Hexamer Antibody Products
Most depleting monoclonal antibody (mAb) drugs work through interactions with Fc-FcγR and Fc-C1q. Optimal interaction with C1q is accomplished by forming hexameric Fc:Fc structures on the surface of target cells. Studies have shown that hexameric hIgG1 reagents significantly enhance mAb efficacy, primarily acting as strong CDC-inducing agents. These hexamers recruit and activate C1, the initial component of the complement system, thereby initiating the complement cascade. Creative Biolabs has developed a variety of hexameric antibody products targeting both hematological and solid tumor cells through IgG hexamerization techniques.
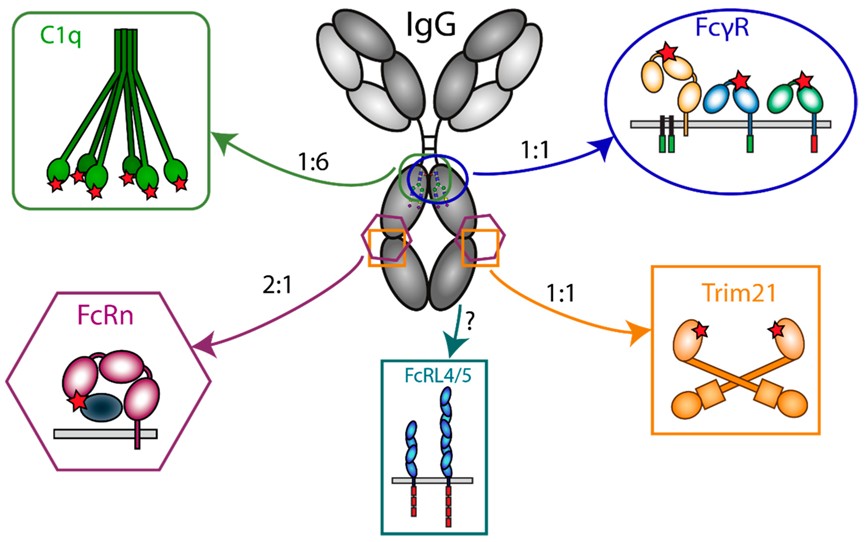 Fig. 1 Interaction of IgG with Fc effector molecules.1, 5
Fig. 1 Interaction of IgG with Fc effector molecules.1, 5
Effector Functions of IgG Hexamers
IgG predominantly exists as a monomer. However, monomeric IgG can assemble into ordered hexamers, enhancing the antibody's efficacy. The identification of hexameric IgG offers a novel strategy for developing therapeutics with improved effector functions through the hexamerization of IgG antibodies. As a potent CDC-inducing agent, IgG hexamers uniquely stand out from IgG monomers by significantly increasing their avidity for the six-headed globular protein C1q.
Enhanced complement activation: IgG antibodies that are bound to a cellular surface form a hexameric structure that increases the avidity of C1q, which allows for optimal complement activation.
Increased cytotoxic activity: Combining hexameric IgG1 antibodies with other targeting antibodies can increase cytotoxic activity. This combination can also improve tumor-specific targeting and reduce the ability of tumors to escape through antigen loss or target internalization.
Improved neutralization capacity: Hexamer-enhancing mutations in the Fc region of IgG antibodies can improve their ability to neutralize viruses and increase anti-viral potency. The neutralization potency of IgG1 hexamers has been tested in both pseudovirus and live virus assays.
