ADCC/CDC Decreased Antibody Products
The Necessary of ADCC/CDC Decreased Antibody Development
Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity (ADCC) and Complement-Dependent Cytotoxicity (CDC) are crucial mechanisms for antibody-mediated target cell elimination. While beneficial in many therapeutic applications, excessive ADCC/CDC can lead to unintended consequences. For example, antibodies may bind to off-target cells or self-antigens, causing harm. Additionally, overactivation of the immune system due to ADCC/CDC often results in a potentially life-threatening cytokine storm. To mitigate these risks and improve the safety profile of therapeutic antibodies, it is essential to develop strategies to decrease ADCC/CDC activity.
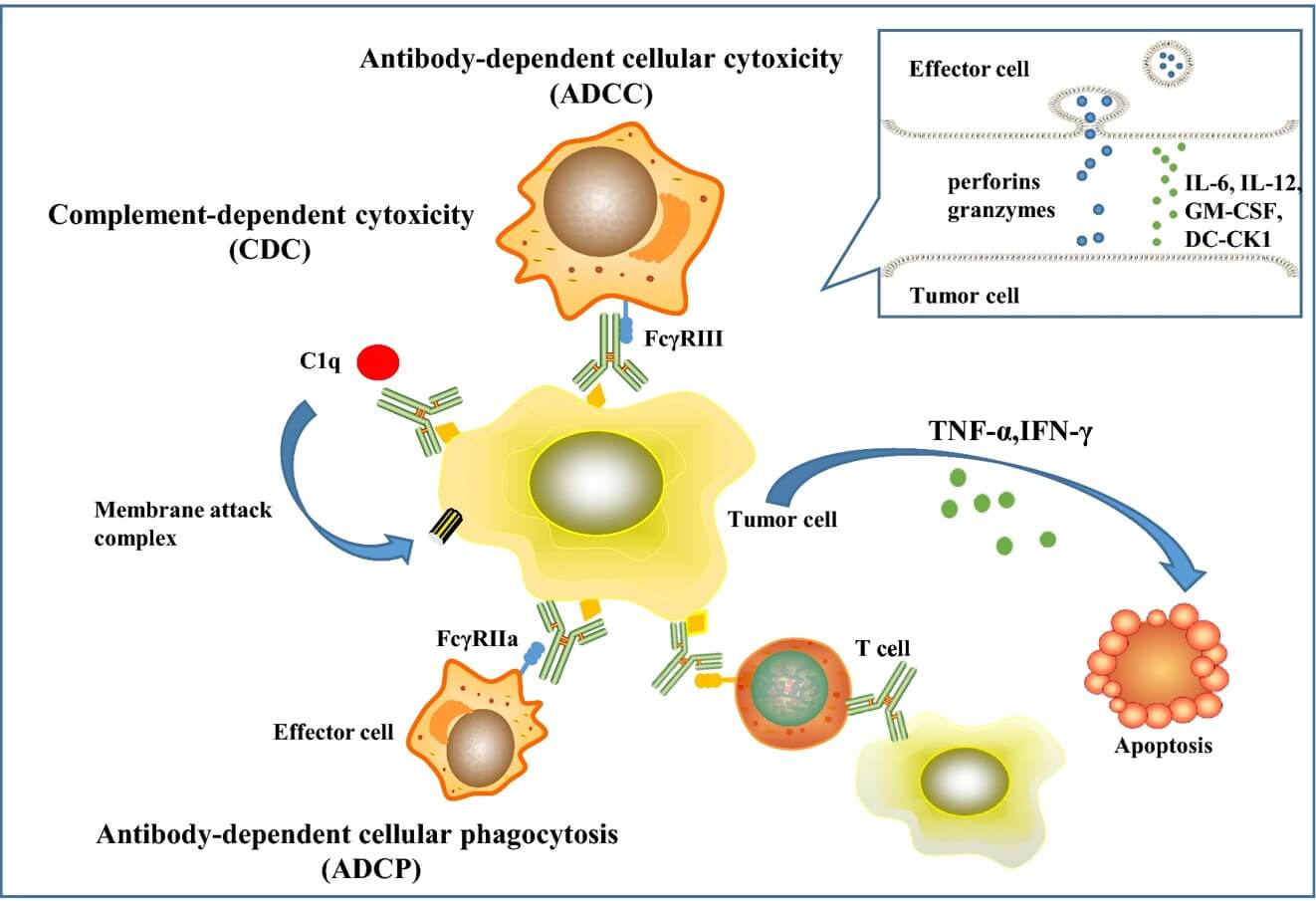 Fig.1 A trifunctional BsAb-mediated killing mechanism.1
Fig.1 A trifunctional BsAb-mediated killing mechanism.1
Our ADCC/CDC Decreased Antibody Production Service: Customized for Your Special Demands
At Creative Biolabs, our ADCC/CDC decreased antibody production service offers a customized solution to produce antibodies with reduced effector functions. By precisely modulating ADCC or CDC activities, we can develop antibodies tailored to specific research needs. Based on our extensive expertise and experience, we provide several strategies such as engineering the Fc domains or antibody formats to decrease antibodies' ADCC/CDC. Moreover, our advanced platform enables the generation of ADCC/CDC-decreased antibodies with enhanced safety profiles, reduced off-target effects, and minimized risk of cytokine release syndrome.
