Oncoprotein-Signal Transducers
Signal transducers act as essential mediators in the intricate communication networks that define cellular and organismal life. These molecules are at the heart of cellular signaling pathways, orchestrating a diverse array of biological processes by conveying signals from the cell's exterior to its interior machinery. The mechanisms through which signal transducers operate are foundational to understanding how cells respond to their environment, regulate their growth, differentiate into various cell types, and maintain homeostasis. At a molecular level, signal transducers can initiate a cascade of biochemical events upon receiving specific external stimuli, such as hormones, neurotransmitters, or environmental stress signals. This process often involves the activation or repression of gene expression, alteration of cellular metabolism, or modulation of cell-to-cell interactions, which are crucial for developmental processes, immune responses, and cellular repair mechanisms. By acting as bridges between extracellular signals and intracellular responses, signal transducers ensure that cells can adapt to changes in their environment, respond to damage, and communicate with each other to coordinate complex multicellular life forms. Their malfunction or dysregulation can lead to a wide range of diseases, including cancer, diabetes, and autoimmune disorders.
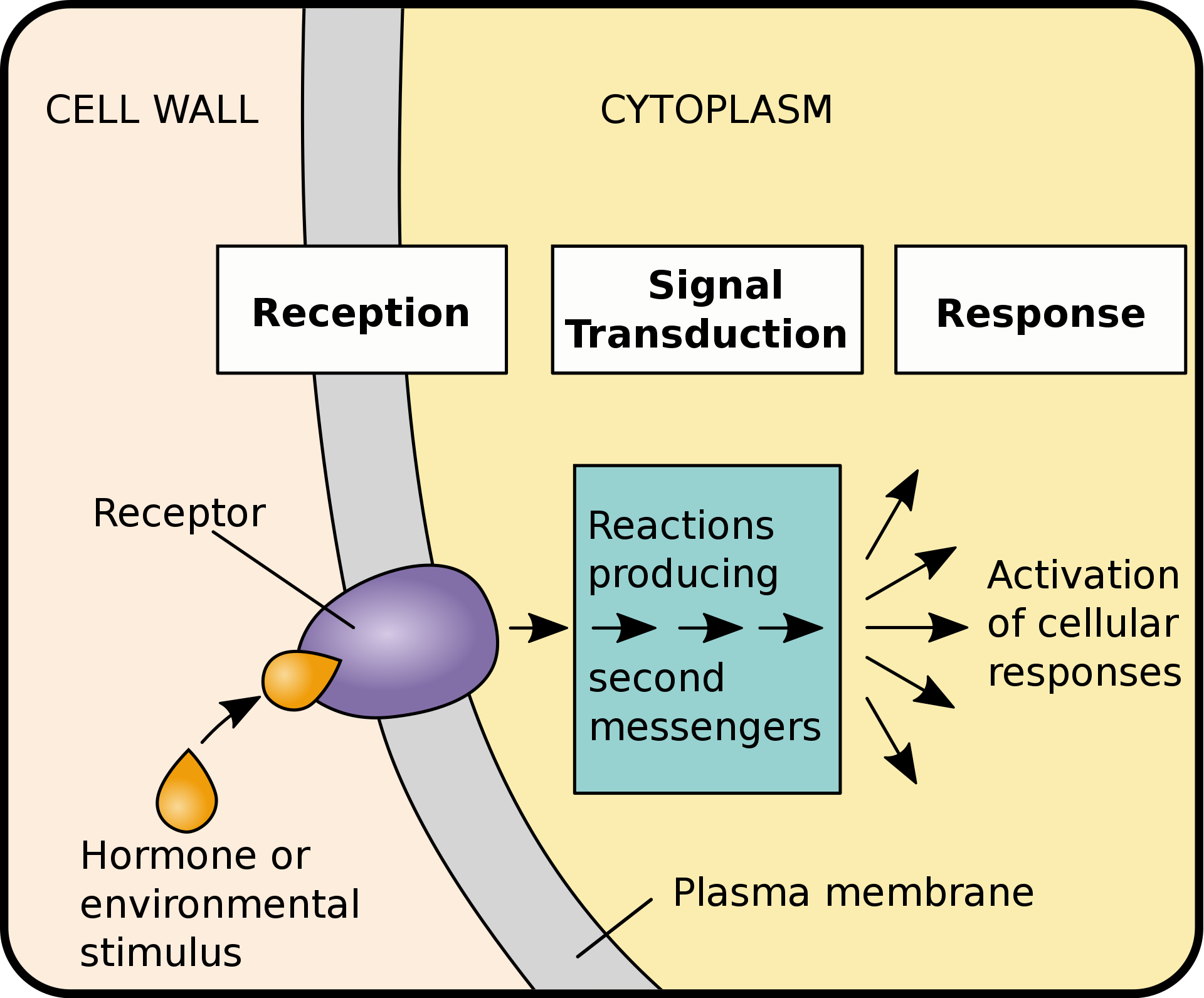 Figure 1 Signal transduction pathways. (Wikipedia)
Figure 1 Signal transduction pathways. (Wikipedia)
Representative Signal Transducers
AKT2
AKT2, a crucial serine/threonine-protein kinase, is one of the three isoforms in the AKT kinase family, which plays a pivotal role in various cellular processes such as glucose metabolism, cell proliferation, apoptosis, transcription, and cell migration. As a central component of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) signaling pathway, AKT2 becomes activated in response to growth factors and insulin, thereby transmitting signals that promote cellular survival and growth. Particularly, in glucose metabolism, AKT2 has a distinctive role in the insulin signaling pathway, facilitating glucose uptake by promoting the translocation of glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT4) to the cell surface in adipocytes and skeletal muscle cells. Moreover, its involvement in cell proliferation and survival is mediated through the phosphorylation and regulation of targets such as the forkhead box O (FOXO) family of transcription factors, glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3), and the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR). Dysregulation of AKT2 has been implicated in various pathologies, including insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes, as well as contributing to the progression of certain cancers by enhancing tumor growth and resistance to apoptosis.