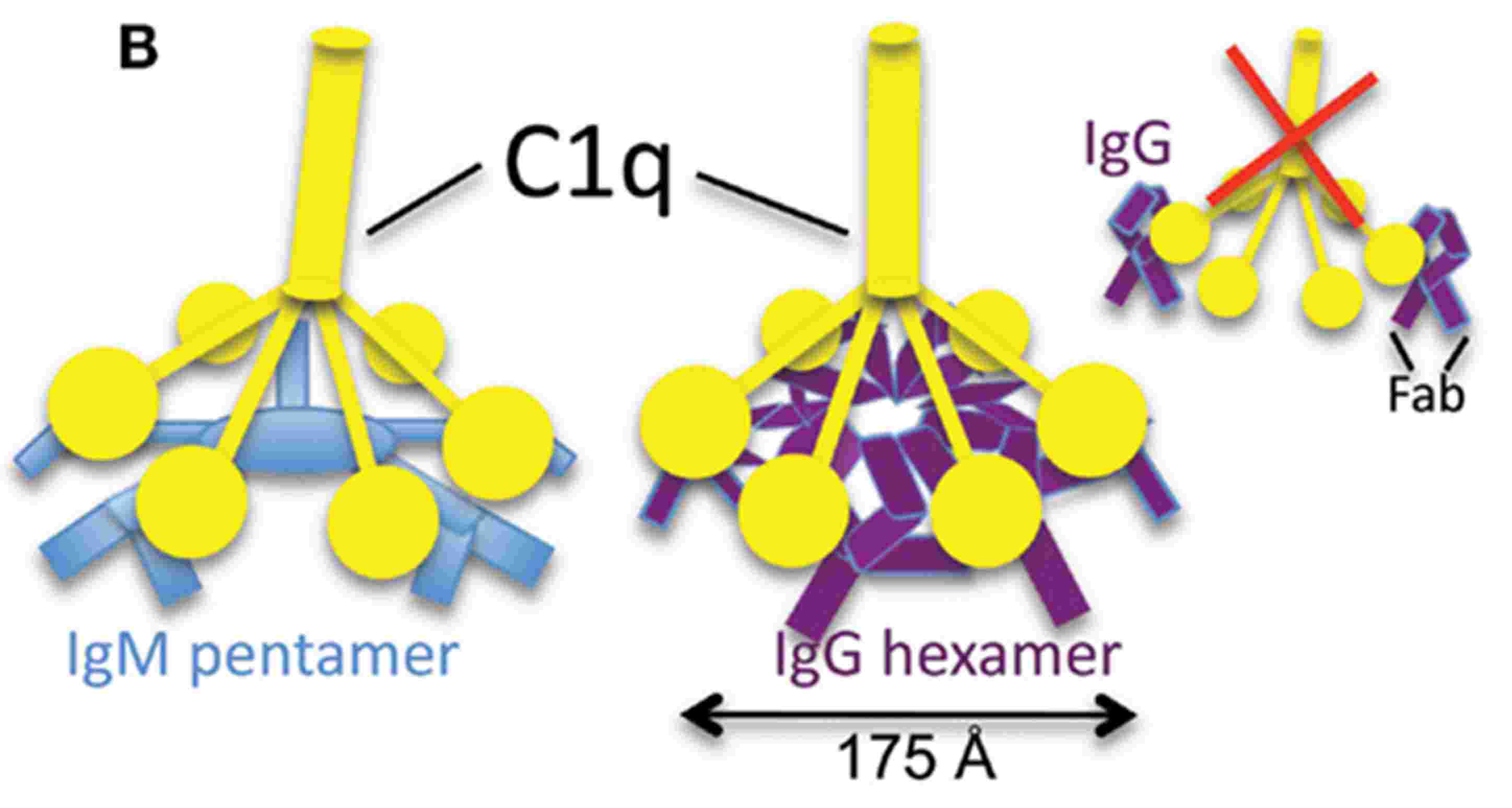 Fig. 2 The interaction modes between C1q and IgM or IgG hexamers, the best classical pathway activators.2, 5
Fig. 2 The interaction modes between C1q and IgM or IgG hexamers, the best classical pathway activators.2, 5
IgG Hexamerization Technology
- Fusing IgG Fc with IgM μtp
IgM exists as polymeric immunoglobulins, featuring an 18-amino acid extension (PTLYNVSLVMSDTAGTCY) at the C-terminus, known as the tailpiece (μtp). This μtp is known to form disulfide bonds between adjacent tailpiece molecules, like the J chain. Leveraging the properties of μtp, a method for IgG hexamerization was developed by fusing the IgM μtp to the C-terminus of hIgG Fc. The fusion of the IgG tailpiece results in spontaneous covalent multimerization and demonstrates high complement activity in vitro. CDC enhancement can be achieved through Fc mutations that promote IgG hexamerization. Mutation of the penultimate cysteine in μtp to a serine disrupts spontaneous and stable hexamerization, favoring the formation of hIgG1 monomers in solution, while increasing the likelihood of non-covalent Fc-Fc interactions, which lead to multimerization.
