog, Indian hedgehog), two kinds of receptors (Patched and Smoothened), and three types of transcription factor Gli (Glioma-associated oncogene): Gli1, Gli2 and Gli3. Gli1 is involved in activating the transcription of the target gene, while Gli2 and Gli3 can both activate and inhibit the transcription of the target gene.
Unlike other signaling pathways that regulate growth and development, vertebrate Hh signaling pathways rely on highly specialized organelles-primary cilia. Primary cilia are microtubule-like organelles protruding from the cell surface, which widely exist on the surface of various types of cells. Primary cilia are receptive organelles that can sense Hh signals and regulate signal pathways. In the absence of Hh ligands, Ptch receptors are located at the bottom of the primary cilia, inhibiting the transfer of Smo to the primary cilia, thus inhibiting its activation, while Gli is phosphorylated by the cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP)-dependent protein kinase A (PKA) and decomposed into Gli inhibitor, which inhibits the transcription of genes in the nucleus. The regulatory subunits and catalytic subunits of PKA are located at the bottom of the ciliated base. It is felt that cAMP promotes the production of GLIR and regulates the activation of Gli2 improperly. When the cilia sensed the Hh signal and Hh bound to the Ptch receptor, relieving the inhibition of Smo, Smo transferred into the primary cilia and interacted with Suppressor of fused homolog (Sufu) at the top of the cilia, causing Gli activation and transduction into the nucleus, binding to the target gene promoter and transcribing the target gene. This pathway is a classical Hh signal activation pathway, which is highly dependent on primary cilia, requiring cilia to maintain good structural and functional integrity. Non-classical Hh signal transduction is independent of receptors, and Gli is directly activated to regulate the expression of target genes.
Overview of hedgehog signaling pathway
Associated Diseases
Related Pathways
References
- Skoda, A. M., Simovic, D., Karin, V., Kardum, V., Vranic, S., & Serman, L. (2018). The role of the Hedgehog signaling pathway in cancer: A comprehensive review. Bosnian journal of basic medical sciences, 18(1), 8.
- Fattahi, S., Pilehchian Langroudi, M., & Akhavan‐Niaki, H. (2018). Hedgehog signaling pathway: Epigenetic regulation and role in disease and cancer development. Journal of cellular physiology, 233(8), 5726-5735.
- Xin, M., Ji, X., De La Cruz, L. K., Thareja, S., & Wang, B. (2018). Strategies to target the Hedgehog signaling pathway for cancer therapy. Medicinal research reviews, 38(3), 870-913.
- Ruch, J. M., & Kim, E. J. (2013). Hedgehog signaling pathway and cancer therapeutics: progress to date. Drugs, 73(7), 613-623.
- Papadopoulos, V., Tsapakidis, K., Del Galdo, N. A. R., Papandreou, C. N., Del Galdo, F., Anthoney, A., ... & Kamposioras, K. (2016). The prognostic significance of the hedgehog signaling pathway in colorectal cancer. Clinical colorectal cancer, 15(2), 116-127.
- KEGG PATHWAY: Hedgehog signaling pathway - Homo sapiens (human).
