Melanoma Biomarkers
Product List
 Loading...
Loading...-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: ELISA, WB, FC, IHC, IP
- Mouse Anti-CEACAM1 Recombinant Antibody (clone 6G5J) (HPAB-0472-CN)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: ELISA, FC
- Mouse Anti-CEACAM1 Recombinant Antibody (clone 18-20) (HPAB-0471-CN)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: ELISA, FC
- Anti-Human CD44 Recombinant Antibody (RG7356) (TAB-128CL)
-
- Derivation: Humanized
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody
-
- Derivation: human
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: IgG4 - kappa
- Application: IP, IF, FuncS, FC, Neut, ELISA, ICC
- Mouse Anti-CD44 Recombinant Antibody (HPAB-1055-FY) (HPAB-1055-FY)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: IP, IHC, Inhib, FC
- Human Anti-C-myc Recombinant Antibody; scFv Fragment (HPAB-1760LY-S(P)) (HPAB-1760LY-S(P))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human scFv
- Application: ELISA
- Mouse Anti-FGFR4 Recombinant Antibody (clone LD1); scFv Fragment (NS-028CN-S(P))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse scFv
- Application: ELISA, WB, FC, IHC, IP
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Type: Mouse IgG1, κ
- Application: FuncS, IHC, Neut, Inhib
-
- Derivation: Phage display
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Type: Human Antibody
- Application: ELISA, FC
-
- Derivation: Humanized
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human IgG
- Application: ELISA
- AbPlus™ Anti-CXCR4 Magnetic Beads (VS-0724-YC1489) (VS-0724-YC1489)
-
- Target: CXCR4
- Target Species: Human
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- AbPlus™ Anti-CCNA2 Magnetic Beads (VS-0724-YC1370) (VS-0724-YC1370)
-
- Target: CCNA2
- Target Species: Human
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- AbPlus™ Anti-CD44 Magnetic Beads (VS-0724-YC1364) (VS-0724-YC1364)
-
- Target: CD44
- Target Species: Human
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- AbPlus™ Anti-CDKN2A Magnetic Beads (VS-0724-YC1355) (VS-0724-YC1355)
-
- Target: CDKN2A
- Target Species: Human
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
-
- Species Reactivity: Mouse
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Mouse
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Mouse
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
- Rabbit Anti-CDKN2A Recombinant Antibody (VS3-FY2607) (VS3-FY2607)
-
- Species Reactivity: Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, ICC, IP
- Rabbit Anti-AKT1 Recombinant Antibody (VS3-FY2622) (VS3-FY2622)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat, Hamster
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IHC, ICC, IP
-
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IHC-P, IP
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IP
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IHC-P, ICC, IF
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, ELISA
- Mouse Anti-MMP2 Recombinant Antibody (VS3-FY2805) (VS3-FY2805)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: WB, ICC
- Rabbit Anti-p53 Recombinant Antibody (VS3-FY2827) (VS3-FY2827)
-
- Species Reactivity: Mouse
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, ICC, IP
- Human Anti-HLA-DRA Recombinant Antibody (clone c44H10) (VS-0724-XY76)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human IgG
- Application: ELISA, BLI
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Monkey IgG4
- Application: ELISA, BLI, Neut
- Mouse Anti-HLA-DRA Recombinant Antibody (clone K8-355) (VS-0724-XY77)
-
- Derivation: Hybridoma
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1 kappa
- Application: ELISA, FC
- AbPlus™ Anti-AKT1 Magnetic Beads (CBACN-016) (VS-0424-XY10)
-
- Target: AKT1
- Target Species: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- AbPlus™ Anti-CCND3 Magnetic Beads (DCS2.2) (VS-0424-XY46)
-
- Target: CCND3
- Target Species: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- AbPlus™ Anti-CD44 Magnetic Beads (1M7.8.1) (VS-0424-XY53)
-
- Target: CD44
- Target Species: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- AbPlus™ Anti-FGFR4 Magnetic Beads (F85-6C5) (VS-0424-XY103)
-
- Target: FGFR4
- Target Species: Human
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- AbPlus™ Anti-HLA-DRA Magnetic Beads (Bra30) (VS-0424-XY125)
-
- Target: HLA-DRA
- Target Species: Human
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- AbPlus™ Anti-MITF Magnetic Beads (C5) (VS-0424-XY187)
-
- Target: MITF
- Target Species: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- AbPlus™ Anti-CCNA1 Magnetic Beads (VS-0724-YC263) (VS-0724-YC263)
-
- Target: CCNA1
- Target Species: Human
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- AbPlus™ Anti-FGF2 Magnetic Beads (VS-0724-YC641) (VS-0724-YC641)
-
- Target: FGF2
- Target Species: Human
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- AbPlus™ Anti-NME1 Magnetic Beads (VS-0724-YC686) (VS-0724-YC686)
-
- Target: NME1
- Target Species: Human
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- AbPlus™ Anti-HSPA4 Magnetic Beads (VS-0724-YC698) (VS-0724-YC698)
-
- Target: HSPA4
- Target Species: Human
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- AbPlus™ Anti-NME1 Magnetic Beads (VS-0724-YC899) (VS-0724-YC899)
-
- Target: NME1
- Target Species: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- AbPlus™ Anti-CCND3 Magnetic Beads (VS-0724-YC1228) (VS-0724-YC1228)
-
- Target: CCND3
- Target Species: Human
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- AbPlus™ Anti-Ccna2 Magnetic Beads (VS-0724-YC1313) (VS-0724-YC1313)
-
- Target: Ccna2
- Target Species: Mouse
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
-
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: ELISA, WB, IHC, ICC, FC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IHC-F, IHC-P, ICC, IF, IP