JAK1
Janus kinase 1 (JAK1) is a critical enzyme within the Janus kinase family, playing an indispensable role in the cytokine-mediated signaling pathways that regulate various biological processes, including cell growth, differentiation, and immune responses. It functions by transducing extracellular signals to the cell nucleus, leading to the activation of transcription factors, particularly the Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription (STAT) proteins. JAK1 is activated upon cytokine or growth factor binding to its respective receptor, facilitating the phosphorylation of specific tyrosine residues on the receptor. This phosphorylation serves as a docking site for STAT proteins, which are subsequently phosphorylated by JAK1. Once phosphorylated, STAT proteins dimerize and translocate to the nucleus, where they influence gene expression. JAK1's role is not confined to a single type of cell or tissue; it is pivotal in various physiological processes such as immunity, hematopoiesis, and inflammation. Its widespread influence underscores its significance in maintaining cellular and systemic homeostasis. However, aberrations in JAK1 signaling pathways have been implicated in numerous pathological conditions, including cancers, autoimmune diseases, and inflammatory disorders.


RAF1
RAF1, also known as c-Raf, is a crucial serine/threonine kinase within the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway, a key regulator of cell division, differentiation, and survival. As a part of the Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK cascade, RAF1 is activated by the binding of Ras to its domain, leading to a series of phosphorylation events that ultimately promote cellular proliferation and prevent apoptosis. Its importance is underscored by its involvement in various physiological processes and its implication in pathological conditions, including cancer. Mutations or dysregulations in RAF1 have been associated with a spectrum of human diseases, notably Noonan syndrome and various types of carcinomas, highlighting its role as a proto-oncogene. Furthermore, RAF1 interacts with other cellular pathways, indicating its multifaceted role in regulating cell fate decisions. This complexity not only underscores the biological significance of RAF1 but also presents challenges in targeting it for therapeutic purposes.