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

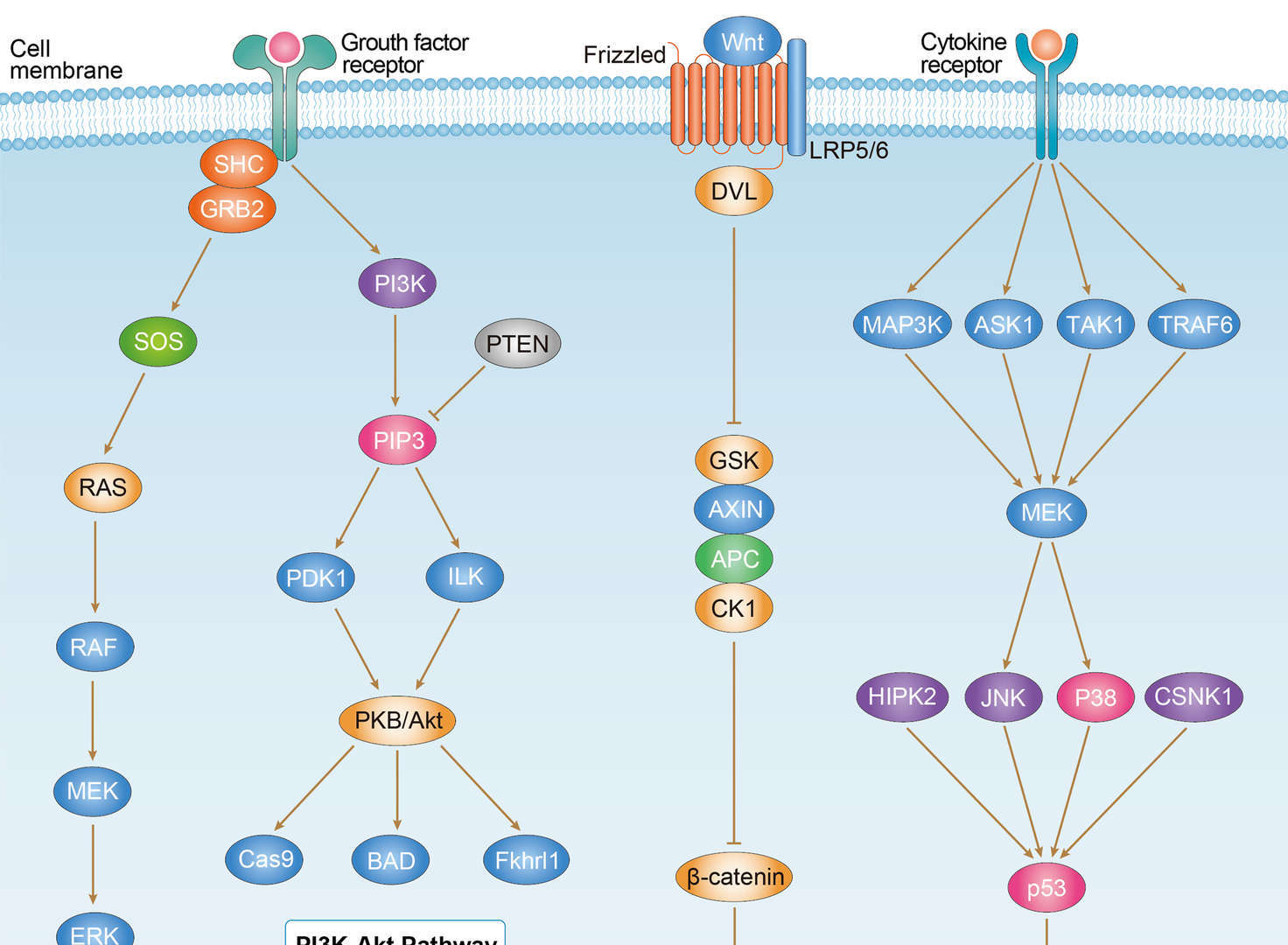 Endometrial Cancer
