BAX
 Loading...
Loading...Anti-BAX Products
 Loading...
Loading...-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rat IgG
- Application: IP, ELISA, WB, Activ, Inhib
- Rabbit Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (clone CBACN-060) (MRO-0155-CN)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IHC, IP, FC
- Mouse Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (clone 3-D2) (MRO-0156-CN)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Type: Mouse IgA
- Application: WB, IF, IHC, FC
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (HPAB-2961LY) (HPAB-2961LY)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human IgG
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (HPAB-2962LY) (HPAB-2962LY)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human IgG
- Application: Inhib, ELISA
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (HPAB-2963LY) (HPAB-2963LY)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human IgG
- Application: Inhib, ELISA
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (HPAB-2964LY) (HPAB-2964LY)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human IgG
- Application: Block, ELISA, WB, FuncS
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (HPAB-2965LY) (HPAB-2965LY)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human IgG
- Application: Inhib, ELISA
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (HPAB-2966LY) (HPAB-2966LY)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human IgG
- Application: Inhib, ELISA
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (HPAB-2967LY) (HPAB-2967LY)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human IgG
- Application: Inhib, ELISA
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (HPAB-2968LY) (HPAB-2968LY)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human IgG
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (HPAB-2969LY) (HPAB-2969LY)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human IgG
- Application: Inhib, ELISA
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (HPAB-2970LY) (HPAB-2970LY)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human IgG
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (HPAB-2971LY) (HPAB-2971LY)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human IgG
- Application: Inhib, ELISA
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (HPAB-2972LY) (HPAB-2972LY)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human IgG
- Application: Inhib, ELISA
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (HPAB-2973LY) (HPAB-2973LY)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human IgG
- Application: Inhib, ELISA
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (HPAB-2974LY) (HPAB-2974LY)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human IgG
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Mouse Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (clone 2D2) (NEUT-038CQ)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Monkey, Canine, Bovine
- Type: Mouse IgG1, κ
- Application: WB, IP, FC, IHC, Neut
- Rabbit Anti-BAX Polyclonal Antibody (MRO-1679-CN) (MRO-1679-CN)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: IF, IHC
- Rabbit Anti-BAX Polyclonal Antibody (MRO-1680-CN) (MRO-1680-CN)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IF, IHC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Monkey
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: WB
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA, WB, IP, ICC
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human, Rat, Mouse
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: IHC
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human, Rat, Mouse
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: WB, IHC
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human, Monkey
- Type: Mouse IgG2a
- Application: WB
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG2b
- Application: WB
- Rabbit Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (VS3-WK891) (VS3-WK891)
-
- Derivation: Rabbit
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, ICC, IHC
-
- Type: Mouse IgG2b
- Application: ELISA, IHC, FC
-
- Type: Mouse IgG2a
- Application: ELISA, WB, FC
-
- Type: Mouse IgG2b
- Application: ELISA, WB, ICC, IHC, FC
-
- Type: Mouse IgG2b
- Application: ELISA, WB, ICC, IHC, FC
- Recombinant Mouse Anti-BAX Antibody (clone 1C1) (VS3-FY142)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: IHC
- Recombinant Mouse Anti-BAX Antibody (clone 6F11) (VS3-FY143)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: WB, IHC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IP
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: ELISA, WB, IHC
- Rabbit Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (clone R07-4G1) (VS3-XY3274)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat, Hamster
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IHC-P, IP, FC
- AbPlus™ Anti-Bax Magnetic Beads (VS-0724-YC93) (VS-0724-YC93)
-
- Target: Bax
- Target Species: Mouse
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- Recombinant Anti-human BAX Antibody (MOB-101)
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: IgG
- Application: ELISA, WB, IF, FuncS
-
- Derivation: Human
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: IgG
- Application: ELISA, IF, FuncS
- Mouse Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (clone 6A7) (MOB-0900MZ)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: IHC-P
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: FC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Rat, Mouse
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: WB, IHC-P, IF
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Rat, Mouse, Chicken
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: IF, ICC, WB, IHC-P
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse scFv
- Application: WB, FuncS
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody; Fab Fragment (HPAB-2961LY-F(E)) (HPAB-2961LY-F(E))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human Fab
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Single Domain Antibody
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: WB, FuncS
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Llama VHH
- Application: WB, ELISA, IP, FuncS
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody; scFv Fragment (HPAB-2971LY-S(P)) (HPAB-2971LY-S(P))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human scFv
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody; scFv Fragment (HPAB-2972LY-S(P)) (HPAB-2972LY-S(P))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human scFv
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody; scFv Fragment (HPAB-2973LY-S(P)) (HPAB-2973LY-S(P))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human scFv
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody; scFv Fragment (HPAB-2974LY-S(P)) (HPAB-2974LY-S(P))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human scFv
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody; Fab Fragment (HPAB-2970LY-F(E)) (HPAB-2970LY-F(E))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human Fab
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody; Fab Fragment (HPAB-2971LY-F(E)) (HPAB-2971LY-F(E))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human Fab
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody; Fab Fragment (HPAB-2972LY-F(E)) (HPAB-2972LY-F(E))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human Fab