Full List of Signal Transducers
| Biomarker | Alternative Names | Gene ID | UniProt ID | Roles |
| ABL1 | ABL Proto-Oncogene 1, Non-Receptor Tyrosine Kinase; V-Abl Abelson Murine Leukemia Viral Oncogene Homolog 1; C-Abl Oncogene 1, Receptor Tyrosine Kinase; Abelson Tyrosine-Protein Kinase 1; Proto-Oncogene C-Abl; EC 2.7.10.2; JTK7; P150; ABL; Abelson Murine Leukemia Viral Oncogene Homolog 1; C-Abl Oncogene 1, Non-Receptor Tyrosine Kinase | 25 | A0A024R8E2 | This gene is a protooncogene that encodes a protein tyrosine kinase involved in a variety of cellular processes, including cell division, adhesion, differentiation, and response to stress. The activity of the protein is negatively regulated by its SH3 domain, whereby deletion of the region encoding this domain results in an oncogene. The ubiquitously expressed protein has DNA-binding activity that is regulated by CDC2-mediated phosphorylation, suggesting a cell cycle function. This gene has been found fused to a variety of translocation partner genes in various leukemias, most notably the t(9;22) translocation that results in a fusion with the 5' end of the breakpoint cluster region gene. Alternative splicing of this gene results in two transcript variants, which contain alternative first exons that are spliced to the remaining common exons. |
| AKT1 | AKT Serine/Threonine Kinase 1; V-Akt Murine Thymoma Viral Oncogene Homolog 1; Protein Kinase B Alpha; Proto-Oncogene C-Akt; RAC-PK-Alpha; EC 2.7.11.1; PKB Alpha; PKB; RAC; V-Akt Murine Thymoma Viral Oncogene-Like Protein 1; RAC-Alpha Serine/Threonine-Protein Kinase | 207 | B0LPE5 | The serine-threonine protein kinase encoded by the AKT1 gene is catalytically inactive in serum-starved primary and immortalized fibroblasts. AKT1 and the related AKT2 are activated by platelet-derived growth factor. The activation is rapid and specific, and it is abrogated by mutations in the pleckstrin homology domain of AKT1. It was shown that the activation occurs through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. In the developing nervous system AKT is a critical mediator of growth factor-induced neuronal survival. Survival factors can suppress apoptosis in a transcription-independent manner by activating the serine/threonine kinase AKT1, which then phosphorylates and inactivates components of the apoptotic machinery. Mutations in this gene have been associated with the Proteus syndrome. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2011] |
| AKT2 | AKT Serine/Threonine Kinase 2; V-Akt Murine Thymoma Viral Oncogene Homolog 2; Protein Kinase B Beta; Protein Kinase Akt-2; RAC-PK-Beta; EC 2.7.11.1; PKB Beta; Putative V-Akt Murine Thymoma Viral Oncoprotein 2; RAC-Beta Serine/Threonine-Protein Kinase | 208 | B4DG79 | This gene is a putative oncogene encoding a protein belonging to a subfamily of serine/threonine kinases containing SH2-like (Src homology 2-like) domains. The gene was shown to be amplified and overexpressed in 2 of 8 ovarian carcinoma cell lines and 2 of 15 primary ovarian tumors. Overexpression contributes to the malignant phenotype of a subset of human ductal pancreatic cancers. The encoded protein is a general protein kinase capable of phophorylating several known proteins. |
| BRAF | B-Raf Proto-Oncogene, Serine/Threonine Kinase; V-Raf Murine Sarcoma Viral Oncogene Homolog B1; V-Raf Murine Sarcoma Viral Oncogene Homolog B; Proto-Oncogene B-Raf; BRAF1; RAFB1; B-Raf Proto-Oncogene Serine/Threonine-Protein Kinase (P94); Murine Sarcoma Viral (V-Raf) Oncogene Homolog B1; Serine/Threonine-Protein Kinase B-Raf | 673 | P15056 | This gene encodes a protein belonging to the RAF family of serine/threonine protein kinases. This protein plays a role in regulating the MAP kinase/ERK signaling pathway, which affects cell division, differentiation, and secretion. Mutations in this gene, most commonly the V600E mutation, are the most frequently identified cancer-causing mutations in melanoma, and have been identified in various other cancers as well, including non-Hodgkin lymphoma, colorectal cancer, thyroid carcinoma, non-small cell lung carcinoma, hairy cell leukemia and adenocarcinoma of lung. Mutations in this gene are also associated with cardiofaciocutaneous, Noonan, and Costello syndromes, which exhibit overlapping phenotypes. A pseudogene of this gene has been identified on the X chromosome. |
| CRK | CRK Proto-Oncogene, Adaptor Protein; V-Crk Avian Sarcoma Virus CT10 Oncogene Homolog; Proto-Oncogene C-Crk; P38; V-Crk Sarcoma Virus CT10 Oncogene-Like Protein; Adapter Molecule Crk; CRKII; | 1398 | P46108 | CRK (CRK Proto-Oncogene, Adaptor Protein) is a Protein Coding gene. Diseases associated with CRK include Sarcoma and Chromosome 17P13.3, Centromeric, Duplication Syndrome. Among its related pathways are RET signaling and NFAT and Cardiac Hypertrophy. Gene Ontology (GO) annotations related to this gene include protein domain specific binding and SH3/SH2 adaptor activity. An important paralog of this gene is CRKL. |