Endometrial Cancer 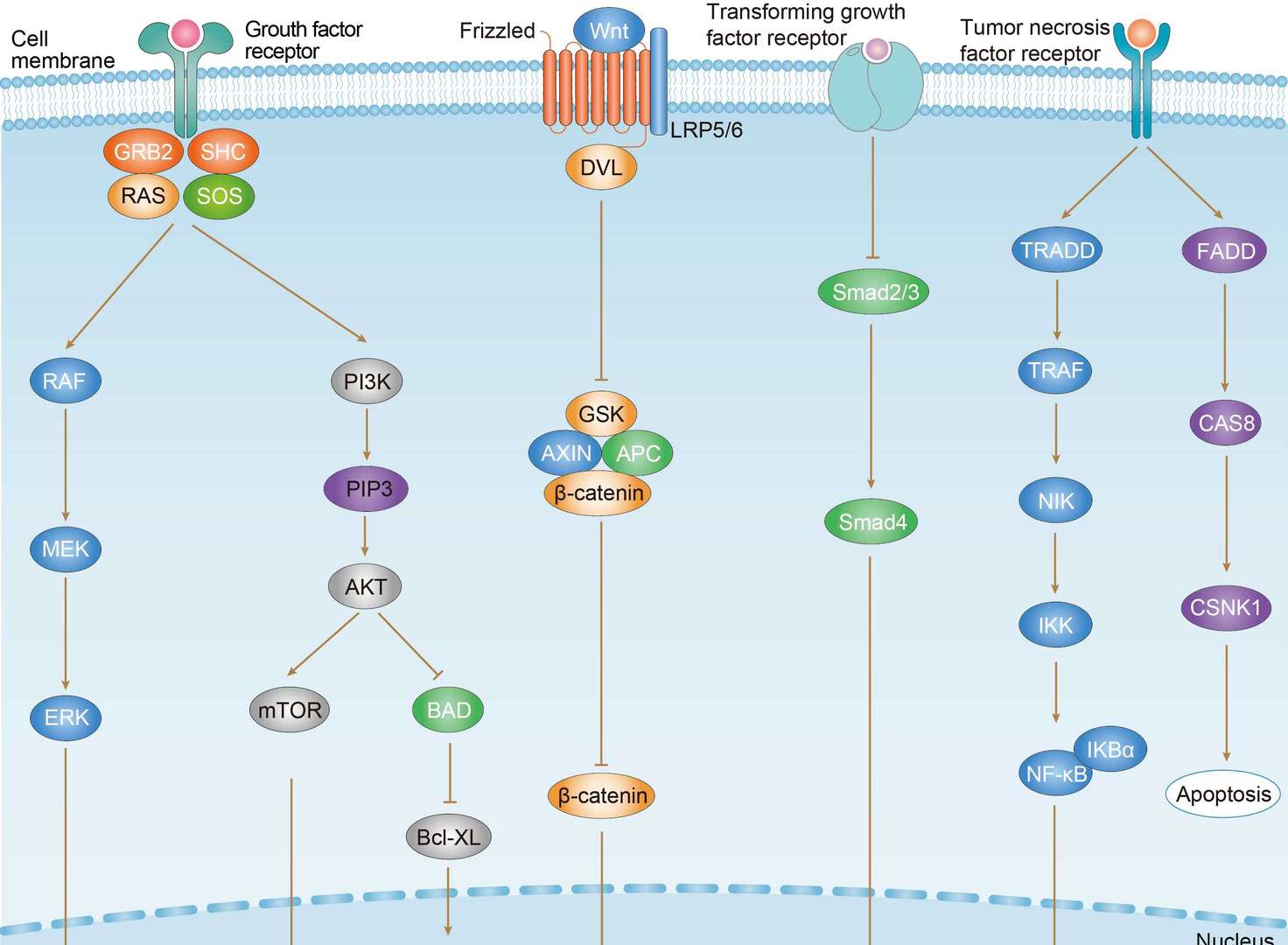 Colorectal Cancer