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IHC-F, IHC-P, ICC, IF, IP
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IHC-P
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB
-
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: ELISA, WB, IHC, FC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IP
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, ICC, IF
-
- Species Reactivity: Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, ICC, IF, IP
-
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: ELISA, ICC, FC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: ELISA, IHC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Bovine, Mouse, Rat, Porcine
- Type: Mouse IgG2b
- Application: ELISA, WB, ICC
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Pig, Rat
- Type: Mouse IgG2b
- Application: ELISA, WB
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG2b, Kappa
- Application: ELISA, IHC
-
- Derivation: Human
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human IgG4
- Application: ELISA
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human, Dog, Pig, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: ELISA, WB
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, ICC, IF
-
- Type: Mouse IgG2a
- Application: ELISA, FC
-
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: ELISA, ICC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Hamster
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB
-
- Species Reactivity: Mouse
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, ICC, IF
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, ICC, IF, IP
- Recombinant Mouse Anti-S100A4 Antibody (clone 3A1B2) (VS3-FY1293)
-
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: ELISA, IHC, FC
- Recombinant Mouse Anti-S100A4 Antibody (clone 4A5A7) (VS3-FY1294)
-
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: ELISA, IHC, FC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG3
- Application: IHC-P
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IHC-Fr, IHC-P, ICC, IF, IP
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, ICC, IF
- Human Anti-CXCR4 Recombinant Antibody (VS-0723-WK67) (VS-0723-WK67)
-
- Derivation: Chimeric (rabbit/human)
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Chimeric (rabbit/human) IgG1
- Application: FC
- Human Anti-FGFR4 Recombinant Antibody (VS-0723-WK114) (VS-0723-WK114)
-
- Derivation: Chimeric (rabbit/human)
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Chimeric (rabbit/human) IgG1
- Application: FC
- Human Anti-CD44 Recombinant Antibody (VS-0723-WK182) (VS-0723-WK182)
-
- Derivation: Chimeric (rabbit/human)
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Chimeric (rabbit/human) IgG1
- Application: FC
- Recombinant Mouse Anti-AKT1 Antibody (VS-0923-FY6) (VS-0923-FY6)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: ELISA, WB
- Recombinant Mouse Anti-CD44 Antibody (VS-0923-FY35) (VS-0923-FY35)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: ELISA, IHC
- Recombinant Mouse Anti-NME1 Antibody (VS-0923-FY120) (VS-0923-FY120)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG2b
- Application: ELISA, WB
- Recombinant Mouse Anti-c-Myc Antibody (VS-0923-FY160) (VS-0923-FY160)
-
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: ELISA, WB, IP, IF
- Human Anti-AKT1 Recombinant Antibody (clone 30769) (VS-0224-XY5)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human IgG
- Application: WB
- Mouse Anti-FGFR4 Recombinant Antibody (VS-0224-XY48) (VS-0224-XY48)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: ELISA, WB, FC, IF, IP, IHC
- Mouse Anti-ITGA2B1 Recombinant Antibody (VS-0224-XY74) (VS-0224-XY74)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Porcine
- Type: Mouse IgG1, kappa
- Application: FC, IP, IHC-Fr, Inhib
- Rat Anti-Mouse S100a4 Recombinant Antibody (VS-0224-XY90) (VS-0224-XY90)
-
- Species Reactivity: Mouse
- Type: Rat IgG2b
- Application: ELISA, WB
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IHC-P
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, ICC, IF
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IHC-P, ICC, IF
- Rabbit Anti-ID1 Recombinant Antibody (clone R01-2A4) (VS3-XY3390)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IHC-P, ICC, IF, FC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IHC-P, ICC, IF, FC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Mouse
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
Our customer service representatives are available 24 hours a day, from Monday to Sunday. Contact Us
Can't find the products you're looking for? Try to filter in the left sidebar.Filter By Tag
Melanoma, a malignancy of melanocytes, the pigment-producing cells in the skin, eyes, and other parts of the body, is a critical health concern globally. Originating from cells that normally confer pigmentation, protection against UV radiation, and thermoregulation, melanoma is characterized by its aggressive nature and potential to metastasize to various organs. The incidence of melanoma has been increasing, particularly in populations with lighter skin, making it a focal point of research and public health initiatives. Risk factors for melanoma include excessive exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light, fair skin, a history of sunburns, numerous moles or atypical nevi, genetic predispositions, and a family history of the disease. Early detection and treatment are pivotal in improving survival rates, with strategies ranging from surgical excision of early-stage lesions to advanced therapies for metastatic disease, such as targeted therapy and immunotherapy. The biology of melanoma is complex, involving genetic mutations and alterations in cell signaling pathways that drive tumor growth and resistance to treatments.
