Head and Neck Cancer Biomarkers
Product List
 Loading...
Loading...-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG2a
- Application: IHC, WB
- Anti-Human CD59 Recombinant Antibody Fab Fragment ((ch)AR36A36.11.1) (TAB-321LC-F(E))
-
- Derivation: Chimeric (mouse/human)
- Type: Chimeric antibody (mouse/human)
- Application: WB, ELISA
-
- Target: EGFR
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Cytokine 1: IL2
- Host: Mouse
- Cytokine 1 Species: Human
- Molecule Class: IL2-IgG2a
-
- Derivation: Chimeric (mouse/human)
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: IgG1 - kappa
- Application: IF, IP, Neut, FuncS, ELISA, FC, ICC
- Mouse Anti-VEGFA Recombinant Antibody (clone mAb G6-31) (HPAB-0330CQ)
-
- Derivation: Chimeric (mouse/human)
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Type: Chimeric (mouse/human) IgG
- Application: ELISA, IF, Block, FuncS
- Mouse Anti-EGFR Recombinant Antibody (clone EGFR) (HPAB-0727-CN)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Type: Mouse IgG1, κ
- Application: ELISA, FC, IHC, Neut
- Human Anti-FGFR3 Recombinant Antibody (clone PRO-001) (HPAB-0160-YC)
-
- Derivation: Combinatorial antibody library
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Type: Human IgG
- Application: FC, FuncS
-
- Derivation: Human
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: IgG
- Application: WB, ELISA, FuncS, IB, FC, SPR, Apop
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: ELISA, WB
-
- Derivation: Chimeric
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: IgG1 - kappa
- Application: FuncS, IF, Neut, ELISA, FC, IP, IHC
-
- Derivation: Humanized (from mouse)
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Fab - G1 - kappa
- Application: IP, IF, FuncS, FC, Neut, ELISA, IHC
-
- Derivation: Humanized (from mouse)
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: IgG1 - kappa
- Application: FC, IP, ELISA, Neut, FuncS, IF, ICC
-
- Derivation: Humanized (from rat)
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: IgG1 - kappa
- Application: Neut, ELISA, IF, IP, FuncS, FC, WB
-
- Derivation: Human
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: IgG1 - kappa
- Application: FC, IP, ELISA, Neut, FuncS, IF, WB
-
- Derivation: Humanized (from mouse)
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: IgG1 - kappa
- Application: ELISA, IP, FC, FuncS, Neut, IF, IHC
-
- Derivation: Human
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: IgG1 - kappa
- Application: FC, IP, ELISA, Neut, FuncS, IF, WB
-
- Derivation: Humanized (from rat)
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: IgG4 - kappa
- Application: WB, ELISA, FC, IP, FuncS, IF, Neut
-
- Derivation: Human
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: IgG2 - kappa
- Application: ELISA, IP, FC, FuncS, Neut, IF, ICC
- Human Anti-IL6 Recombinant Antibody (HPAB-S0077-YC) (HPAB-S0077-YC)
-
- Derivation: Humanized
- Species Reactivity: Human, Cynomolgus, Rat, Mouse
- Type: Humanized IgG
- Application: ELISA, Block
- Rabbit Anti-IL6 Recombinant Antibody (HPAB-AP711-YC) (HPAB-AP711-YC)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Cynomolgus, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA, Block, FuncS
- Rat Anti-EGFR Recombinant Antibody (clone ratML66); Fab Fragment (HPAB-0766-FY-S(P))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rat Fab
- Application: ELISA, IHC, FC
- Human Anti-EGFR Recombinant Antibody (HPAB-AP066-YC) (HPAB-AP066-YC)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human IgG
- Application: Inhib, ADCC
- Anti-human IL6 scFv Fragment (SK2a) (TAB-671LC-S(P))
-
- Type: Human antibody
- Application: ELISA
- Anti-Human FGFR3 Recombinant Antibody (15D8) (TAB-064WM)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Application: Neut, ELISA
- Anti-Human EGFR Recombinant Antibody (TAB-014MZ-VHH) (TAB-014MZ-VHH)
-
- Type: Single domain antibody