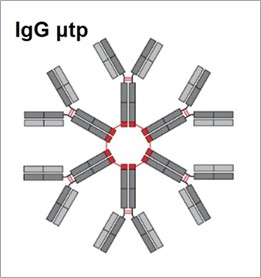 Fig. 3 Schematic of the hIgG μtp hexamer.3, 5
Fig. 3 Schematic of the hIgG μtp hexamer.3, 5
- IgG Fc mutation
Natural human IgG antibodies can form hexamers after binding to cell surface antigens, which in turn can activate the classical complement pathway. The assembly into hexamers can be enhanced by specific mutations in the IgG Fc domain that can boost complement activation and lead to the clustering of cell surface receptors, as well as promote Fc domain-mediated hexamerization. Studies have shown that the self-association of IgG variants with specific point mutations exhibited large enhancement in CDC activity above the wild-type by up to a hundredfold. IgG molecules with single mutations located in the CH3 domain (E430, E345, or S440) of the antibody, facilitate interactions between Fc domains after cell surface binding, resulting in enhanced hexamer formation.
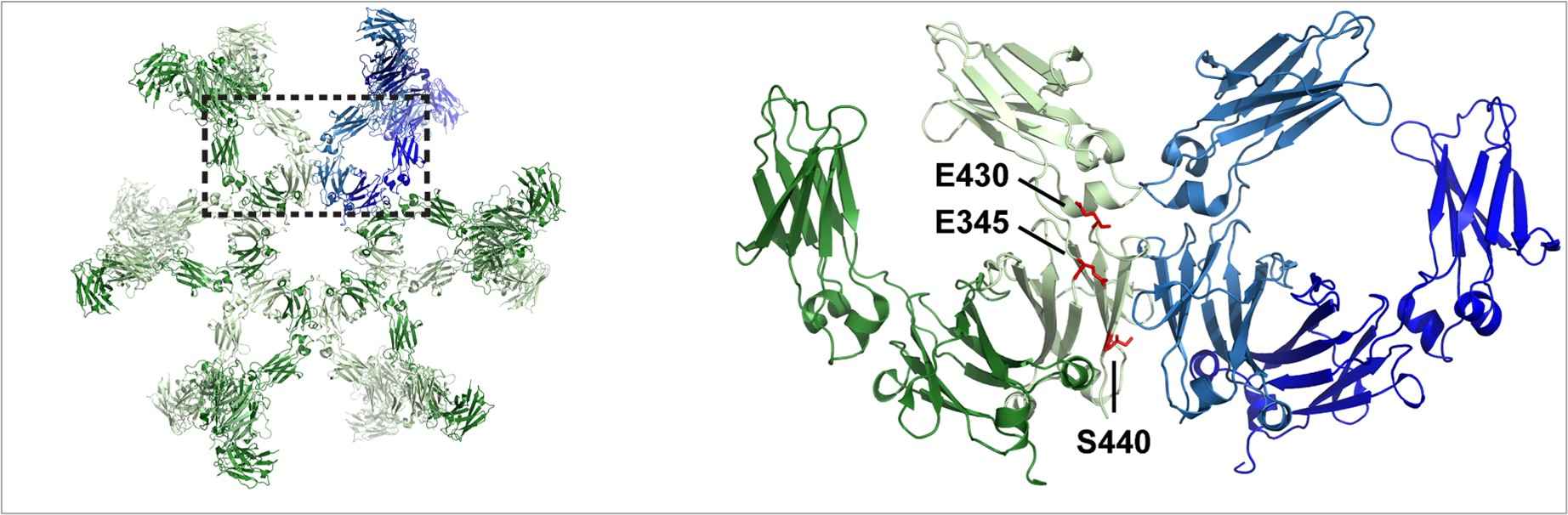 Fig. 4 The crystal structure of IgG1 antibody hexamer.4, 5
Fig. 4 The crystal structure of IgG1 antibody hexamer.4, 5
Creative Biolabs' antibody hexamers have demonstrated increased monoclonal antibody (mAb) efficacy, primarily by acting as potent complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) agents. By selectively enhancing their affinity for C1q, these IgG hexamers exhibit significantly improved complement activity. If hexameric antibodies can contribute to your project, please feel free to contact us for a formal quote.