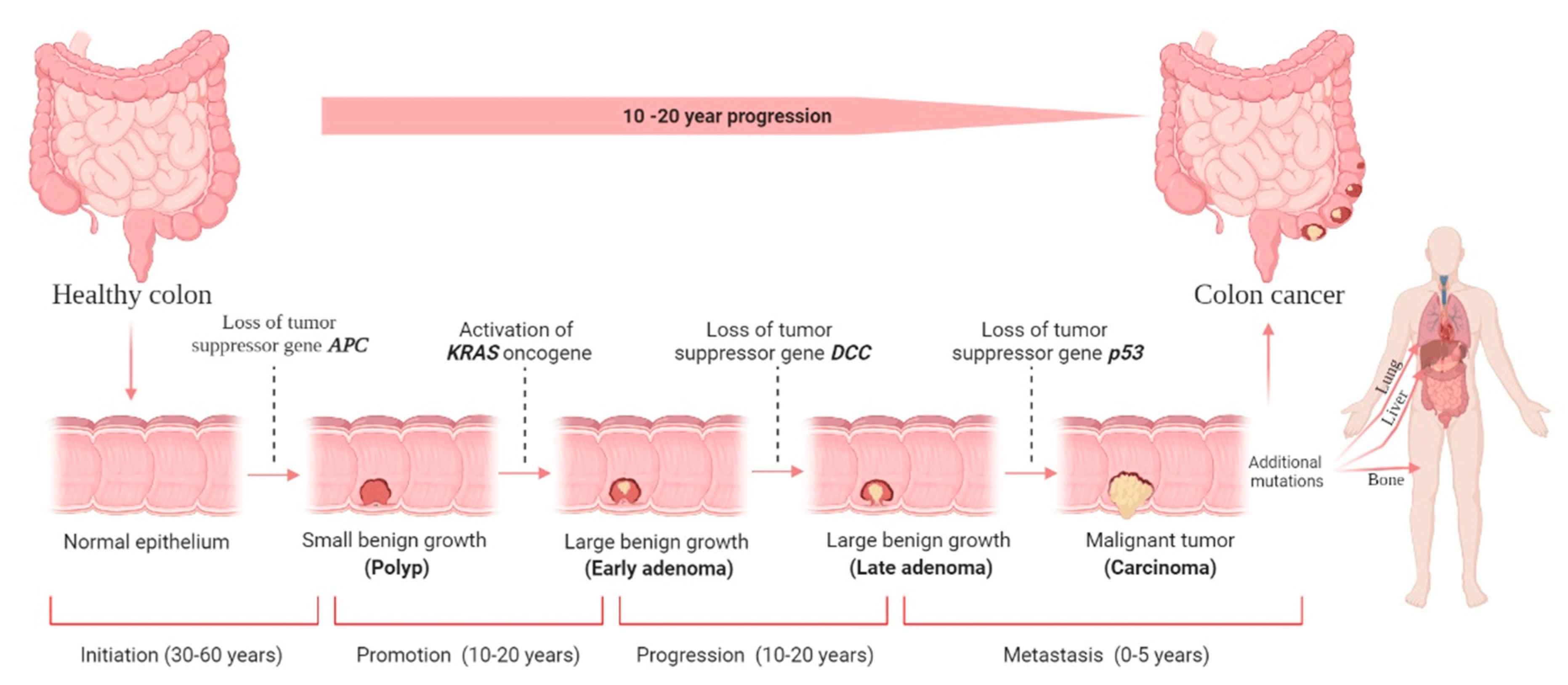 Figure 1 Biologic events and molecular changes in the progression of melanoma. (Miller, 2006)
Figure 1 Biologic events and molecular changes in the progression of melanoma. (Miller, 2006)
Representative Biomarkers of Melanoma
AKT1
AKT1, a crucial serine/threonine kinase, plays a pivotal role in multiple cellular processes, including metabolism, apoptosis, and proliferation, by transmitting signals within cells. It is one of the central components of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway, which is essential for cell survival and growth. Dysregulation of AKT1 has been implicated in various cancers, including melanoma, highlighting its importance in tumor development and progression. In melanoma, AKT1 activation promotes cell proliferation, survival, and resistance to apoptosis, contributing to the aggressive nature of this skin cancer. It does so by phosphorylating a range of substrates involved in apoptosis (such as BAD) and cell cycle progression, thereby supporting the survival and expansion of melanoma cells. The overexpression or hyperactivation of AKT1 in melanoma is often associated with poor prognosis and resistance to therapies, making it a significant target for therapeutic intervention.



CDH1
CDH1, also known as E-cadherin (epithelial cadherin), is a crucial cell adhesion molecule that plays a significant role in maintaining the structural integrity and function of epithelial tissues. This protein is encoded by the CDH1 gene located on chromosome 16q22.1 and is fundamentally involved in cell-cell adhesion, signaling pathways, and maintaining epithelial cell polarity. Its role extends beyond structural support, influencing processes such as cellular migration, proliferation, and differentiation, which are vital for tissue development and homeostasis. In the context of melanoma, a type of skin cancer originating from melanocytes, CDH1's function becomes critically relevant. Alterations or downregulation of CDH1 expression have been associated with the progression and metastasis of melanoma. The loss of E-cadherin-mediated adhesion allows melanoma cells to detach from the primary tumor mass, facilitating their invasion into surrounding tissues and dissemination to distant sites. This mechanism underscores the importance of CDH1 not only in maintaining cellular cohesion and tissue architecture but also in its role as a tumor suppressor, where its dysfunction can contribute to cancer progression, invasion, and metastasis.



ITGB3
Integrin Beta-3 (ITGB3) is a critical protein involved in the complex biology of cellular adhesion and signaling, playing pivotal roles in various biological processes, including thrombosis, inflammation, and wound healing. ITGB3 partners with integrin alpha subunits to form receptors that facilitate cell-to-cell and cell-to-extracellular matrix interactions, crucial for maintaining tissue architecture and homeostasis. Research has shown that ITGB3 is overexpressed in melanoma cells, contributing to tumor growth, metastasis, and resistance to therapy. It mediates these effects by enhancing cell migration, invasion, and survival, linking extracellular cues to intracellular signaling pathways that promote tumor progression and dissemination. Specifically, ITGB3 interacts with the tumor microenvironment, supporting angiogenesis (the formation of new blood vessels) necessary for tumor growth and metastasis. Its involvement in activating key signaling pathways, such as the FAK (Focal Adhesion Kinase) and PI3K/AKT pathways, further underscores its role in melanoma's aggressive behavior, making it a potential target for therapeutic intervention in managing this malignancy.