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody; Fab Fragment (HPAB-2973LY-F(E)) (HPAB-2973LY-F(E))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human Fab
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody; Fab Fragment (HPAB-2974LY-F(E)) (HPAB-2974LY-F(E))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human Fab
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Mouse Anti-NHP BAX Recombinant Antibody (clone 2D2) (VS-1024-XY47)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Non-human primate
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: WB, IHC
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody; scFv Fragment (HPAB-2961LY-S(P)) (HPAB-2961LY-S(P))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human scFv
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody; scFv Fragment (HPAB-2962LY-S(P)) (HPAB-2962LY-S(P))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human scFv
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody; scFv Fragment (HPAB-2963LY-S(P)) (HPAB-2963LY-S(P))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human scFv
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Recombinant Anti-human BAX Antibody Fab Fragment (MOB-101-F(E))
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Fab
- Application: IP, FuncS
- Recombinant Anti-human BAX Antibody scFv Fragment (MOB-101-S(P))
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: scFv
- Application: ELISA, IF, FuncS
- Recombinant Human Anti-human BAX Antibody Fab Fragment (MHH-101-F(E))
-
- Derivation: Human
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Fab
- Application: ELISA, WB, FC, FuncS
- Recombinant Human Anti-human BAX Antibody scFv Fragment (MHH-101-S(P))
-
- Derivation: Human
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: scFv
- Application: WB, Neut, FuncS
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rat scFv
- Application: ELISA, WB, Inhib
- Llama Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (TAB-0056CL-VHH) (TAB-0056CL-VHH)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Llama VHH
- Application: ELISA, FuncS, Apop, BI
- Llama Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (TAB-0057CL-VHH) (TAB-0057CL-VHH)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Llama VHH
- Application: ELISA, FuncS, Apop, BI
- Llama Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (TAB-0058CL-VHH) (TAB-0058CL-VHH)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Llama VHH
- Application: ELISA, FuncS, Apop, BI
- Llama Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (TAB-0059CL-VHH) (TAB-0059CL-VHH)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Llama VHH
- Application: ELISA, FuncS, Apop, BI
- Llama Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (TAB-0060CL-VHH) (TAB-0060CL-VHH)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Llama VHH
- Application: ELISA, FuncS, Apop, BI
- Llama Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody (TAB-0061CL-VHH) (TAB-0061CL-VHH)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Llama VHH
- Application: ELISA, FuncS, Apop, BI
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rat Fab
- Application: ELISA, WB, Inhib
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody; scFv Fragment (HPAB-2964LY-S(P)) (HPAB-2964LY-S(P))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human scFv
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody; scFv Fragment (HPAB-2965LY-S(P)) (HPAB-2965LY-S(P))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human scFv
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody; scFv Fragment (HPAB-2966LY-S(P)) (HPAB-2966LY-S(P))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human scFv
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody; scFv Fragment (HPAB-2967LY-S(P)) (HPAB-2967LY-S(P))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human scFv
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody; scFv Fragment (HPAB-2968LY-S(P)) (HPAB-2968LY-S(P))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human scFv
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody; scFv Fragment (HPAB-2969LY-S(P)) (HPAB-2969LY-S(P))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human scFv
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody; scFv Fragment (HPAB-2970LY-S(P)) (HPAB-2970LY-S(P))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human scFv
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody; Fab Fragment (HPAB-2962LY-F(E)) (HPAB-2962LY-F(E))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human Fab
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody; Fab Fragment (HPAB-2963LY-F(E)) (HPAB-2963LY-F(E))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human Fab
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody; Fab Fragment (HPAB-2964LY-F(E)) (HPAB-2964LY-F(E))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human Fab
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody; Fab Fragment (HPAB-2965LY-F(E)) (HPAB-2965LY-F(E))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human Fab
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody; Fab Fragment (HPAB-2966LY-F(E)) (HPAB-2966LY-F(E))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human Fab
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody; Fab Fragment (HPAB-2967LY-F(E)) (HPAB-2967LY-F(E))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human Fab
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody; Fab Fragment (HPAB-2968LY-F(E)) (HPAB-2968LY-F(E))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human Fab
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-BAX Recombinant Antibody; Fab Fragment (HPAB-2969LY-F(E)) (HPAB-2969LY-F(E))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human Fab
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat, Chicken (Predicted), Goat (Predicted), Pig (Predicted)
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IF, FC, IP
- Anti-Mouse BAX Immunohistochemistry Kit (VS-0525-XY699)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Target: BAX
- Application: IHC
- Anti-Human BAX Immunohistochemistry Kit (VS-0525-XY698)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Target: BAX
- Application: IHC
- Recombinant Anti-human BaX Intrabody [(D-Arg)9] (IAB-B001(A))
-
- Species Reactivity: human
- Type: vhh-(D-Arg)9
- Application: ELISA, ICC, FuncS
-
- Derivation: Phage display library screening
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: IHC-P
- Recombinant Anti-human BaX Intrabody [+36GFP] (IAB-B001(G))
-
- Species Reactivity: human
- Type: vhh-(+36GFP)
- Application: PCA, Neut, FuncS
- Recombinant Anti-human BaX Intrabody [Tat] (IAB-B001(T))
-
- Species Reactivity: human
- Type: vhh-Tat
- Application: WB, Neut, FuncS
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG2a
- Application: IHC
- Anti-BAX Immunohistochemistry Kit (VS-0325-XY225)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Target: BAX
- Application: IHC
- Anti-BAX Antibody Prodrug, Protease Activated (3C10) (VS-1025-YC174)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Host Animal: Rat
- Target: BAX
- Application: ISZ, Cyt, FuncS
Can't find the products you're looking for? Try to filter in the left sidebar.Filter By Tag
Our customer service representatives are available 24 hours a day, from Monday to Sunday. Contact Us
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.