| CTNNB1 | Catenin Beta 1; Catenin (Cadherin-Associated Protein), Beta 1, 88kDa; CTNNB; Catenin (Cadherin-Associated Protein), Beta 1 (88kD); Catenin (Cadherin-Associated Protein), Beta 1; Catenin Beta-1; | 1499 | A0A024R2Q3 | Catenin beta-1, also known as beta-catenin (β-catenin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CTNNB1 gene. |
| FES | FPS | 2242 | P07332 | This gene encodes the human cellular counterpart of a feline sarcoma retrovirus protein with transforming capabilities. The gene product has tyrosine-specific protein kinase activity and that activity is required for maintenance of cellular transformation. Its chromosomal location has linked it to a specific translocation event identified in patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia but it is also involved in normal hematopoiesis as well as growth factor and cytokine receptor signaling. Alternative splicing results in multiple variants encoding different isoforms.[provided by RefSeq, Jan 2009] |
| FGR | FGR Proto-Oncogene, Src Family Tyrosine Kinase; Gardner-Rasheed Feline Sarcoma Viral (V-Fgr) Oncogene Homolog; V-Fgr Feline Gardner-Rasheed Sarcoma Viral Oncogene Homolog; Feline Gardner-Rasheed Sarcoma Viral Oncogene Homolog; Proto-Oncogene C-Fgr; EC 2.7.10.2; P58c-Fgr; P55-Fgr; P58-Fgr; SRC2 | 2268 | P09769 | This gene is a member of the Src family of protein tyrosine kinases (PTKs). The encoded protein contains N-terminal sites for myristylation and palmitylation, a PTK domain, and SH2 and SH3 domains which are involved in mediating protein-protein interactions with phosphotyrosine-containing and proline-rich motifs, respectively. The protein localizes to plasma membrane ruffles, and functions as a negative regulator of cell migration and adhesion triggered by the beta-2 integrin signal transduction pathway. Infection with Epstein-Barr virus results in the overexpression of this gene. Multiple alternatively spliced variants, encoding the same protein, have been identified. |
| FLT3 | Fms Related Tyrosine Kinase 3; Stem Cell Tyrosine Kinase 1; Fms-Like Tyrosine Kinase 3; FL Cytokine Receptor; CD135 Antigen; EC 2.7.10.1;6 CD135; FLK-2; STK1; FLK2 | 2322 | P36888 | This gene encodes a class III receptor tyrosine kinase that regulates hematopoiesis. This receptor is activated by binding of the fms-related tyrosine kinase 3 ligand to the extracellular domain, which induces homodimer formation in the plasma membrane leading to autophosphorylation of the receptor. The activated receptor kinase subsequently phosphorylates and activates multiple cytoplasmic effector molecules in pathways involved in apoptosis, proliferation, and differentiation of hematopoietic cells in bone marrow. Mutations that result in the constitutive activation of this receptor result in acute myeloid leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia. |
| GIP | GIP; gastric inhibitory polypeptide | 2695 | P09681 | This gene encodes an incretin hormone and belongs to the glucagon superfamily. The encoded protein is important in maintaining glucose homeostasis as it is a potent stimulator of insulin secretion from pancreatic beta-cells following food ingestion and nutrient absorption. This gene stimulates insulin secretion via its G protein-coupled receptor activation of adenylyl cyclase and other signal transduction pathways. It is a relatively poor inhibitor of gastric acid secretion. |
| GNAS | GNAS; Extra Large Alphas Protein; Adenylate Cyclase-Stimulating G Alpha Protein; GNAS Complex Locus; PHP1C; Guanine Nucleotide Regulatory Protein; Neuroendocrine Secretory Protein; AHO; Guanine Nucleotide Binding Protein (G Protein), Alpha Stimulating Act | 2778 | O95467 | This locus has a highly complex imprinted expression pattern. It gives rise to maternally, paternally, and biallelically expressed transcripts that are derived from four alternative promoters and 5' exons. Some transcripts contain a differentially methylated region (DMR) at their 5' exons, and this DMR is commonly found in imprinted genes and correlates with transcript expression. An antisense transcript is produced from an overlapping locus on the opposite strand. One of the transcripts produced from this locus, and the antisense transcript, are paternally expressed noncoding RNAs, and may regulate imprinting in this region. In addition, one of the transcripts contains a second overlapping ORF, which encodes a structurally unrelated protein - Alex. Alternative splicing of downstream exons is also observed, which results in different forms of the stimulatory G-protein alpha subunit, a key element of the classical signal transduction pathway linking receptor-ligand interactions with the activation of adenylyl cyclase and a variety of cellular reponses. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Mutations in this gene result in pseudohypoparathyroidism type 1a, pseudohypoparathyroidism type 1b, Albright hereditary osteodystrophy, pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism, McCune-Albright syndrome, progressive osseus heteroplasia, polyostotic fibrous dysplasia of bone, and some pituitary tumors. |