Full List of Melanoma Biomarkers
| Biomarker | Alternative Names | Gene ID | UniProt ID | Roles |
| AIM2 | Absent In Melanoma 2; Interferon-Inducible Protein AIM2; PYHIN4 | 911829 | Q05320 | AIM2 is a member of the IFI20X /IFI16 family. It plays a putative role in tumorigenic reversion and may control cell proliferation. Interferon-gamma induces expression of AIM2. |
| AKT1 | AKT Serine/Threonine Kinase 1; V-Akt Murine Thymoma Viral Oncogene Homolog 1; Protein Kinase B Alpha; Proto-Oncogene C-Akt; RAC-PK-Alpha; EC 2.7.11.1; PKB Alpha; PKB; RAC; V-Akt Murine Thymoma Viral Oncogene-Like Protein 1; RAC-Alpha Serine/Threonine-Protein Kinase | 207 | P31749 | The serine-threonine protein kinase encoded by the AKT1 gene is catalytically inactive in serum-starved primary and immortalized fibroblasts. AKT1 and the related AKT2 are activated by platelet-derived growth factor. The activation is rapid and specific, and it is abrogated by mutations in the pleckstrin homology domain of AKT1. It was shown that the activation occurs through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. In the developing nervous system AKT is a critical mediator of growth factor-induced neuronal survival. Survival factors can suppress apoptosis in a transcription-independent manner by activating the serine/threonine kinase AKT1, which then phosphorylates and inactivates components of the apoptotic machinery. Mutations in this gene have been associated with the Proteus syndrome. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2011] |
| BCL6 | B Cell CLL/Lymphoma 6; Zinc Finger Protein 51; Zinc Finger And BTB Domain-Containing Protein 27; B-Cell Lymphoma 5 Protein; Protein LAZ-3; ZBTB27; ZNF51; BCL-5; BCL-6; BCL5 | 604 | P41182 | The protein encoded by this gene is a zinc finger transcription factor and contains an N-terminal POZ domain. This protein acts as a sequence-specific repressor of transcription, and has been shown to modulate the transcription of STAT-dependent IL-4 responses of B cells. This protein can interact with a variety of POZ-containing proteins that function as transcription corepressors. This gene is found to be frequently translocated and hypermutated in diffuse large-cell lymphoma (DLCL), and may be involved in the pathogenesis of DLCL. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different protein isoforms have been found for this gene. |
| CCNA1 | CCNA1; Cyclin A1; Cyclin-A1; CT146 | 8900 | P78396 | The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the highly conserved cyclin family, whose members are characterized by a dramatic periodicity in protein abundance through the cell cycle. Cyclins function as regulators of CDK kinases. Different cyclins exhibit distinct expression and degradation patterns which contribute to the temporal coordination of each mitotic event. The cyclin encoded by this gene was shown to be expressed in testis and brain, as well as in several leukemic cell lines, and is thought to primarily function in the control of the germline meiotic cell cycle. This cyclin binds both CDK2 and CDC2 kinases, which give two distinct kinase activities, one appearing in S phase, the other in G2, and thus regulate separate functions in cell cycle. This cyclin was found to bind to important cell cycle regulators, such as Rb family proteins, transcription factor E2F-1, and the p21 family proteins. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. |
| CCNA2 | Cyclin A2; Cyclin-A; CCN1; CCNA; Cyclin-A2; Cyclin A | 890 | P20248 | CCNA2 (Cyclin A2) is a Protein Coding gene. Diseases associated with CCNA2 include Splenic Diffuse Red Pulp Small B-Cell Lymphoma and Valproate Embryopathy. Among its related pathways are CDK-mediated phosphorylation and removal of Cdc6 and Signaling events mediated by PRL. Gene Ontology (GO) annotations related to this gene include protein kinase binding. An important paralog of this gene is CCNA1. |
| CCND3 | Cyclin D3 | 896 | P30281 | The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the highly conserved cyclin family, whose members are characterized by a dramatic periodicity in protein abundance through the cell cycle. Cyclins function as regulators of CDK kinases. Different cyclins exhibit distinct expression and degradation patterns which contribute to the temporal coordination of each mitotic event. This cyclin forms a complex with and functions as a regulatory subunit of CDK4 or CDK6, whose activtiy is required for cell cycle G1/S transition. This protein has been shown to interact with and be involved in the phosphorylation of tumor suppressor protein Rb. The CDK4 activity associated with this cyclin was reported to be necessary for cell cycle progression through G2 phase into mitosis after UV radiation. Several transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. |
| CD44 | CD44 Molecule (Indian Blood Group); Hematopoietic Cell E- And L-Selectin Ligand; GP90 Lymphocyte Homing/Adhesion Receptor; Chondroitin Sulfate Proteoglycan 8; Extracellular Matrix Receptor III; Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycan; Phagocytic Glycoprotein 1; Hyaluronate Receptor; Hermes Antigen; CD44 Antigen; ECMR-III; HUTCH-I; Epican; CDW44; MDU2; MDU3 | 960 | P16070 | The protein encoded by this gene is a cell-surface glycoprotein involved in cell-cell interactions, cell adhesion and migration. It is a receptor for hyaluronic acid (HA) and can also interact with other ligands, such as osteopontin, collagens, and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs). This protein participates in a wide variety of cellular functions including lymphocyte activation, recirculation and homing, hematopoiesis, and tumor metastasis. Transcripts for this gene undergo complex alternative splicing that results in many functionally distinct isoforms, however, the full length nature of some of these variants has not been determined. Alternative splicing is the basis for the structural and functional diversity of this protein, and may be related to tumor metastasis. |
| Cd8a | Ly-2; Ly-B; Ly-35; Lyt-2 | 12525 | P01731 | Enables identical protein binding activity. Acts upstream of or within several processes, including cytotoxic T cell differentiation; defense response to virus; and positive regulation of calcium-mediated signaling. Located in external side of plasma membrane. Is expressed in several structures, including endocrine gland; exocrine gland; genitourinary system; gut; and hemolymphoid system gland. Orthologous to human CD8A (CD8a molecule). |