In addition, we employ a comprehensive set of strict quality control techniques to ensure the excellent quality of the ADCC/CDC-decreased antibodies. We provide specialized services to detect ADCC/CDC-decreased antibodies, such as ADCC & CDC assays, FcγR binding detection, complement binding assays, etc. Whether your research focuses on autoimmune diseases, cancer, or other areas, our expertise in antibody engineering and production can help you achieve your specific goals.
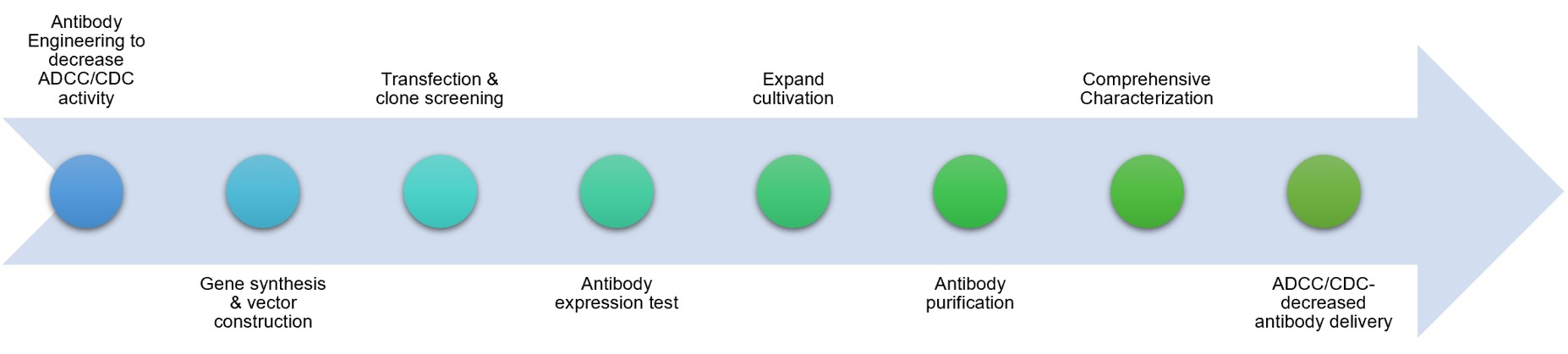 Fig.2 Our service process.
Fig.2 Our service process.
ADCC/CDC Decrease Strategies
|
|
||
| Glycosylation Modifications | Amino Acid Mutations | IgG Isotype Switching | Bispecific Antibodies |
| Altering the glycosylation pattern of the Fc region can impact the binding affinity of the antibody to Fc receptors and complement proteins. | Specific amino acid substitutions in the Fc region can weaken the interaction with Fc receptors and complement proteins. | Different IgG isotypes have varying degrees of ADCC/CDC activity. Switching to an isotype with a lower effector function can reduce these activities. | By designing bispecific antibodies with a reduced Fc domain or a modified Fc domain, ADCC/CDC can be attenuated. |
Our Service Highlights
- Customized antibody design and production to meet your specific needs.
- Advanced Engineering techniques to fine-tune ADCC/CDC activity.
- Rigorous quality control for highest standards ADCC/CDC-decreased antibody production.
- Efficient production of high-quality ADCC/CDC-reduced antibodies.
- Comprehensive characterization for detailed analysis of ADCC/CDC-decreased antibody properties.
Customer Speaking
Jo***y ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ Excellent! 20/Oct/2024
I was delighted with Creative Biolabs' professionalism and personalized attention. Their team created antibodies with precisely lowered ADCC/CDC activity to fulfill our unique study requirements. The final product's excellent quality and uniformity were guaranteed by stringent quality control procedures. Furthermore, these antibodies performed well in our pre-clinical tests, indicating effectiveness with minimal adverse effects. This is a huge victory for my project.
Are you seeking a tailored antibody solution that prioritizes specificity and minimizes off-target effects? Please don't hesitate to contact us for more details about our ADCC/CDC decreased antibody production service and high-quality ADCC/CDC antibody products.
- Wu, Yuze, et al. "Recent advances and challenges of bispecific antibodies in solid tumors." Experimental hematology & oncology 10.1 (2021): 56. Distributed under Open Access License CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.