Background
Cancer-related genes, Human disease related genes, Transporters
Intracellular
Low cell type specificity
Low immune cell specificity
Low cell line specificity
Homodimer. Forms higher oligomers under stress conditions. Forms heterooligomers with BAK (PubMed:29531808). Interacts with BCL2L11. Interaction with BCL2L11 promotes BAX oligomerization and association with mitochondrial membranes, with subsequent release of cytochrome c. Forms heterodimers with BCL2, BCL2L1 isoform Bcl-X(L), BCL2L2, MCL1 and A1 (PubMed:25609812). Interacts with SH3GLB1. Interacts with humanin; forms fibers with humanin which results in BAX conformational changes and sequestering of BAX into the fibers, preventing BAX activation (PubMed:12732850, 31690630). Interacts with SFN and YWHAZ; the interaction occurs in the cytoplasm. Under stress conditions, JNK-mediated phosphorylation of SFN and YWHAZ, releases BAX to mitochondria. Interacts with RNF144B, which regulates the ubiquitin-dependent stability of BAX. Interacts with CLU under stress conditions that cause a conformation change leading to BAX oligomerization and association with mitochondria. Does not interact with CLU in unstressed cells. Interacts with FAIM2/LFG2. Interacts with RTL10/BOP. Interacts (via a C-terminal 33 residues) with NOL3 (via CARD domain); inhibits BAX activation and translocation and consequently cytochrome c release from mitochondria. Interacts with GIMAP3/IAN4 and GIMAP5/IAN5; this interaction is increased, when cells initiate