| CD8B | CD8b Molecule; CD8 Antigen, Beta Polypeptide 1 (P37); CD8B1; T Lymphocyte Surface Glycoprotein Beta Chain; T-Cell Surface Glycoprotein CD8 Beta Chain; CD8b Antigen; | 24931 | P05541 | CD8B (CD8b Molecule) is a Protein Coding gene. Diseases associated with CD8B include Mucinous Stomach Adenocarcinoma. Among its related pathways are T-Cell Receptor and Co-stimulatory Signaling and Innate Immune System. Gene Ontology (GO) annotations related to this gene include coreceptor activity and MHC class I protein binding. |
| CDH1 | Arc-1; BCDS1; CD324; CDHE; ECAD; LCAM; UVO | 999 | P12830 | This gene encodes a classical cadherin of the cadherin superfamily. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants, at least one of which encodes a preproprotein that is proteolytically processed to generate the mature glycoprotein. This calcium-dependent cell-cell adhesion protein is comprised of five extracellular cadherin repeats, a transmembrane region and a highly conserved cytoplasmic tail. Mutations in this gene are correlated with gastric, breast, colorectal, thyroid and ovarian cancer. Loss of function of this gene is thought to contribute to cancer progression by increasing proliferation, invasion, and/or metastasis. The ectodomain of this protein mediates bacterial adhesion to mammalian cells and the cytoplasmic domain is required for internalization. This gene is present in a gene cluster with other members of the cadherin family on chromosome 16. |
| CDKN1A | Cyclin Dependent Kinase Inhibitor 1A; Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitor 1A (P21, Cip1); CDK-Interacting Protein 1; CDKN1; CAP20; MDA-6; CIP1; SDI1; WAF1; P21 | 1026 | A0A024RCX5 | Based on molecular docking results, Ligands-3, 5, 14, and 16 were screened among 17 different Pyrrolone-fused benzosuberene compounds as potent and specific inhibitors without any cross-reactivity against different CDK isoforms. Analysis of MD simulations and MM-PBSA studies, revealed the binding energy profiles of all the selected complexes. |
| CDKN2A | Cyclin Dependent Kinase Inhibitor 2A; Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitor 2A (Melanoma, P16, Inhibits CDK4); Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 4 Inhibitor A; Cyclin-Dependent Kinase Inhibitor 2A; Multiple Tumor Suppressor 1; Alternative Reading Frame; P16-INK4A; P16INK4A; P14ARF; CDKN2; CDK4I; MTS-1; MTS1; MLM | 1029 | P42771 | CDKN2A loss has been shown to be a significant event in a number of cancer types. While no targeted therapeutic has been engaged in clinical trials, the prognostic impact has been studied by a number of meta-analyses. In majority of cases CDKN2A is inactivated by homozygous deletions. One of the mechanisms by which loss of CDKN2A can occur is by hypermethylation of the promoter region for the gene. |
| CEACAM1 | CEACAM1; carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1 (biliary glycoprotein); BGP; BGP1; BGPI; carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 1; antigen CD66; CD66a antigen | 634 | P13688 | This gene encodes a member of the carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) gene family, which belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily. Two subgroups of the CEA family, the CEA cell adhesion molecules and the pregnancy-specific glycoproteins, are located within a 1.2 Mb cluster on the long arm of chromosome 19. Eleven pseudogenes of the CEA cell adhesion molecule subgroup are also found in the cluster. The encoded protein was originally described in bile ducts of liver as biliary glycoprotein. Subsequently, it was found to be a cell-cell adhesion molecule detected on leukocytes, epithelia, and endothelia. The encoded protein mediates cell adhesion via homophilic as well as heterophilic binding to other proteins of the subgroup. Multiple cellular activities have been attributed to the encoded protein, including roles in the differentiation and arrangement of tissue three-dimensional structure, angiogenesis, apoptosis, tumor suppression, metastasis, and the modulation of innate and adaptive immune responses. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been reported, but the full-length nature of all variants has not been defined. |
| c-Myc | MYC Proto-Oncogene, BHLH Transcription Factor; V-Myc Avian Myelocytomatosis Viral Oncogene Homolog; Class E Basic Helix-Loop-Helix Protein 39; Transcription Factor P64; Proto-Oncogene C-Myc; BHLHe39; Myc-Related Translation/Localization Regulatory Factor | 4609 | P01106 | This gene is a proto-oncogene and encodes a nuclear phosphoprotein that plays a role in cell cycle progression, apoptosis and cellular transformation. The encoded protein forms a heterodimer with the related transcription factor MAX. This complex binds to the E box DNA consensus sequence and regulates the transcription of specific target genes. Amplification of this gene is frequently observed in numerous human cancers. Translocations involving this gene are associated with Burkitt lymphoma and multiple myeloma in human patients. There is evidence to show that translation initiates both from an upstream, in-frame non-AUG (CUG) and a downstream AUG start site, resulting in the production of two isoforms with distinct N-termini. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2017] |
| CXCR4 | CD184; D2S201E; FB22; HM89; HSY3RR; LAP-3; LAP3; LCR1; LESTR; NPY3R; NPYR; NPYRL; NPYY3R; WHIM; WHIMS | 7852 | P61073 | This gene encodes a CXC chemokine receptor specific for stromal cell-derived factor-1. The protein has 7 transmembrane regions and is located on the cell surface. It acts with the CD4 protein to support HIV entry into cells and is also highly expressed in breast cancer cells. Mutations in this gene have been associated with WHIM (warts, hypogammaglobulinemia, infections, and myelokathexis) syndrome. Alternate transcriptional splice variants, encoding different isoforms, have been characterized. |
| DDIT3 | DNA Damage Inducible Transcript 3; C/EBP Zeta; Growth Arrest And DNA Damage-Inducible Protein GADD153; CCAAT/Enhancer-Binding Protein Homologous Protein; C/EBP-Homologous Protein 10; CHOP-10; GADD153; CHOP10 | 1649 | P35638 | This gene encodes a member of the CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein (C/EBP) family of transcription factors. The protein functions as a dominant-negative inhibitor by forming heterodimers with other C/EBP members, such as C/EBP and LAP (liver activator protein), and preventing their DNA binding activity. The protein is implicated in adipogenesis and erythropoiesis, is activated by endoplasmic reticulum stress, and promotes apoptosis. Fusion of this gene and FUS on chromosome 16 or EWSR1 on chromosome 22 induced by translocation generates chimeric proteins in myxoid liposarcomas or Ewing sarcoma. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding two isoforms with different length have been identified. |