| HRAS | HRAS; Harvey rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog; CTLO; HAMSV; HRAS1; RASH1; p21ras; C-H-RAS; H-RASIDX; C-BAS/HAS; C-HA-RAS1; GTPase HRas; p19 H-RasIDX protein; c-has/bas p21 protein; transforming protein p21; Ha-Ras1 proto-oncoprotein; c-ras-Ki-2 activated oncogene; GTP- and GDP-binding peptide B; transformation gene: oncogene HAMSV; Harvey rat sarcoma viral oncoprotein; Ras family small GTP binding protein H-Ras; v-Ha-ras Harvey rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog | 3265 | P01112 | This gene belongs to the Ras oncogene family, whose members are related to the transforming genes of mammalian sarcoma retroviruses. The products encoded by these genes function in signal transduction pathways. These proteins can bind GTP and GDP, and they have intrinsic GTPase activity. This protein undergoes a continuous cycle of de- and re-palmitoylation, which regulates its rapid exchange between the plasma membrane and the Golgi apparatus. Mutations in this gene cause Costello syndrome, a disease characterized by increased growth at the prenatal stage, growth deficiency at the postnatal stage, predisposition to tumor formation, mental retardation, skin and musculoskeletal abnormalities, distinctive facial appearance and cardiovascular abnormalities. Defects in this gene are implicated in a variety of cancers, including bladder cancer, follicular thyroid cancer, and oral squamous cell carcinoma. Multiple transcript variants, which encode different isoforms, have been identified for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| JAK1 | JAK1 | 3716 | P23458 | JAK1 is a human tyrosine kinase protein essential for signaling for certain type I and type II cytokines. It interacts with the common gamma chain (γc) of type I cytokine receptors, to elicit signals from the IL-2 receptor family (e.g. IL-2R, IL-7R, IL-9R and IL-15R), the IL-4 receptor family (e.g. IL-4R and IL-13R), the gp130 receptor family (e.g. IL-6R, IL-11R, LIF-R, OSM-R, cardiotrophin-1 receptor (CT-1R), ciliary neurotrophic factor receptor (CNTF-R), neurotrophin-1 receptor (NNT-1R) and Leptin-R). It is also important for transducing a signal by type I (IFN-α/β) and type II (IFN-γ) interferons, and members of the IL-10 family via type II cytokine receptors. |
| JAK2 | JAK2 | 3717 | O60674 | Janus kinase 2 (commonly called JAK2) is a non-receptor tyrosine kinase. It is a member of the Janus kinase family and has been implicated in signaling by members of the type II cytokine receptor family (e.g. interferon receptors), the GM-CSF receptor family (IL-3R, IL-5R and GM-CSF-R), the gp130 receptor family (e.g., IL-6R), and the single chain receptors (e.g. Epo-R, Tpo-R, GH-R, PRL-R). |
| KRAS | NS; NS3; CFC2; RALD; K-Ras; KRAS1; KRAS2; RASK2; KI-RAS; C-K-RAS; K-RAS2A; K-RAS2B; K-RAS4A; K-RAS4B; c-Ki-ras2 | 3845 | P01116 | This gene, a Kirsten ras oncogene homolog from the mammalian ras gene family, encodes a protein that is a member of the small GTPase superfamily. A single amino acid substitution is responsible for an activating mutation. The transforming protein that results is implicated in various malignancies, including lung adenocarcinoma, mucinous adenoma, ductal carcinoma of the pancreas and colorectal carcinoma. Alternative splicing leads to variants encoding two isoforms that differ in the C-terminal region. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| MOS | c-mos | 17451 | P00540 | MOS is a serine/threonine kinase that activates the MAP kinase cascade through direct phosphorylation of the MAP kinase activator MEK (MAP2K1; MIM 176872). |
| MYD88 | Myeloid Differentiation Primary Response 88; Myeloid Differentiation Primary Response Gene (88); Myeloid Differentiation Primary Response Protein MyD88; Mutant Myeloid Differentiation Primary Response 88; MYD88D | 4615 | Q99836 | This gene encodes a cytosolic adapter protein that plays a central role in the innate and adaptive immune response. This protein functions as an essential signal transducer in the interleukin-1 and Toll-like receptor signaling pathways. These pathways regulate that activation of numerous proinflammatory genes. The encoded protein consists of an N-terminal death domain and a C-terminal Toll-interleukin1 receptor domain. Patients with defects in this gene have an increased susceptibility to pyogenic bacterial infections. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. |
| NRAS | NRAS Proto-Oncogene, GTPase; Neuroblastoma RAS Viral (V-Ras) Oncogene Homolog; Neuroblastoma RAS Viral Oncogene Homolog; Transforming Protein N-Ras; V-Ras Neuroblastoma RAS Viral Oncogene Homolog; N-Ras Protein Part 4; GTPase NRas; HRAS1 | 4893 | P01111 | This is an N-ras oncogene encoding a membrane protein that shuttles between the Golgi apparatus and the plasma membrane. This shuttling is regulated through palmitoylation and depalmitoylation by the ZDHHC9-GOLGA7 complex. The encoded protein, which has intrinsic GTPase activity, is activated by a guanine nucleotide-exchange factor and inactivated by a GTPase activating protein. Mutations in this gene have been associated with somatic rectal cancer, follicular thyroid cancer, autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome, Noonan syndrome, and juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2011] |