Colorectal Cancer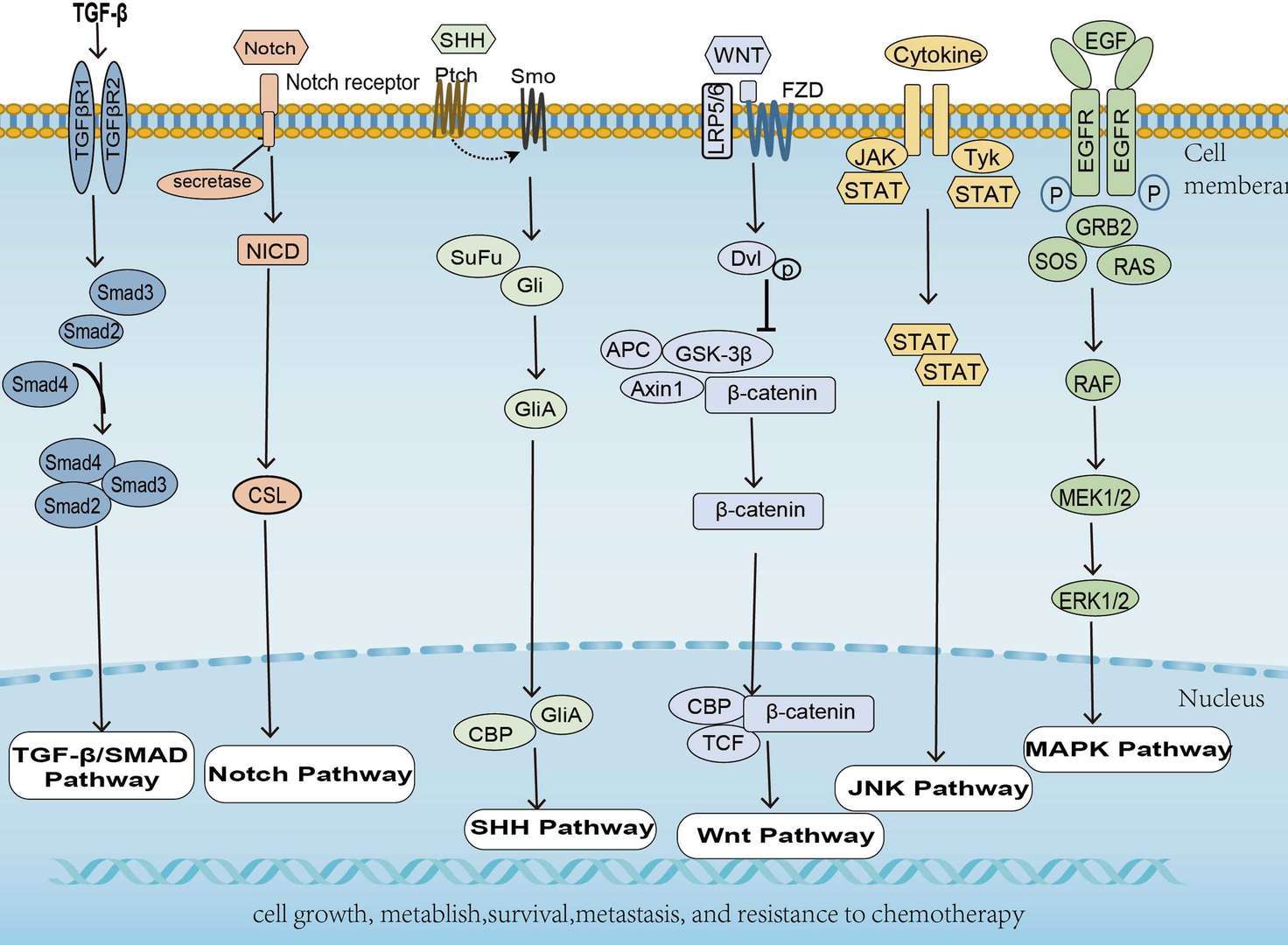 Pancreatic Cancer
Pancreatic Cancer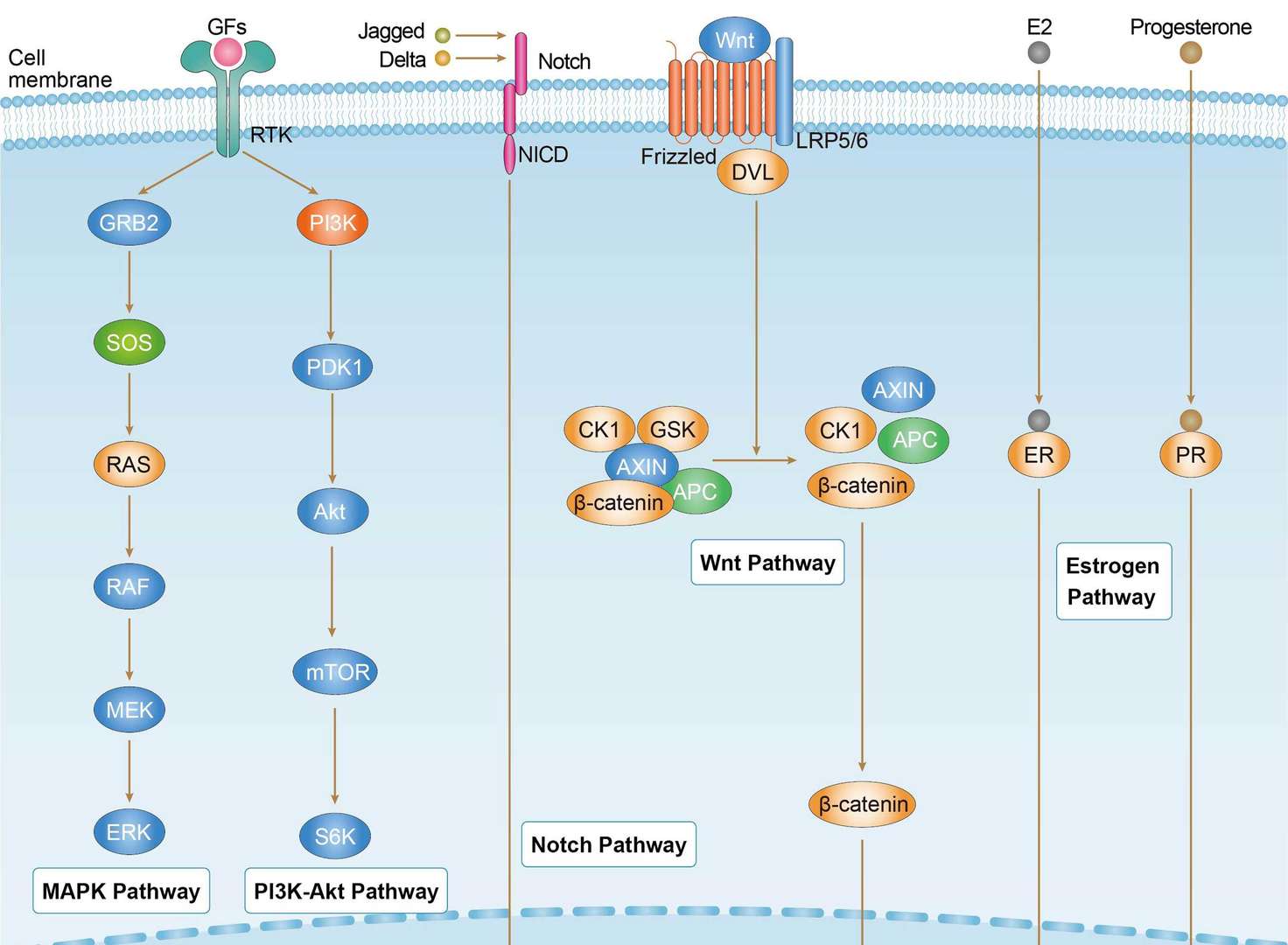 