| EPAS1 | Endothelial PAS Domain Protein 1; Class E Basic Helix-Loop-Helix Protein 73; Basic-Helix-Loop-Helix-PAS Protein MOP2; PAS Domain-Containing Protein 2; Member Of PAS Protein 2; HIF-1-Alpha-Like Factor; HIF-2-Alpha; HIF2-Alpha; BHLHe73; EPAS-1; HIF2A | 2034 | Q99814 | This gene encodes a transcription factor involved in the induction of genes regulated by oxygen, which is induced as oxygen levels fall. The encoded protein contains a basic-helix-loop-helix domain protein dimerization domain as well as a domain found in proteins in signal transduction pathways which respond to oxygen levels. Mutations in this gene are associated with erythrocytosis familial type 4. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2009] |
| EZH2 | WVS; ENX1; KMT6; WVS2; ENX-1; EZH2b; KMT6A; EZH2 | 2146 | Q15910 | This gene encodes a member of the Polycomb-group (PcG) family. PcG family members form multimeric protein complexes, which are involved in maintaining the transcriptional repressive state of genes over successive cell generations. This protein associates with the embryonic ectoderm development protein, the VAV1 oncoprotein, and the X-linked nuclear protein. |
| FGF2 | Fibroblast Growth Factor 2; Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 (Basic); Heparin-Binding Growth Factor 2; HBGF-2; FGF-2; BFGF | 2247 | P09038 | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family. FGF family members bind heparin and possess broad mitogenic and angiogenic activities. This protein has been implicated in diverse biological processes, such as limb and nervous system development, wound healing, and tumor growth. The mRNA for this gene contains multiple polyadenylation sites, and is alternatively translated from non-AUG (CUG) and AUG initiation codons, resulting in five different isoforms with distinct properties. The CUG-initiated isoforms are localized in the nucleus and are responsible for the intracrine effect, whereas, the AUG-initiated form is mostly cytosolic and is responsible for the paracrine and autocrine effects of this FGF. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| FGFR4 | CD334; JTK2; TKF | 2264 | P22455 | The protein encoded by this gene is a tyrosine kinase and cell surface receptor for fibroblast growth factors. The encoded protein is involved in the regulation of several pathways, including cell proliferation, cell differentiation, cell migration, lipid metabolism, bile acid biosynthesis, vitamin D metabolism, glucose uptake, and phosphate homeostasis. This protein consists of an extracellular region, composed of three immunoglobulin-like domains, a single hydrophobic membrane-spanning segment, and a cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase domain. The extracellular portion interacts with fibroblast growth factors, setting in motion a cascade of downstream signals, ultimately influencing mitogenesis and differentiation. |
| FXYD5 | FXYD5; FXYD domain containing ion transport regulator 5; RIC; IWU1; KCT1; OIT2; DYSAD; HSPC113; PRO6241; FXYD domain-containing ion transport regulator 5; dysadherin; keratinocytes associated transmembrane protein 1; | 53827 | Q96DB9 | FXYD5 (also termed dysadherin or RIC) is a structurally and functionally unique member of the FXYD family. As other FXYD proteins, FXYD5 specifically interacts with the Na,K-ATPase and alters its kinetics by increasing Vmax However, unlike other family members FXYD5 appears to have additional functions, which cannot be readily explained by modulation of transport kinetics. Knockdown of FXYD5 in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells largely decreases expression and secretion of the chemokine CCL2 (MCP-1). A related effect has also been observed in renal cell carcinoma cells. |
| HLA-DRA | HLA-DRA1 | 3122 | P01903 | HLA-DRA is one of the HLA class II alpha chain paralogues. This class II molecule is a heterodimer consisting of an alpha and a beta chain, both anchored in the membrane. This molecule is expressed on the surface of various antigen presenting cells such as B lymphocytes, dendritic cells, and monocytes/macrophages, and plays a central role in the immune system and response by presenting peptides derived from extracellular proteins, in particular, pathogen-derived peptides to T cells. The alpha chain is approximately 33-35 kDa and its gene contains 5 exons. Exon 1 encodes the leader peptide, exons 2 and 3 encode the two extracellular domains, and exon 4 encodes the transmembrane domain and the cytoplasmic tail. DRA does not have polymorphisms in the peptide binding part and acts as the sole alpha chain for DRB1, DRB3, DRB4 and DRB5. |
| HSPA4 | Heat Shock Protein Family A (Hsp70) Member 4; Heat Shock 70-Related Protein APG-2; Heat Shock 70kDa Protein 4; Heat Shock 70kD Protein 4; Hsp70 RY; Hsp70RY; Epididymis Secretory Sperm Binding Protein Li 5a; Heat Shock 70 KDa Protein 4; Heat Shock Protein, 110 KDa | 3308 | P34932 | HSPA4 (Heat Shock Protein Family A (Hsp70) Member 4) is a Protein Coding gene. Diseases associated with HSPA4 include Ischemia and Leishmaniasis. Among its related pathways are Glucocorticoid Pathway (Peripheral Tissue), Pharmacodynamics and CCR5 Pathway in Macrophages. An important paralog of this gene is HSPA4L. |
| ID1 | DNA-binding protein inhibitor ID-1; Class B basic helix-loop-helix protein 24; bHLHb24; Inhibitor of DNA binding 1; Inhibitor of differentiation 1; ID1; BHLHB24 ID | 3397 | P41134 | Transcriptional regulator (lacking a basic DNA binding domain) which negatively regulates the basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factors by forming heterodimers and inhibiting their DNA binding and transcriptional activity. Implicated in regulating a variety of cellular processes, including cellular growth, senescence, differentiation, apoptosis, angiogenesis, and neoplastic transformation. Inhibits skeletal muscle and cardiac myocyte differentiation. Regulates the circadian clock by repressing the transcriptional activator activity of the CLOCK-ARNTL/BMAL1 heterodimer (By similarity). |