| PIK3CA | Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-Bisphosphate 3-Kinase Catalytic Subunit Alpha; Phosphoinositide-3-Kinase, Catalytic, Alpha Polypeptide; Serine/Threonine Protein Kinase PIK3CA; PtdIns-3-Kinase Subunit P110-Alpha; PI3K-Alpha; Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-Bisphosphate 3-Kinase Catalytic Subunit, Alpha Isoform; Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-Bisphosphate 3-Kinase Catalytic Subunit Alpha Isoform; Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-Bisphosphate 3-Kinase 110 KDa Catalytic Subunit Alpha; Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-Bisphosphate 3-Kinase 110 KDa Catalytic Subunit Alpha; Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-Bisphosphate 3-Kinase, Catalytic Subunit Alpha; Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase, Catalytic, Alpha Polypeptide; Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase, Catalytic, 110-KD, Alpha; Phosphoinositide-3-Kinase Catalytic Alpha Polypeptide; PI3-Kinase P110 Subunit Alpha; PtdIns-3-Kinase Subunit Alpha | 5290 | P42336 | Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase is composed of an 85 kDa regulatory subunit and a 110 kDa catalytic subunit. The protein encoded by this gene represents the catalytic subunit, which uses ATP to phosphorylate PtdIns, PtdIns4P and PtdIns(4,5)P2. This gene has been found to be oncogenic and has been implicated in cervical cancers. A pseudogene of this gene has been defined on chromosome 22. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2016] |
| PIM1 | Pim-1 Proto-Oncogene, Serine/Threonine Kinase; EC 2.7.11.1; Proto-Oncogene Serine/Threonine-Protein Kinase Pim-1; Pim-1 Oncogene (Proviral Integration Site 1); Serine/Threonine-Protein Kinase Pim-1; Pim-1 Kinase 44 KDa Isoform; Pim-1 Oncogene; Oncogene PIM1; PIM | 5292 | P11309 | The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the Ser/Thr protein kinase family, and PIM subfamily. This gene is expressed primarily in B-lymphoid and myeloid cell lines, and is overexpressed in hematopoietic malignancies and in prostate cancer. It plays a role in signal transduction in blood cells, contributing to both cell proliferation and survival, and thus provides a selective advantage in tumorigenesis. Both the human and orthologous mouse genes have been reported to encode two isoforms (with preferential cellular localization) resulting from the use of alternative in-frame translation initiation codons, the upstream non-AUG (CUG) and downstream AUG codons (PMIDs:16186805, 1825810).[provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011] |
| RAF1 | Raf-1 Proto-Oncogene, Serine/Threonine Kinase; V-Raf-1 Murine Leukemia Viral Oncogene Homolog 1; C-Raf Proto-Oncogene, Serine/Threonine Kinase; Proto-Oncogene C-RAF; EC 2.7.11.1; Raf-1; CRAF; V-Raf-1 Murine Leukemia Viral Oncogene-Like Protein 1; RAF Proto-Oncogene Serine/Threonine-Protein Kinase | 5894 | P04049 | This gene is the cellular homolog of viral raf gene (v-raf). The encoded protein is a MAP kinase kinase kinase (MAP3K), which functions downstream of the Ras family of membrane associated GTPases to which it binds directly. Once activated, the cellular RAF1 protein can phosphorylate to activate the dual specificity protein kinases MEK1 and MEK2, which in turn phosphorylate to activate the serine/threonine specific protein kinases, ERK1 and ERK2. Activated ERKs are pleiotropic effectors of cell physiology and play an important role in the control of gene expression involved in the cell division cycle, apoptosis, cell differentiation and cell migration. Mutations in this gene are associated with Noonan syndrome 5 and LEOPARD syndrome 2. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| SRC | SRC Proto-Oncogene, Non-Receptor Tyrosine Kinase; V-Src Avian Sarcoma (Schmidt-Ruppin A-2) Viral Oncogene Homolog; Proto-Oncogene C-Src; EC 2.7.10.2; P60-Src; SRC1; Proto-Oncogene Tyrosine-Protein Kinase Src; Protooncogene SRC, Rous Sarcoma | 396442 | P00523 | This gene is highly similar to the v-src gene of Rous sarcoma virus. This proto-oncogene may play a role in the regulation of embryonic development and cell growth. The protein encoded by this gene is a tyrosine-protein kinase whose activity can be inhibited by phosphorylation by c-SRC kinase. Mutations in this gene could be involved in the malignant progression of colon cancer. Two transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] |