Breast Cancer
Breast Cancer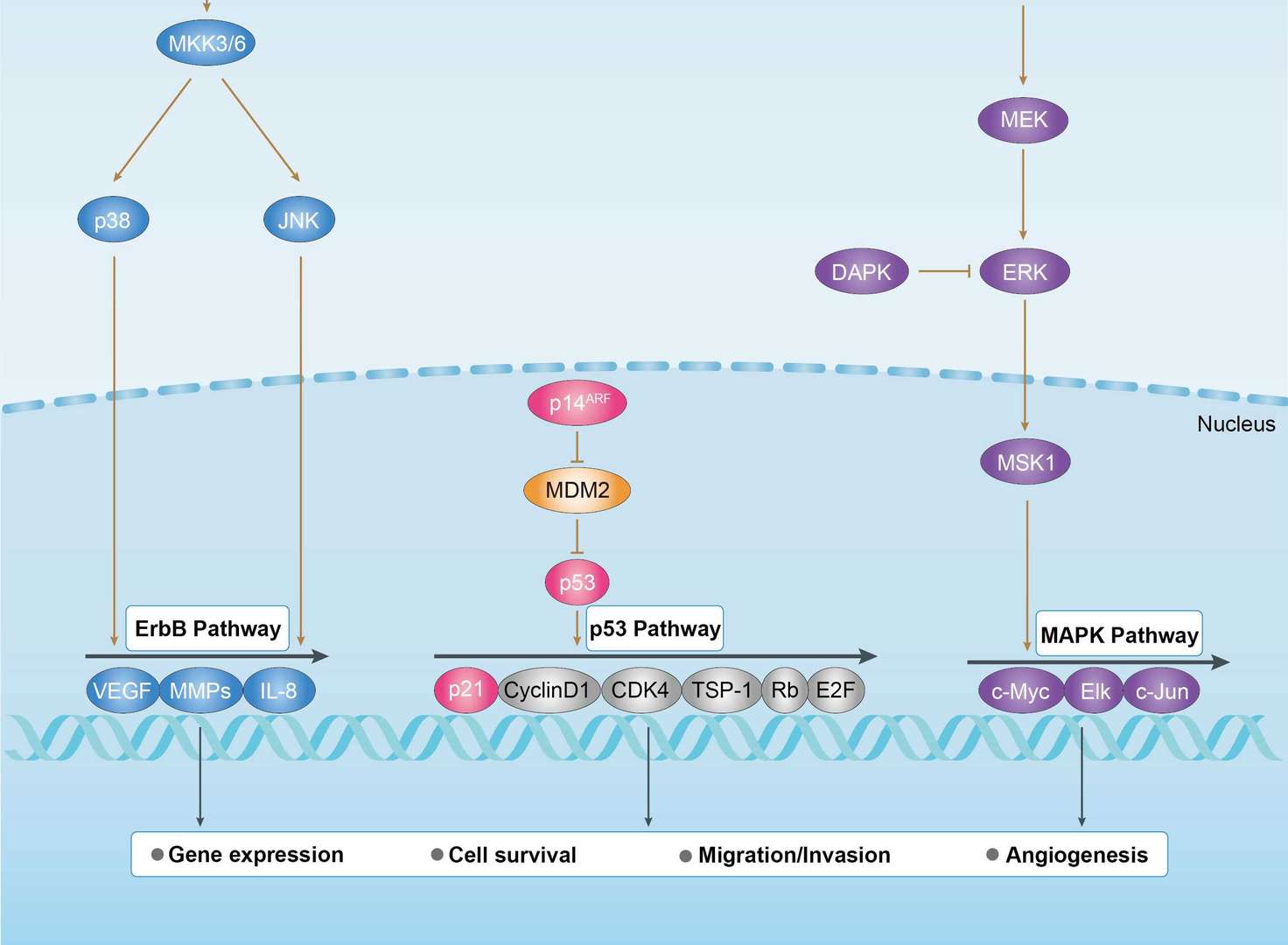 Bladder cancer