apoptosis upon IL2 withdrawal (PubMed:16509771). Interacts with IRF3; the interaction is direct, increases upon Sendai virus infection and mediates the formation of the apoptosis complex TOMM70:HSP90AA1:IRF3:BAX (PubMed:25609812). Interacts with MOAP1, facilitating BAX-dependent mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization and apoptosis (PubMed:11060313, 16199525). Interacts with BCL2L10/BCL-B (PubMed:23235460). [Isoform Sigma]: Interacts with BCL2A1 and BCL2L1 isoform Bcl-X(L). (Microbial infection) Interacts with adenovirus E1B 19K protein; this interaction blocks BAX oligomerization (PubMed:11462023). (Microbial infection) Interacts with human cytomegalovirus/HHV-5 protein vMIA/UL37. (Microbial infection) Interacts with enterovirus protein 2B; this interaction activates BAX-induced apoptosis.


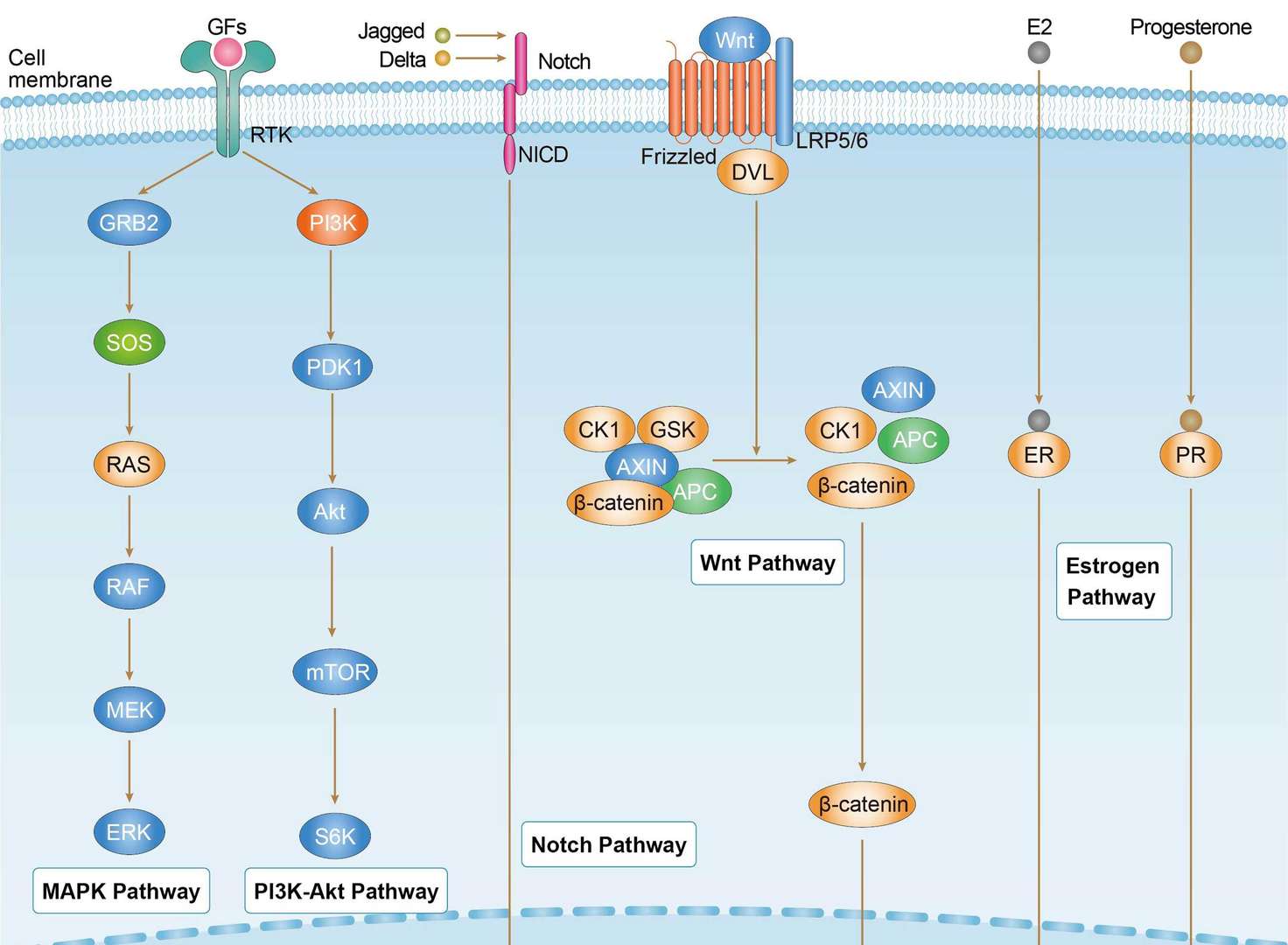 Breast Cancer
Breast Cancer
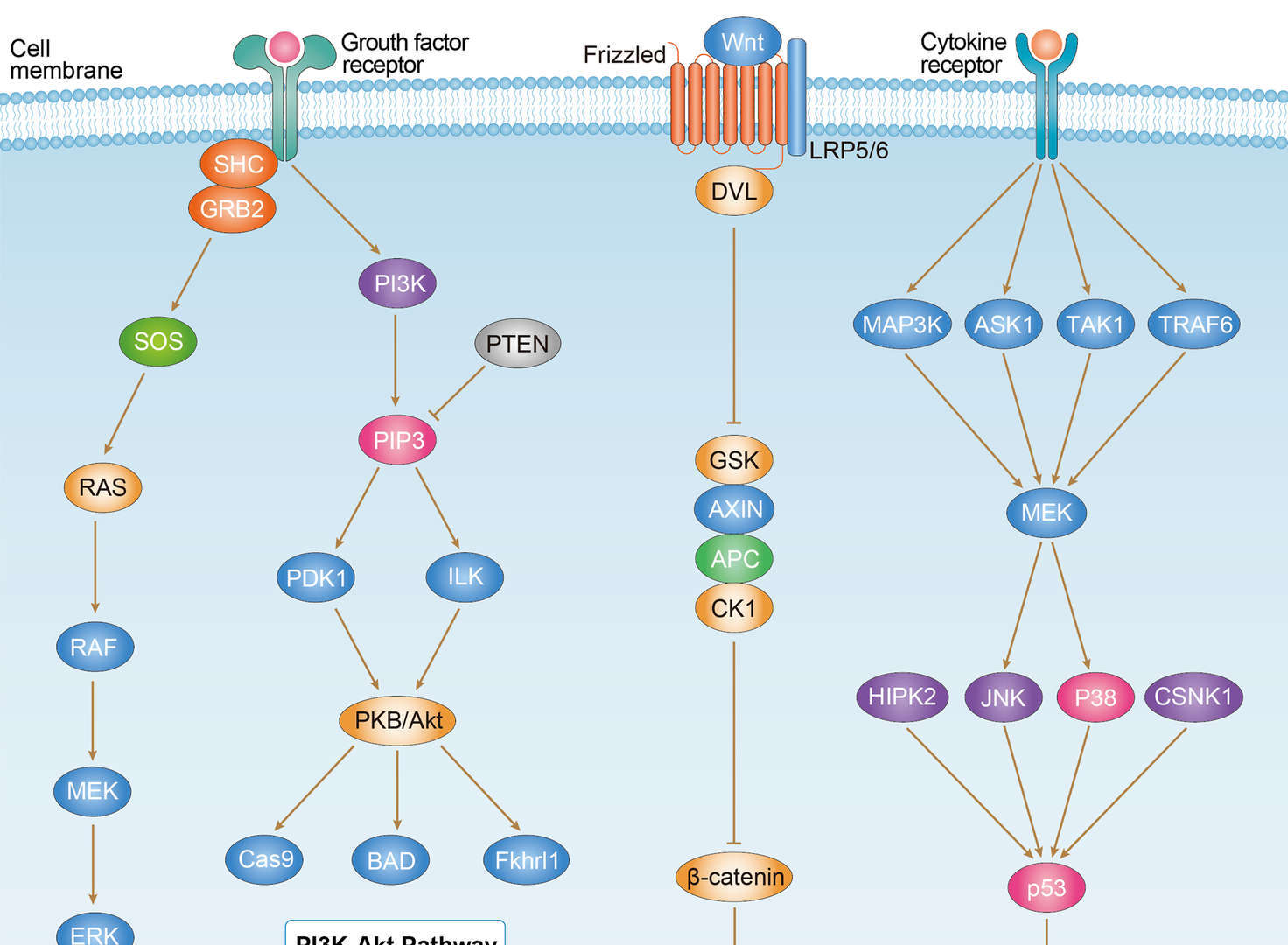 Endometrial Cancer
Endometrial Cancer
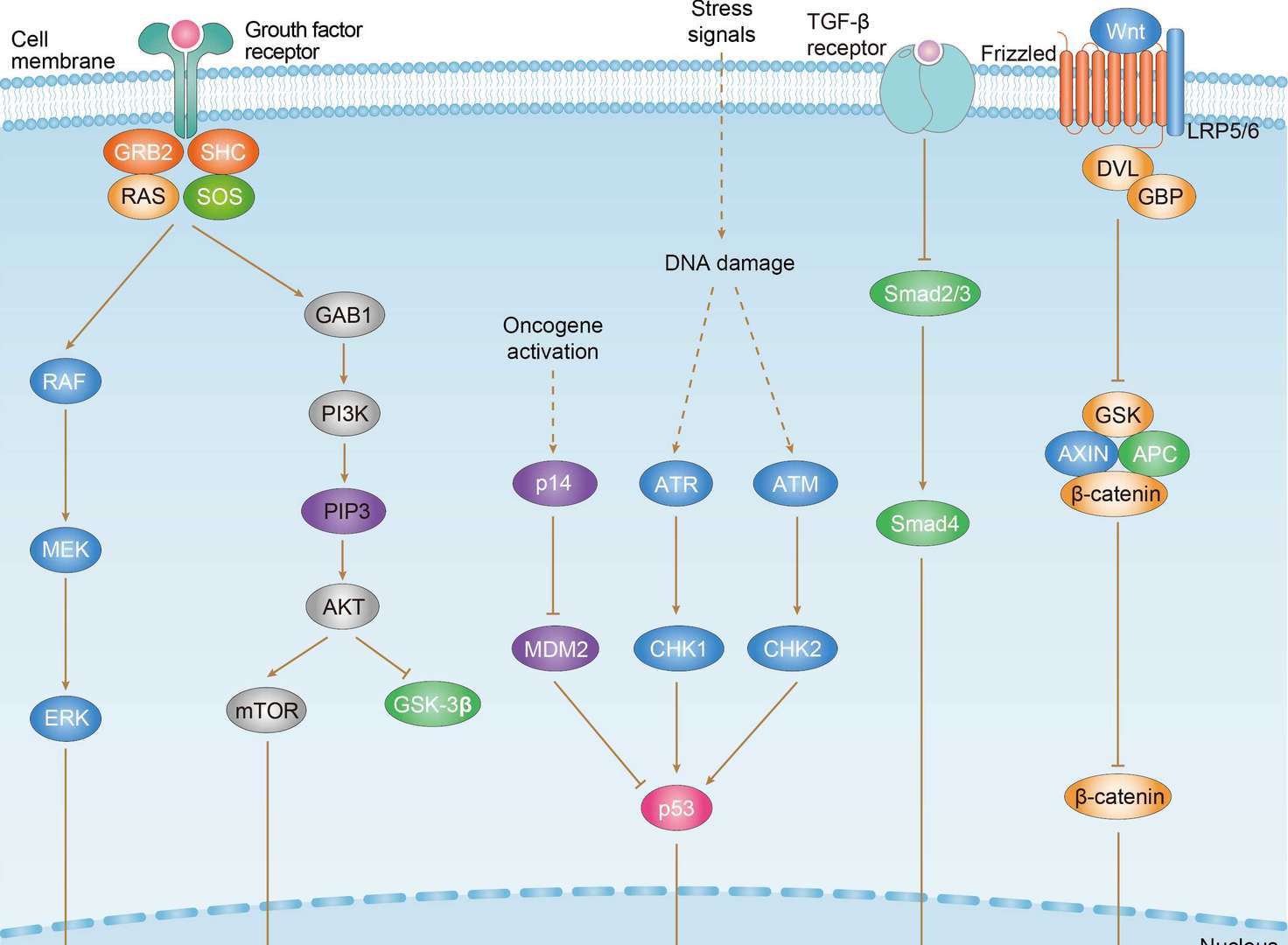 Gastric Cancer