| VAV1 | VAV | 7409 | P15498 | This gene is a member of the VAV gene family. The VAV proteins are guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) for Rho family GTPases that activate pathways leading to actin cytoskeletal rearrangements and transcriptional alterations. The encoded protein is important in hematopoiesis, playing a role in T-cell and B-cell development and activation. The encoded protein has been identified as the specific binding partner of Nef proteins from HIV-1. Coexpression and binding of these partners initiates profound morphological changes, cytoskeletal rearrangements and the JNK/SAPK signaling cascade, leading to increased levels of viral transcription and replication. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding multiple isoforms have been observed for this gene. |
| YES1 | YES Proto-Oncogene 1, Src Family Tyrosine Kinase; V-Yes-1 Yamaguchi Sarcoma Viral Oncogene Homolog 1; Proto-Oncogene C-Yes; EC 2.7.10.2; P61-YES; Yes; YES1 Proto-Oncogene, Src Family Tyrosine Kinase; Proto-Oncogene Tyrosine-Protein Kinase YES | 7525 | P07947 | This gene is the cellular homolog of the Yamaguchi sarcoma virus oncogene. The encoded protein has tyrosine kinase activity and belongs to the src family of proteins. This gene lies in close proximity to thymidylate synthase gene on chromosome 18, and a corresponding pseudogene has been found on chromosome 22. |
Tested Data-Supported Products for Signal Transducers
- Signal transduction pathways. https://simple.wikipedia.org/wiki/Signal_transduction. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY-SA 4.0, without modification.
 Loading...
Loading...- Anti-Human FLT3 Recombinant Antibody (IMC-EB10) (TAB-291CL)
-
- Derivation: Human
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody
- Application: WB, IHC, FC, Cyt, ELISA
- Human Anti-FLT3 Recombinant Antibody (clone NC7) (HPAB-0183CQ)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human IgG1, κ
- Application: ELISA, Neut
- Human Anti-GIP Recombinant Antibody (TAB-267CQ) (TAB-267CQ)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Humanized antibody
- Application: Neut
- Mouse Anti-GIP Recombinant Antibody (TAB-266CQ) (TAB-266CQ)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: Neut
- Mouse Anti-FLT3 Recombinant Antibody (TAB-011CQ) (TAB-011CQ)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1, κ
- Application: ELISA, FC
- AbPlus™ Anti-GNAS Magnetic Beads (VS-0724-YC1559) (VS-0724-YC1559)
-
- Target: GNAS
- Target Species: Human
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- AbPlus™ Anti-HRAS Magnetic Beads (VS-0724-YC1294) (VS-0724-YC1294)
-
- Target: HRAS
- Target Species: Human
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- AbPlus™ Anti-FLT3 Magnetic Beads (VS-0724-YC1172) (VS-0724-YC1172)
-
- Target: FLT3
- Target Species: Human
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- AbPlus™ Anti-YES1 Magnetic Beads (VS-0724-YC376) (VS-0724-YC376)
-
- Target: YES1
- Target Species: Human
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- AbPlus™ Anti-MYD88 Magnetic Beads (VS-0724-YC155) (VS-0724-YC155)
-
- Target: MYD88
- Target Species: Human
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- AbPlus™ Anti-VAV1 Magnetic Beads (VS-0724-YC100) (VS-0724-YC100)
-
- Target: VAV1
- Target Species: Human
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- AbPlus™ Anti-NRAS Magnetic Beads (JF10-11) (VS-0424-XY205)
-
- Target: NRAS
- Target Species: Human, Mouse, Rat, Zebrafish
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- AbPlus™ Anti-JAK2 Magnetic Beads (CBACN-632) (VS-0424-XY162)
-
- Target: JAK2
- Target Species: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- AbPlus™ Anti-AKT1 Magnetic Beads (CBACN-016) (VS-0424-XY10)
-
- Target: AKT1
- Target Species: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1, κ
- Application: ELISA, IHC
- Mouse Anti-YES1 Recombinant Antibody (VS3-FY2923) (VS3-FY2923)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: WB
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IP
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IHC-P, ICC, IF, IP, FC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IHC-P, ICC, IF
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IP
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IHC-P
-
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IHC-P, IP
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, FC
- Mouse Anti-FES Recombinant Antibody (VS3-FY2704) (VS3-FY2704)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: WB, IHC
- Rabbit Anti-CTNNB1 Recombinant Antibody (VS3-FY2679) (VS3-FY2679)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat, Hamster
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IHC, IP
- Rabbit Anti-AKT1 Recombinant Antibody (VS3-FY2622) (VS3-FY2622)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat, Hamster
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IHC, ICC, IP
- Mouse Anti-JAK1 Recombinant Antibody (clone 3F12) (VS3-WK1613)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: IHC-P, WB