Bladder cancer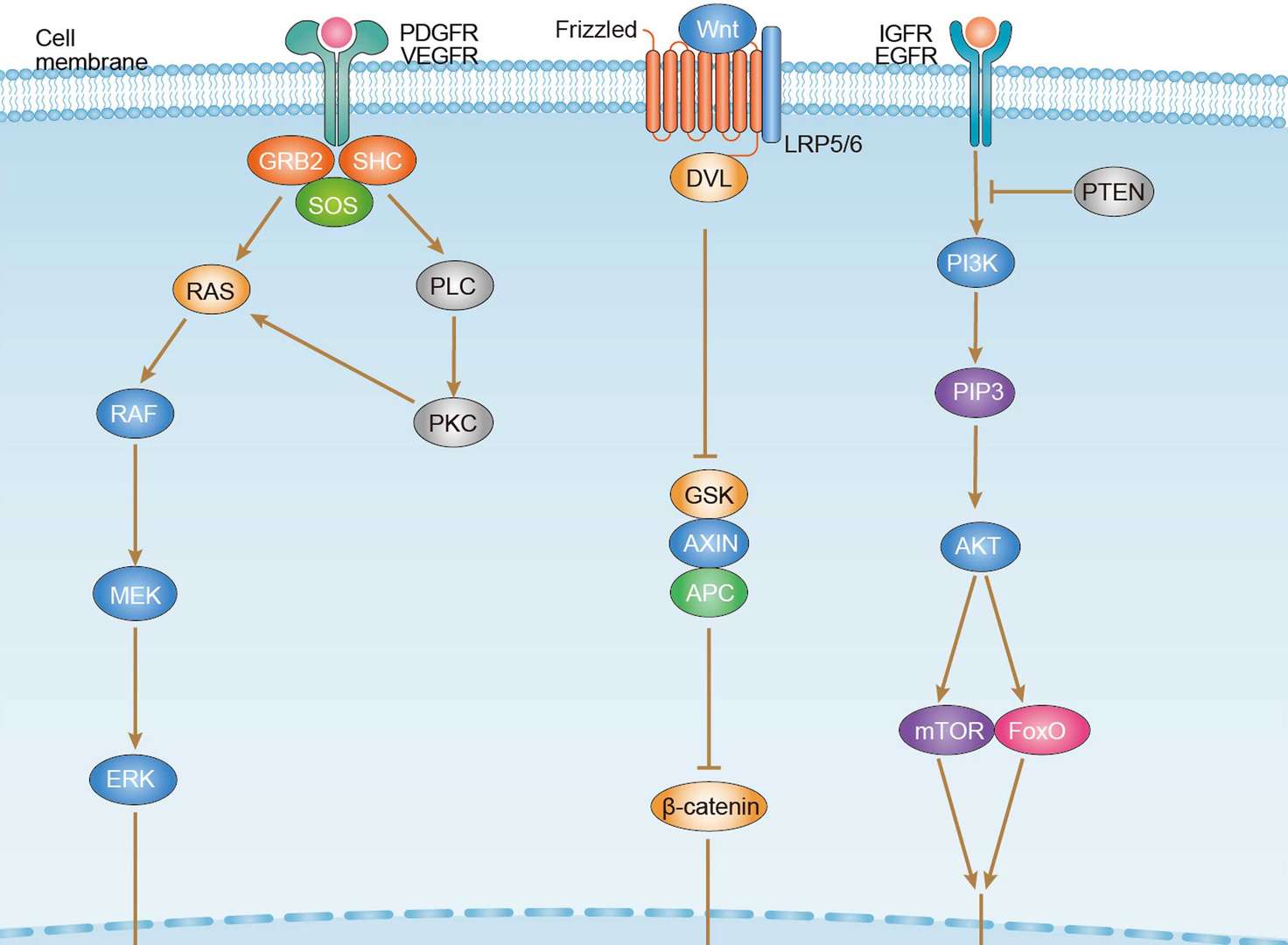 Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Hepatocellular