| ITGB1 | Integrin Subunit Beta 1 | 3688 | P05556 | Integrins are heterodimeric proteins made up of alpha and beta subunits. At least 18 alpha and 8 beta subunits have been described in mammals. Integrin family members are membrane receptors involved in cell adhesion and recognition in a variety of processes including embryogenesis, hemostasis, tissue repair, immune response and metastatic diffusion of tumor cells. This gene encodes a beta subunit. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants which encode different protein isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| ITGB3 | Integrin Subunit Beta 3 | 3690 | P05106 | The ITGB3 protein product is the integrin beta chain beta 3. Integrins are integral cell-surface proteins composed of an alpha chain and a beta chain. A given chain may combine with multiple partners resulting in different integrins. Integrin beta 3 is found along with the alpha IIb chain in platelets. Integrins are known to participate in cell adhesion as well as cell-surface mediated signalling. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| JNK1 | JNK; MAPK8; PRKM8; SAPK1; JNK-46; JNK1A2; SAPK1c; JNK21B1/2 | 5599 | P45983 | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the MAP kinase family. MAP kinases act as an integration point for multiple biochemical signals, and are involved in a wide variety of cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, transcription regulation and development. This kinase is activated by various cell stimuli, and targets specific transcription factors, and thus mediates immediate-early gene expression in response to cell stimuli. The activation of this kinase by tumor-necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) is found to be required for TNF-alpha induced apoptosis. This kinase is also involved in UV radiation induced apoptosis, which is thought to be related to cytochrom c-mediated cell death pathway. Studies of the mouse counterpart of this gene suggested that this kinase play a key role in T cell proliferation, apoptosis and differentiation. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been reported. |
| KPNA2 | QIP2; RCH1; IPOA1; PTAC58; SRP1alpha; SRP1-alpha; importin subunit alpha-1; RAG cohort protein 1 importin subunit alpha-2 importin-alpha-P1 karyopherin alpha 2 (RAG cohort 1, importin alpha 1) nuclear pore-targeting complex 58kD component pendulin | 3838 | P52292 | The import of proteins into the nucleus is a process that involves at least 2 steps. The first is an energy-independent docking of the protein to the nuclear envelope and the second is an energy-dependent translocation through the nuclear pore complex. Imported proteins require a nuclear localization sequence (NLS) which generally consists of a short region of basic amino acids or 2 such regions spaced about 10 amino acids apart. Proteins involved in the first step of nuclear import have been identified in different systems. These include the Xenopus protein importin and its yeast homolog, SRP1 (a suppressor of certain temperature-sensitive mutations of RNA polymerase I in Saccharomyces cerevisiae), which bind to the NLS. KPNA2 protein interacts with the NLSs of DNA helicase Q1 and SV40 T antigen and may be involved in the nuclear transport of proteins. KPNA2 also may play a role in V(D)J recombination. |
| MAP2 | MAP-2A; MAP2B; MAP2C; MAP2 | 4133 | P11137 | Microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP2) is a neuronal phosphoprotein that regulates the structure and stability of microtubules, neuronal morphogenesis, cytoskeleton dynamics and organelle trafficking in axons and dendrites. Phosphorylation of MAP2 modulates its association with the cytoskeleton and is developmentally regulated. Serine 136, threonine 1620 and threonine 1623 of MAP2 are phosphorylated by GSK3 and p44/42 MAP kinases. Phosphorylation at threonine 1620/1623 by GSK3 inhibits MAP2 association with microtubules and microtubule stability. |
| MCAM | Melanoma Cell Adhesion Molecule; S-Endo 1 Endothelial-Associated Antigen; Melanoma-Associated Antigen MUC18; Cell Surface Glycoprotein P1H12; Melanoma-Associated Antigen A32; Gicerin | 4162 | P43121 | MCAM (Melanoma Cell Adhesion Molecule) is a Protein Coding gene. Diseases associated with MCAM include Melanoma and Melanoma Metastasis. Among its related pathways are Adhesion. An important paralog of this gene is BCAM. |
| MITF | Melanogenesis Associated Transcription Factor; Microphthalmia-Associated Transcription Factor; Class E Basic Helix-Loop-Helix Protein 32; BHLHe32; Microphtalmia-Associated Transcription Factor; Homolog Of Mouse Microphthalmia; Waardenburg Syndrome, Type 2A | 4286 | O75030 | The protein encoded by this gene is a transcription factor that contains both basic helix-loop-helix and leucine zipper structural features. The encoded protein regulates melanocyte development and is responsible for pigment cell-specific transcription of the melanogenesis enzyme genes. Heterozygous mutations in the this gene cause auditory-pigmentary syndromes, such as Waardenburg syndrome type 2 and Tietz syndrome. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2017] |
| MKI67 | Marker Of Proliferation Ki-67; Antigen Identified By Monoclonal Antibody Ki-67; Protein Phosphatase 1, Regulatory Subunit 105; Antigen KI-67; Antigen Ki67; Proliferation-Related Ki-67 Antigen | 4288 | P46013 | This gene encodes a nuclear protein that is associated with and may be necessary for cellular proliferation. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been described. A related pseudogene exists on chromosome X. [provided by RefSeq, Mar 2009] |
| MMP2 | Matrix Metallopeptidase 2; Matrix Metalloproteinase-2; EC 3.4.24.24; CLG4A; MMP-2; TBE-1; Matrix Metalloproteinase 2 (Gelatinase A, 72kDa Gelatinase, 72kDa Type IV Collagenase); Matrix Metallopeptidase 2 (Gelatinase A, 72kDa Gelatinase, 72kDa Type IV Collagenase); Matrix Metalloproteinase-II; 72 KDa Type IV Collagenase | 4313 | P08253 | This gene is a member of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) gene family, that are zinc-dependent enzymes capable of cleaving components of the extracellular matrix and molecules involved in signal transduction. The protein encoded by this gene is a gelatinase A, type IV collagenase, that contains three fibronectin type II repeats in its catalytic site that allow binding of denatured type IV and V collagen and elastin. Unlike most MMP family members, activation of this protein can occur on the cell membrane. This enzyme can be activated extracellularly by proteases, or, intracellulary by its S-glutathiolation with no requirement for proteolytical removal of the pro-domain. This protein is thought to be involved in multiple pathways including roles in the nervous system, endometrial menstrual breakdown, regulation of vascularization, and metastasis. Mutations in this gene have been associated with Winchester syndrome and Nodulosis-Arthropathy-Osteolysis (NAO) syndrome. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2014] |