References
- de Taeye, Steven W., Theo Rispens, and Gestur Vidarsson. "The ligands for human IgG and their effector functions." Antibodies 8.2 (2019): 30.
- Gaboriaud, Christine, et al. "Deciphering the fine details of c1 assembly and activation mechanisms:"mission impossible"?." Frontiers in immunology 5 (2014): 565.
- Sopp, Joshua M., et al. "On-target IgG hexamerization driven by a C-terminal IgM tail-piece fusion variant confers augmented complement activation." Communications Biology 4.1 (2021): 1031.
- de Jong, Rob N., et al. "A novel platform for the potentiation of therapeutic antibodies based on antigen-dependent formation of IgG hexamers at the cell surface." PLoS biology 14.1 (2016): e1002344.
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
 Loading...
Loading...-
- Derivation: Humanized
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: ELISA, WB, FC, ADCC, CDC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: ELISA, WB, SPR, ADCC, CDC, Inhib
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: DB, WB, IP, ELISA, FC, CDC
-
- Derivation: Humanized
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: ELISA, Inhib, CDC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: CDC
-
- Derivation: Humanized
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: IB, CDC, Inhib
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: ELISA, Inhib, CDC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: ELISA, WB, FC, ADCC, CDC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: FC, WB, ELISA, Cyt, CDC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: ELISA, FC, CDC, ADCC
-
- Derivation: Humanized
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: ELISA, CDC, SPR
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: ELISA, WB, SPR, ADCC, CDC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: FC, Inhib, CDC
-
- Derivation: Humanized
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: CDC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: ELISA, FC, CDC
-
- Derivation: Chimeric (rat/human)
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: ELISA, FC, ADCC, CDC, SPR
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: WB, ELISA, IF, CDC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Monkey
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: ELISA, ADCC, CDC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: ELISA, Block, FC, IF, Activ, CDC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: ELISA, Cyt, CDC
-
- Derivation: Chimeric (human/mouse)
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: ELISA, Inhib, CDC
-
- Derivation: Humanized
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: ELISA, FC, CDC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: Inhib, CDC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Monkey
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: ELISA, Inhib, ADCC, ADCP, CDC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: FC, ADCC, CDC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Monkey
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: CDC
-
- Derivation: Humanized
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: ELISA, CDC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Marmoset, Chimpanzee
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: IHC, FC, ADCC, CDC
-
- Derivation: Hybridoma
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: ELISA, WB, CDC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: ELISA, ADCC, CDC
-
- Derivation: Chimeric (mouse/human)
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: ELISA, IF, ADCC, CDC, Cyt
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: Apop, CDC, FC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: CDC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: CDC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: ELISA, FC, CDC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: CDC, ADCC, ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: FC, CDC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: FC, WB, BI, ELISA, CDC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: FC, CDC, IP
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: FC, Activ, Agonist, IF, WB, Cyt, CDC
-
- Derivation: Humanized
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: IP, IF, FuncS, FC, Neut, ELISA, CDC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: ELISA, Block, CDC
-
- Derivation: Chimeric (mouse/human)
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: FC, ADCC, CDC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: FC, ADCC, CDC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: CDC
-
- Species Reactivity: Cynomolgus
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: CDC, ADCC, Inhib, FC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: CDC
-
- Derivation: Chimeric (rabbit/human)
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: ELISA, SPR, FC, ADCC, CDC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: ELISA, FC, CDC
-
- Derivation: Humanized
- Species Reactivity: Human, Cynomolgus
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: Cyt, FC, CDC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody hexamer
- Application: ELISA, CDC
Our customer service representatives are available 24 hours a day, from Monday to Sunday. Contact Us
Can't find the products you're looking for? Try to filter in the left sidebar.Filter By Tag
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.