- Anti-Human CD59 Recombinant Antibody Fab Fragment (1E8) (TAB-318LC-F(E))
-
- Application: FC, ELISA
- Mouse Anti-EGFR Recombinant Antibody (TAB-326MZ) (TAB-326MZ)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: FC
- Mouse Anti-EGFR Recombinant Antibody (TAB-271MZ) (TAB-271MZ)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG2b
- Application: FuncS
- Human Anti-MMP13 Recombinant Antibody (TAB-0820CL) (TAB-0820CL)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human IgG
- Application: ELISA, IHC
- Human Anti-IL6 Recombinant Antibody (TAB-0173CL) (TAB-0173CL)
-
- Derivation: Humanized
- Species Reactivity: Human, Cynomolgus, African green monkey
- Type: Human IgG1
- Application: ELISA, Block, In vivo
- Anti-Human MMP9 Recombinant Antibody (TAB-533CL) (TAB-533CL)
-
- Derivation: Humanized
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody
- Application: WB, Inhib
- Anti-Human MMP8 Recombinant Antibody (TAB-532CL)
-
- Derivation: Humanized
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody
- Anti-Human EGFR Recombinant Antibody (ABT-806) (TAB-228CL)
-
- Derivation: Humanized
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody
- Application: WB, IHC
- AbPlus™ Anti-KRT19 Magnetic Beads (VS-0724-YC1430) (VS-0724-YC1430)
-
- Target: KRT19
- Target Species: Human
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- AbPlus™ Anti-KRT19 Magnetic Beads (VS-0724-YC1429) (VS-0724-YC1429)
-
- Target: KRT19
- Target Species: Human
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- AbPlus™ Anti-CDKN2A Magnetic Beads (VS-0724-YC1355) (VS-0724-YC1355)
-
- Target: CDKN2A
- Target Species: Human
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- AbPlus™ Anti-Cd59 Magnetic Beads (VS-0724-YC1325) (VS-0724-YC1325)
-
- Target: Cd59
- Target Species: Rat
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- AbPlus™ Anti-CTSD Magnetic Beads (VS-0724-YC1036) (VS-0724-YC1036)
-
- Target: CTSD
- Target Species: Human
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- AbPlus™ Anti-Ctsd Magnetic Beads (VS-0724-YC901) (VS-0724-YC901)
-
- Target: Ctsd
- Target Species: Mouse
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- AbPlus™ Anti-Sparc Magnetic Beads (VS-0724-YC635) (VS-0724-YC635)
-
- Target: Sparc
- Target Species: Mouse
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- AbPlus™ Anti-SFN Magnetic Beads (VS-0724-YC546) (VS-0724-YC546)
-
- Target: SFN
- Target Species: Human
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- AbPlus™ Anti-Sfn Magnetic Beads (VS-0724-YC524) (VS-0724-YC524)
-
- Target: Sfn
- Target Species: Mouse
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- AbPlus™ Anti-AFP Magnetic Beads (VS-0724-YC295) (VS-0724-YC295)
-
- Target: AFP
- Target Species: Human
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- AbPlus™ Anti-VEGFA Magnetic Beads (A.4.6.1) (VS-0424-XY273)
-
- Target: VEGFA
- Target Species: Human, Rat
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- AbPlus™ Anti-IL6 Magnetic Beads (AS16) (VS-0424-XY151)
-
- Target: IL6
- Target Species: Human
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- AbPlus™ Anti-EGFR Magnetic Beads (pSEX81-6) (VS-0424-XY84)
-
- Target: EGFR
- Target Species: Human
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- AbPlus™ Anti-CTSD Magnetic Beads (VS-0424-XY74) (VS-0424-XY74)
-
- Target: CTSD
- Target Species: Human
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- AbPlus™ Anti-BMI1 Magnetic Beads (229F6) (VS-0424-XY31)
-
- Target: BMI1
- Target Species: Human, Mouse, Rabbit, Rat
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- Rabbit Anti-IL6 Recombinant Antibody (clone Ab1) (VS-0824-CJ5)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Monkey, Rat, Mouse, Dog
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgM, κ
- Application: FC, IHC, IF
- Mouse Anti-EGFR Recombinant Antibody (VS-0524-YC36) (VS-0524-YC36)
-