| NCOA3 | Nuclear Receptor Coactivator 3; Thyroid Hormone Receptor Activator Molecule 1; Receptor-Associated Coactivator 3; Class E Basic Helix-Loop-Helix Protein 42; Steroid Receptor Coactivator Protein 3; Amplified In Breast Cancer 1 Protein; CBP-Interacting Protein; EC 2.3.1.48; BHLHe42; TRAM-1; AIB-1; SRC-3; AIB1 | 8202 | Q9Y6Q9 | The protein encoded by this gene is a nuclear receptor coactivator that interacts with nuclear hormone receptors to enhance their transcriptional activator functions. The encoded protein has histone acetyltransferase activity and recruits p300/CBP-associated factor and CREB binding protein as part of a multisubunit coactivation complex. This protein is initially found in the cytoplasm but is translocated into the nucleus upon phosphorylation. Several transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. In addition, a polymorphic repeat region is found in the C-terminus of the encoded protein. |
| NME1 | NME/NM23 Nucleoside Diphosphate Kinase 1; Non-Metastatic Cells 1, Protein (NM23A) Expressed In; Tumor Metastatic Process-Associated Protein; Metastasis Inhibition Factor Nm23; Granzyme A-Activated DNase; NDP Kinase A; EC 2.7.4.6; NM23-H1; NDPKA; GAAD | 4830 | P15531 | This gene (NME1) was identified because of its reduced mRNA transcript levels in highly metastatic cells. Nucleoside diphosphate kinase (NDK) exists as a hexamer composed of 'A' (encoded by this gene) and 'B' (encoded by NME2) isoforms. Mutations in this gene have been identified in aggressive neuroblastomas. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Co-transcription of this gene and the neighboring downstream gene (NME2) generates naturally-occurring transcripts (NME1-NME2), which encodes a fusion protein comprised of sequence sharing identity with each individual gene product. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| NME2 | NME/NM23 Nucleoside Diphosphate Kinase 2; Non-Metastatic Cells 2, Protein (NM23B) Expressed In; C-Myc Purine-Binding Transcription Factor PUF; Histidine Protein Kinase NDKB; NDP Kinase B; EC 2.7.4.6;6 NM23-H2; NM23B; Epididymis Secretory Sperm Binding Protein Li 155an; Non-Metastatic Cells 2, Protein (NM23) Expressed In; Nucleoside Diphosphate Kinase B | 4831 | P22392 | Nucleoside diphosphate kinase (NDK) exists as a hexamer coNME2sed of 'A' (encoded by NME1) and 'B' (encoded by this gene) isoforms. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. Read-through transcription from the neighboring upstream gene (NME1) generates naturally-occurring transcripts (NME1-NME2) that encode a fusion protein comprised of sequence sharing identity with each individual gene product. |
| p53 | 7157 | K7PPA8 | ||
| PLK1 | PLK1; PLK; Serine/threonine-protein kinase PLK1; Polo-like kinase 1; PLK-1; Serine/threonine-protein kinase 13; STPK13 | 5347 | P53350 | The Ser/Thr protein kinase encoded by this gene belongs to the CDC5/Polo subfamily. It is highly expressed during mitosis and elevated levels are found in many different types of cancer. Depletion of this protein in cancer cells dramatically inhibited cell proliferation and induced apoptosis; hence, it is a target for cancer therapy. |
| S100A4 | S100 Calcium Binding Protein A4; S100 Calcium-Binding Protein A4 (Calcium Protein, Calvasculin, Metastasin, Murine Placental Homolog); Placental Calcium-Binding Protein; Fibroblast-Specific Protein-1; Protein Mts1; MTS1; CAPL; S100 Calcium Binding Protein A4 (Calcium Protein, Calvasculin, Metastasin, Murine Placental Homolog); Leukemia Multidrug Resistance Associated Protein; Malignant Transformation Suppression 1 | 6275 | P26447 | The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the S100 family of proteins containing 2 EF-hand calcium-binding motifs. S100 proteins are localized in the cytoplasm and/or nucleus of a wide range of cells, and involved in the regulation of a number of cellular processes such as cell cycle progression and differentiation. S100 genes include at least 13 members which are located as a cluster on chromosome 1q21. This protein may function in motility, invasion, and tubulin polymerization. Chromosomal rearrangements and altered expression of this gene have been implicated in tumor metastasis. Multiple alternatively spliced variants, encoding the same protein, have been identified. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| SKP2 | S-Phase Kinase Associated Protein 2; S-Phase Kinase-Associated Protein 2, E3 Ubiquitin Protein Ligase; F-Box/LRR-Repeat Protein 1; P45skp2; FBXL1; S-Phase Kinase-Associated Protein 2 (P45); CDK2/Cyclin A-Associated Protein P45 | 6502 | Q13309 | This gene encodes a member of the F-box protein family which is characterized by an approximately 40 amino acid motif, the F-box. The F-box proteins constitute one of the four subunits of ubiquitin protein ligase complex called SCFs (SKP1-cullin-F-box), which function in phosphorylation-dependent ubiquitination. The F-box proteins are divided into 3 classes: Fbws containing WD-40 domains, Fbls containing leucine-rich repeats, and Fbxs containing either different protein-protein interaction modules or no recognizable motifs. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the Fbls class; in addition to an F-box, this protein contains 10 tandem leucine-rich repeats. This protein is an essential element of the cyclin A-CDK2 S-phase kinase. It specifically recognizes phosphorylated cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B (CDKN1B, also referred to as p27 or KIP1) predominantly in S phase and interacts with S-phase kinase-associated protein 1 (SKP1 or p19). In addition, this gene is established as a protooncogene causally involved in the pathogenesis of lymphomas. Alternative splicing of this gene generates three transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2011] |
Tested Data-Supported Products Targeting Melanoma Biomarkers
- Miller, Arlo J., and Martin C. Mihm Jr. "Melanoma." New England Journal of Medicine 355.1 (2006): 51-65.
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.





































































