Gastric Cancer
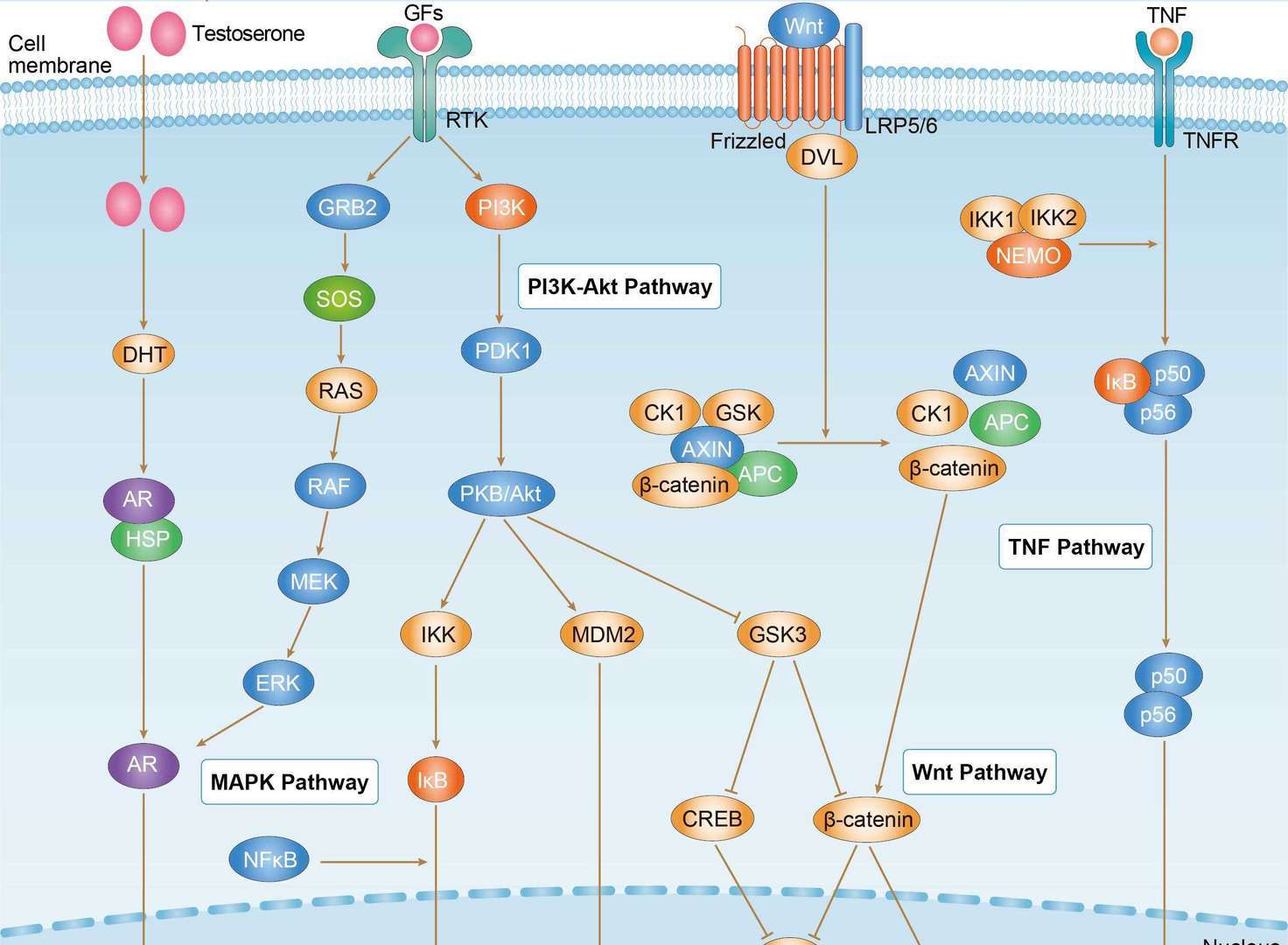 Prostate Cancer
Prostate Cancer
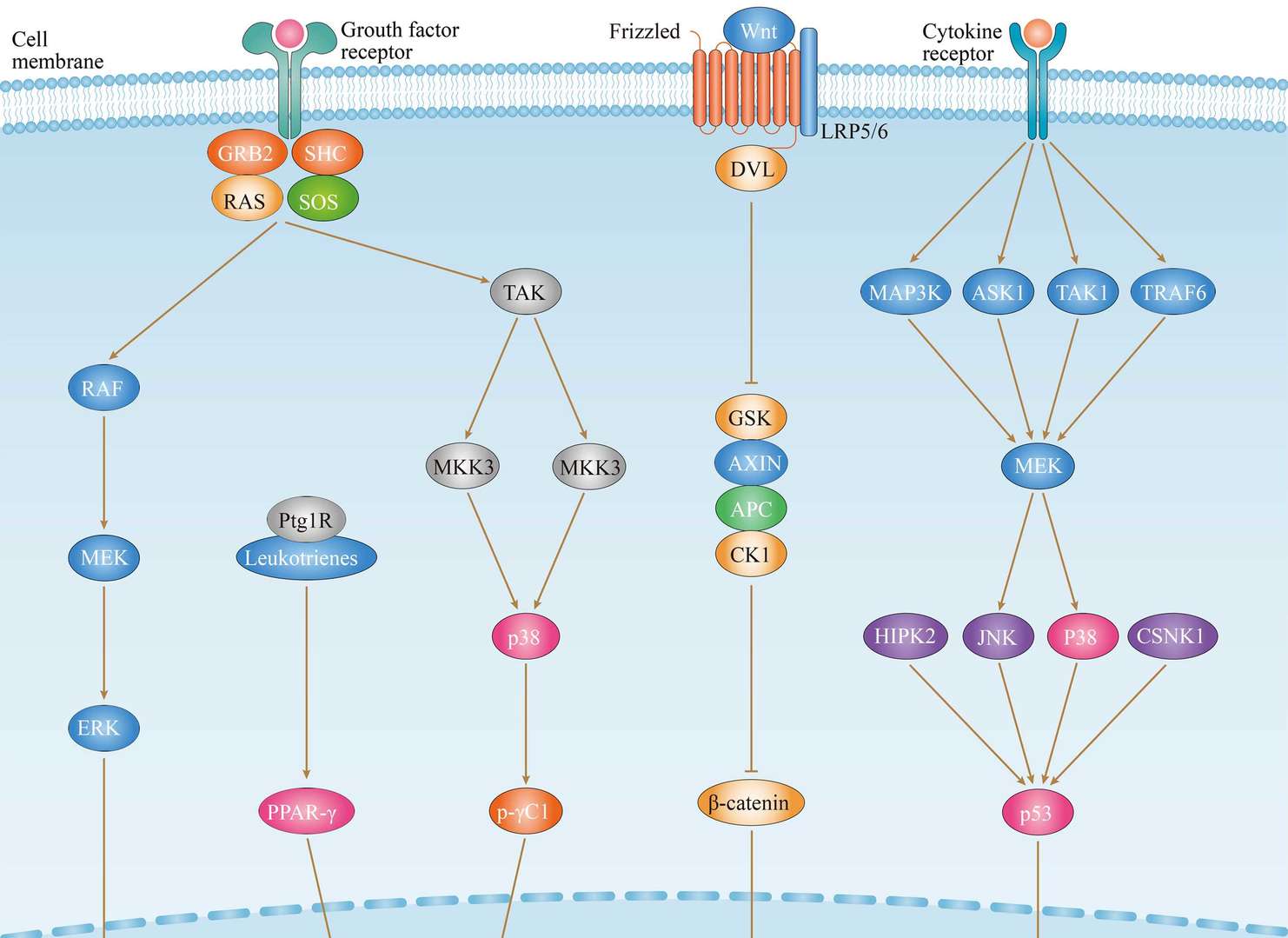 Throid Cancer
Throid Cancer
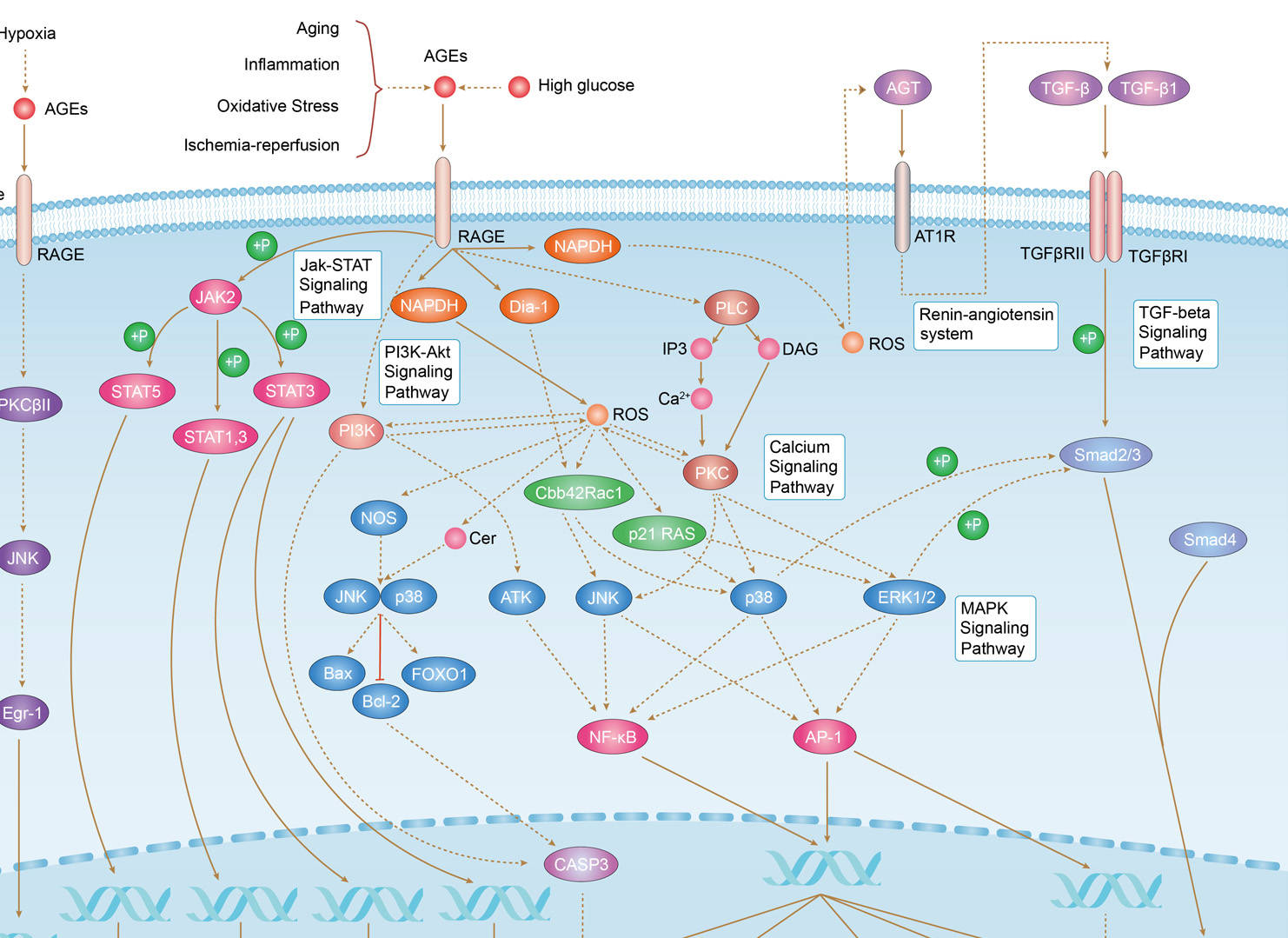 AGE-RAGE Signaling Pathway in Diabetic Complications
AGE-RAGE Signaling Pathway in Diabetic Complications
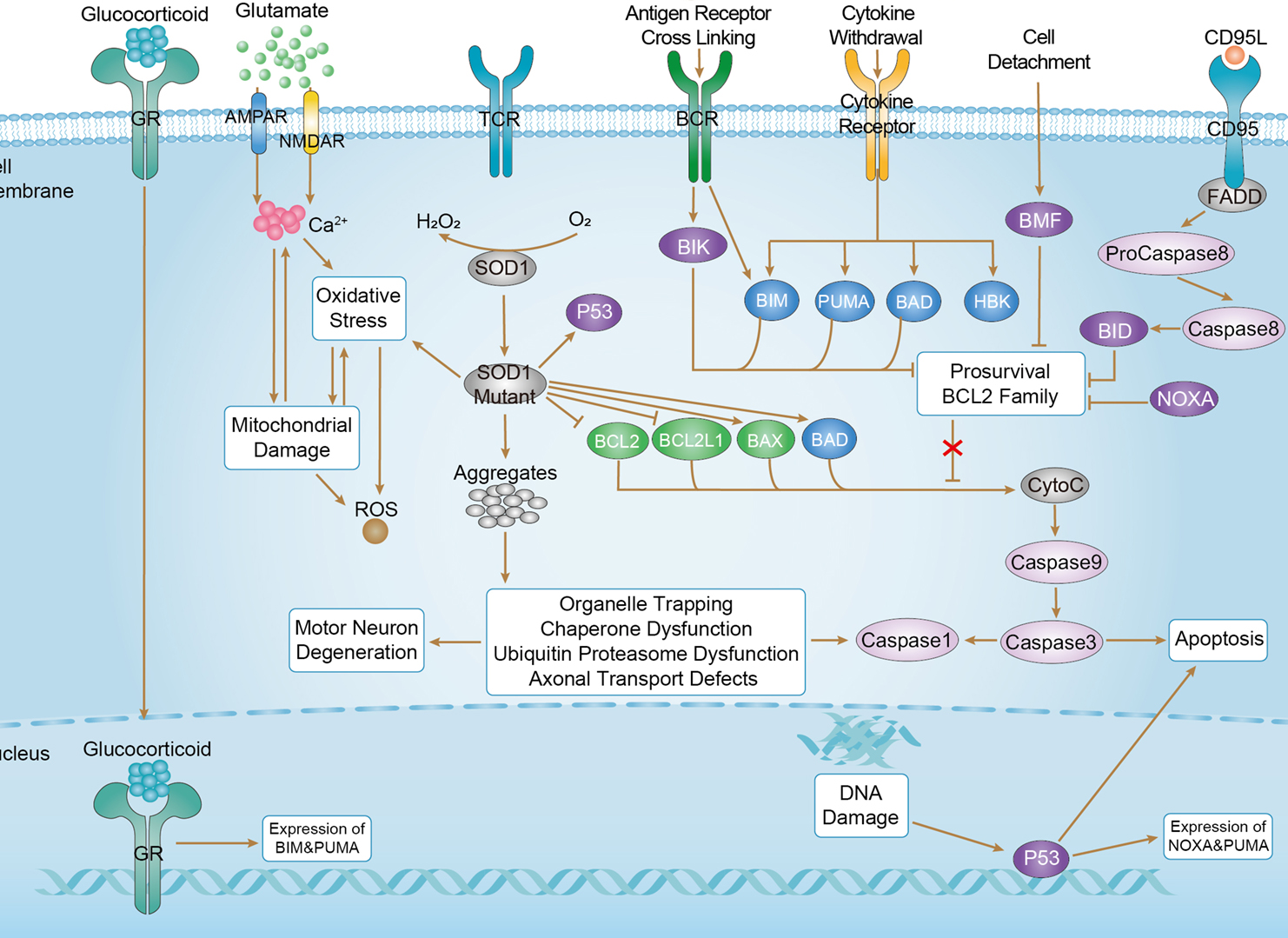 Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
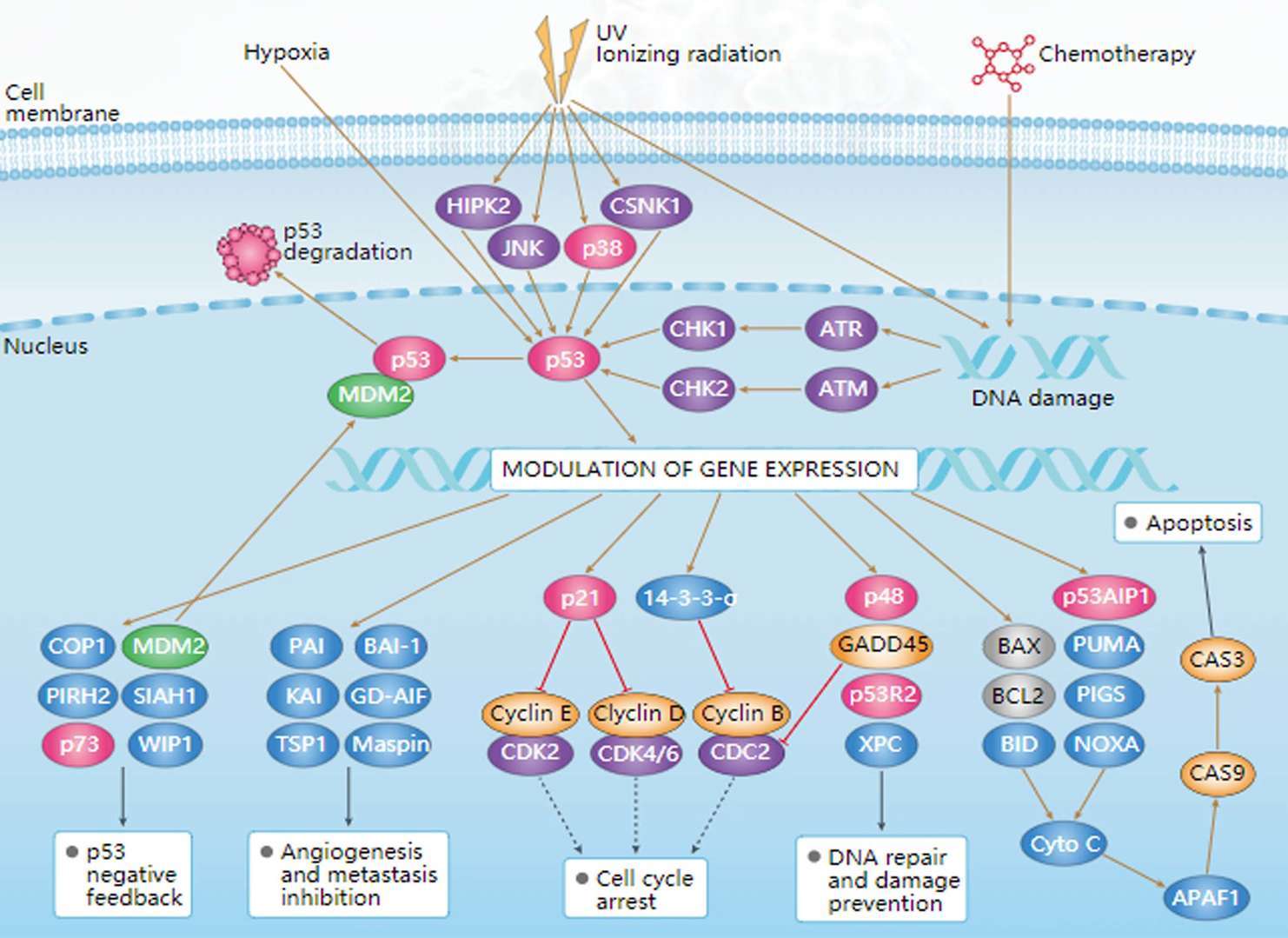 p53 Signaling Pathway
p53 Signaling Pathway