- Derivation: Hybridoma
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Application: ELISA, FC, Inhib
- Anti-EGFR Recombinant Antibody (clone MAb 425) (VS-0524-YC33)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Application: ELISA, FC, Block, Cyt
- Human Anti-EGFR Recombinant Antibody (VS-0524-YC32) (VS-0524-YC32)
-
- Derivation: Chimeric (rat/human)
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human IgG1
- Application: ELISA, FC, ADCC
- Rat Anti-EGFR Recombinant Antibody (VS-0524-YC31) (VS-0524-YC31)
-
- Derivation: Hybridoma
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rat IgG2b
- Application: ELISA, FC
- Mouse Anti-MMP2 Recombinant Antibody (VS3-FY2805) (VS3-FY2805)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: WB, ICC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, ICC, IF
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IHC-P, ICC, IF, IP
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, ICC, IF, IP
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, ICC, IF
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, ICC, IF, IP, FC
-
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IHC-P, ICC, IF
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB
- Rabbit Anti-KRT19 Recombinant Antibody (VS3-FY2756) (VS3-FY2756)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IHC, ICC, IP
- Mouse Anti-EGFR Recombinant Antibody (VS3-FY2695) (VS3-FY2695)
-
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: WB, ICC, IP
- Rabbit Anti-CDKN2A Recombinant Antibody (VS3-FY2607) (VS3-FY2607)
-
- Species Reactivity: Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, ICC, IP
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Mouse
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Mouse
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Mouse
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Mouse
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Mouse
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Mouse
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Mouse
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Mouse
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Mouse
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Mouse
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Mouse
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Mouse
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Mouse
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Mouse
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
Our customer service representatives are available 24 hours a day, from Monday to Sunday. Contact Us
Can't find the products you're looking for? Try to filter in the left sidebar.Filter By Tag
Head and neck cancer encompasses a diverse group of malignancies that arise in the head and neck region, including the oral cavity, pharynx, larynx, paranasal sinuses, nasal cavity, and salivary glands. These cancers are primarily linked to tobacco use, alcohol consumption, and human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, with a significant proportion of oropharyngeal cancers being HPV-positive. The global incidence of head and neck cancers varies widely, reflecting regional habits and risk factor exposure. Clinical manifestations can include a persistent sore throat, hoarseness, a lump in the neck, and difficulty swallowing, but early-stage disease may be asymptomatic. Diagnosis typically involves physical examination, imaging studies, and biopsy. Treatment options are multidisciplinary, combining surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy, with the choice of treatment depending on the cancer's location, stage, and the patient's overall health. Recent advances in molecular biology and immunotherapy offer new hope for targeted treatments, improving outcomes and reducing toxicity. Despite advancements, the prognosis for head and neck cancer patients remains variable, with early detection and treatment being crucial for survival.