Carcinoma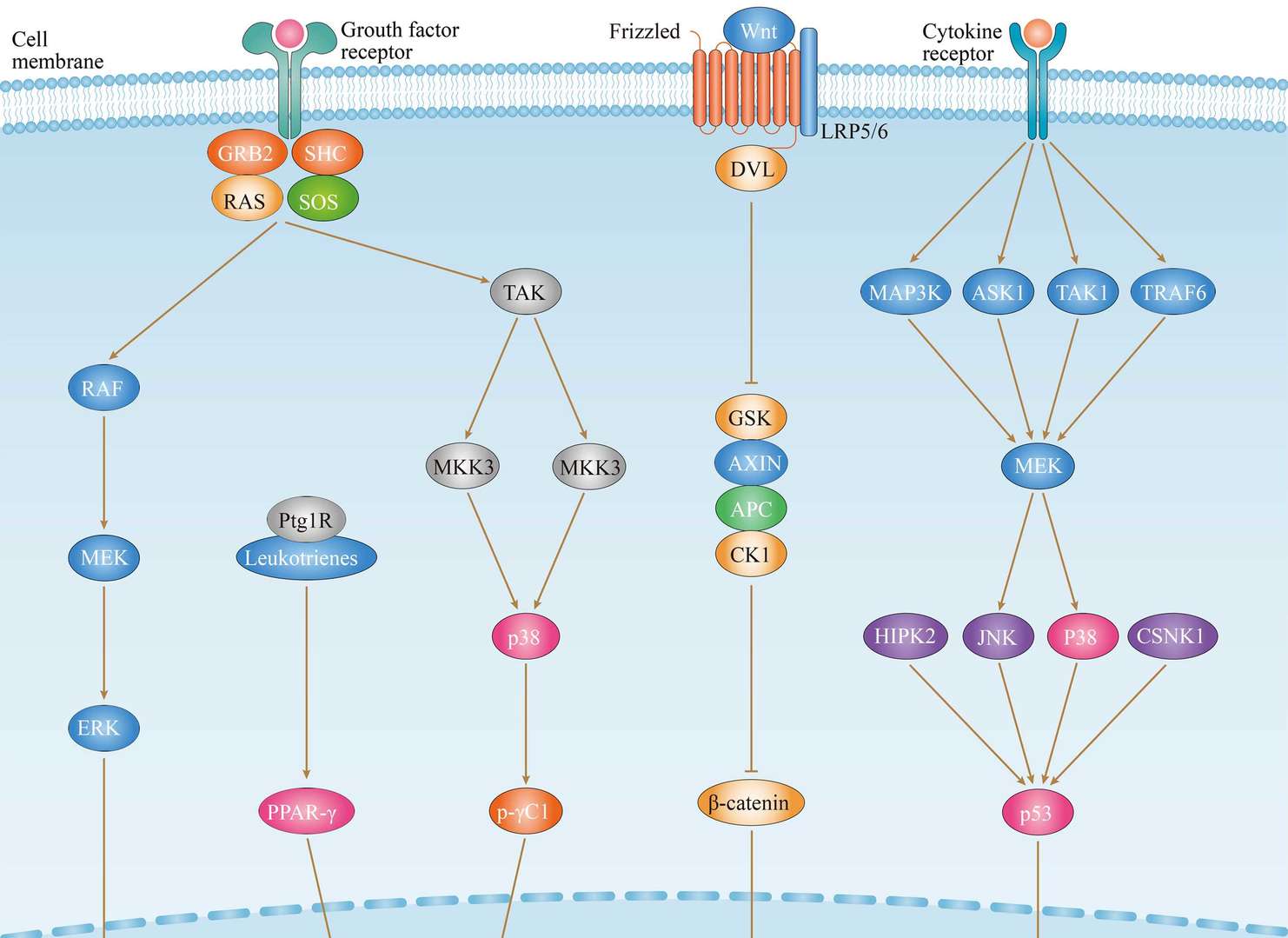 Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid Cancer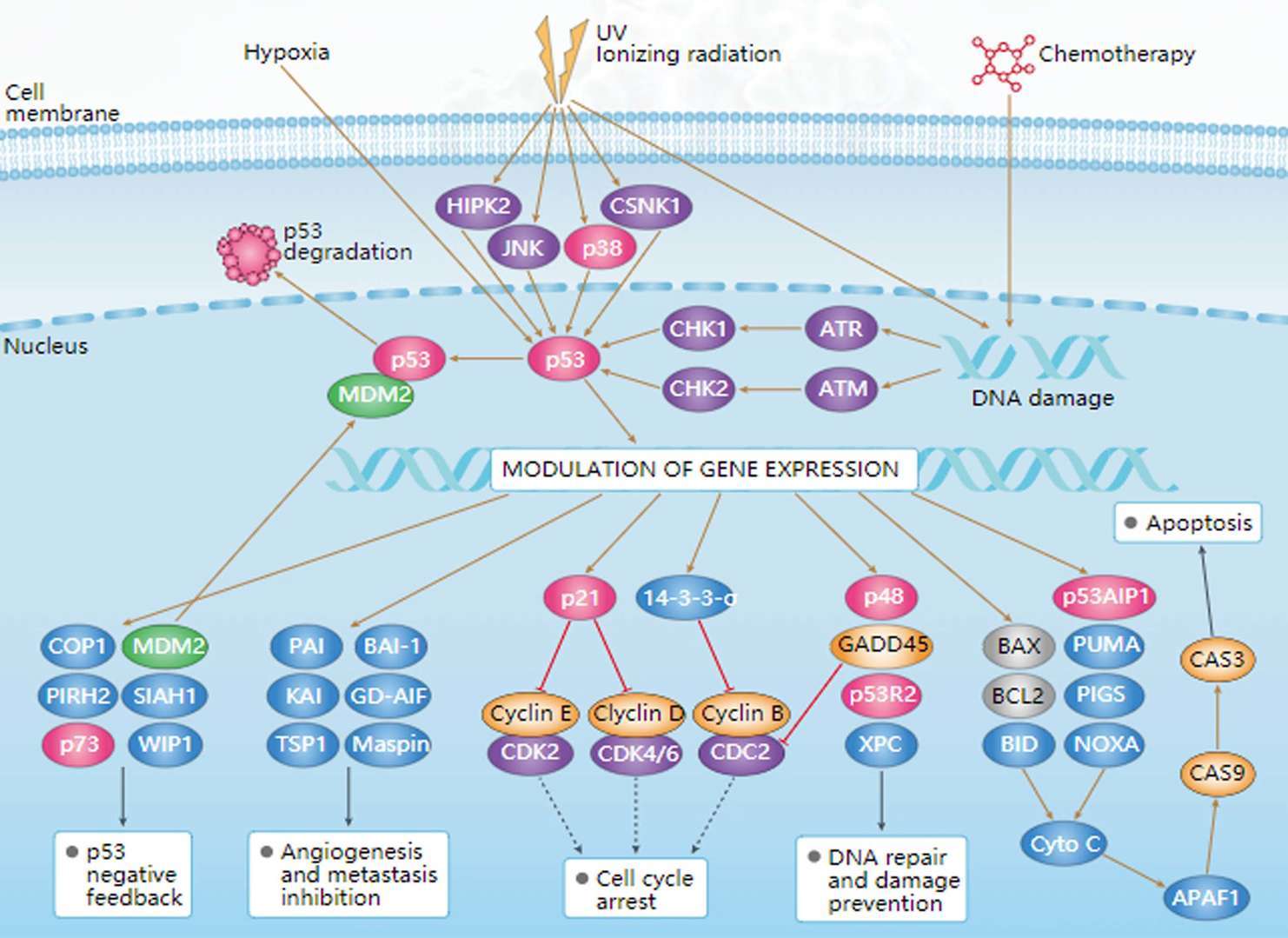 p53 Signaling Pathway
p53 Signaling Pathway