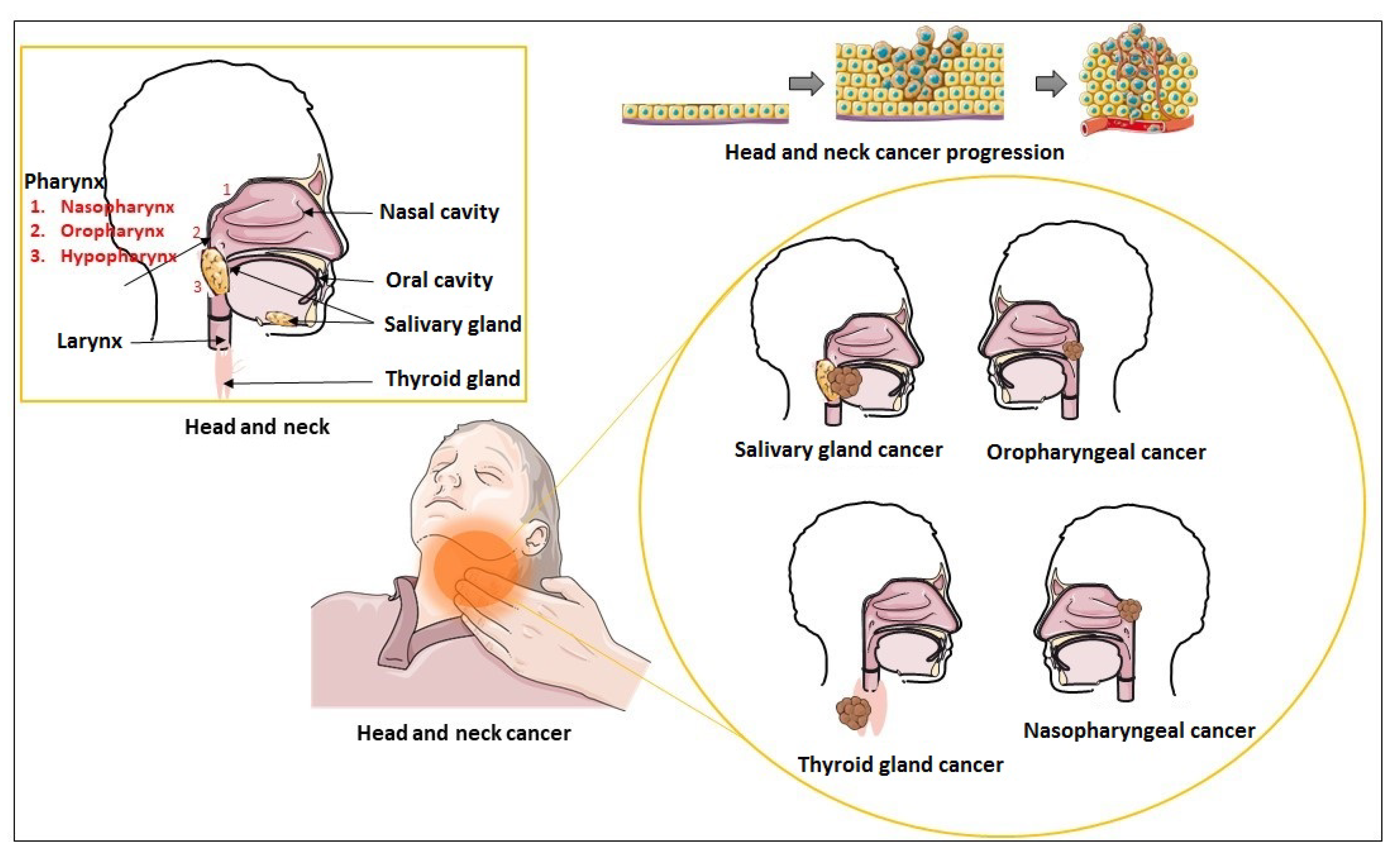 Figure 1 Schematic representation of head and neck region and types of head and neck carcinoma. 1
Figure 1 Schematic representation of head and neck region and types of head and neck carcinoma. 1
Representative Biomarkers of Head and Neck Cancer
KRT19
Keratin 19 (KRT19) is a type I keratin protein, the smallest in the keratin family, known for its pivotal role in the structural integrity of epithelial cells. It is encoded by the KRT19 gene and is particularly significant in the cytoskeleton of epithelial cells, contributing to cell integrity and stability. In the context of head and neck cancer, KRT19 has gained attention for its involvement in the disease's progression and metastasis. Research indicates that KRT19 is overexpressed in several types of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas (HNSCC), suggesting a potential role in tumorigenesis and as a biomarker for cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Its expression is associated with enhanced cell migration and invasion, key features of cancer metastasis. Additionally, KRT19 has been studied for its utility in circulating tumor cell (CTC) detection, offering a minimally invasive method for monitoring disease progression and response to treatment.



FGFR3
The Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 3 (FGFR3) is a critical receptor tyrosine kinase involved in various cellular processes including cell differentiation, proliferation, and regulation of apoptotic pathways. Structurally, FGFR3 is composed of an extracellular domain, which binds fibroblast growth factors (FGFs), a single transmembrane domain, and an intracellular tyrosine kinase domain that initiates downstream signaling pathways upon activation. In the context of head and neck cancer, aberrations in FGFR3 signaling have been implicated in tumorigenesis and progression. Mutations, amplifications, or overexpression of FGFR3 can lead to altered cell growth and survival, contributing to the oncogenic process. The dysregulation of FGFR3 signaling pathways is associated with various aspects of cancer biology including enhanced tumor growth, resistance to apoptosis, angiogenesis, and metastasis. Consequently, FGFR3 has been identified as a potential therapeutic target, with research focusing on the development of FGFR inhibitors that could disrupt these oncogenic signaling pathways.


CXCL8
CXCL8, also known as Interleukin-8 (IL-8), is a small cytokine belonging to the CXC chemokine family, playing a pivotal role in the immune system by attracting neutrophils and other inflammatory mediators to sites of infection or injury. This chemokine is produced by various cell types, including macrophages, epithelial cells, and endothelial cells, in response to inflammatory stimuli. It operates primarily through its receptors, CXCR1 and CXCR2, activating multiple signal transduction pathways that lead to enhanced migration, survival, and proliferation of immune cells. In the context of head and neck cancer, CXCL8 has been implicated in tumorigenesis, progression, and metastasis. It contributes to the tumor microenvironment by promoting angiogenesis, the recruitment of tumor-associated macrophages, and the evasion of immune surveillance. Furthermore, CXCL8 has been associated with resistance to chemotherapy and radiotherapy, making it a potential target for therapeutic intervention.


Full List of Head and Neck Cancer Biomarkers
Tested Data-Supported Products Targeting Head and Neck Cancer Biomarkers
- Mastronikolis, Nicholas S et al. “The Role of Exosomes in Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Cell Functional Properties in Head and Neck Cancer.” Cancers vol. 15,7 2156. 5 Apr. 2023, doi:10.3390/cancers15072156. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.