- Mouse Anti-MYD88 Recombinant Antibody (clone 2H12) (VS3-WK1601)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: IHC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat, Hamster
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IP
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IP
- Human Anti-AKT1 Recombinant Antibody (clone 30769) (VS-0224-XY5)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human IgG
- Application: WB
- Recombinant Mouse Anti-AKT1 Antibody (VS-0923-FY6) (VS-0923-FY6)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: ELISA, WB
- Recombinant Rabbit Anti-SRC Antibody (clone R05-7H8) (VS3-FY1389)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IHC-P
-
- Species Reactivity: Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IP
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IHC-P
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, ICC, IF
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IHC-P
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: IHC-P
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, ICC, IF, IP
- Mouse Anti-JAK2 Recombinant Antibody (VS4-WK260) (VS4-WK260)
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: ELISA, IHC
- Mouse Anti-JAK1 Recombinant Antibody (VS4-WK259) (VS4-WK259)
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: ELISA, IHC
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: ELISA, WB, IHC
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Pig, Rat
- Type: Mouse IgG2b
- Application: ELISA, WB
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, ICC, IF
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG2b
- Application: IHC-P
-
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: ELISA, WB, IHC, FC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: WB, IHC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IP
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: WB, IHC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: IHC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: WB, IHC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: WB, IHC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: WB, IHC
- Rabbit Anti-AKT1 Polyclonal Antibody (VS3-WK1562)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, ELISA
- Mouse Anti-CTNNB1 Recombinant Antibody (VS3-WK1430) (VS3-WK1430)
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human, Rat, Mouse
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: WB
- Mouse Anti-CTNNB1 Recombinant Antibody (VS3-WK1358) (VS3-WK1358)
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human, Rat, Mouse
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: WB, IHC-P
- Rabbit Anti-MYD88 Recombinant Antibody (VS3-WK1125) (VS3-WK1125)
-
- Derivation: Rabbit
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, ICC, IF, IHC, FC
- Mouse Anti-YES1 Recombinant Antibody (clone 2F3E6) (VS3-XY1612)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: ELISA, WB
- Mouse Anti-SRC Recombinant Antibody (clone 5D10C4) (VS3-XY1463)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG2a
- Application: ELISA, WB
- Mouse Anti-SRC Recombinant Antibody (clone 4F1E8) (VS3-XY1462)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG2b
- Application: ELISA, WB
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: ELISA, WB, IHC, FC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: ELISA, WB, IHC, FC
- Mouse Anti-JAK1 Recombinant Antibody (clone 1G1) (VS3-XY946)
-
- Species Reactivity: Mouse
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: WB, IP, IF, IHC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: ELISA, WB, IHC
- Mouse Anti-FGR Recombinant Antibody (clone 6G2) (VS3-XY712)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: ELISA, WB, IHC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: ELISA, WB, IHC, FC, ICC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: WB, IP, IF, IHC
-
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: ELISA, WB
-
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: IHC, FC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: ELISA, WB
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1, κ
- Application: WB, IHC-P
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG3, κ
- Application: WB, IF, IHC-P
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1, κ
- Application: IF, FC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, ICC, IHC, IP
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: WB, IF
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG2b, κ
- Application: WB, IHC-P
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG2b, κ
- Application: IHC-P
- Mouse Anti-AKT2 Recombinant Antibody (VS3-CJ874) (VS3-CJ874)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: WB, ICC, IF, IHC, IP, ChIP
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IHC, IP
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, ICC, IF, IHC, IP, FC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, ICC, IF, IHC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: WB, IHC
- Mouse Anti-AKT1 Recombinant Antibody (VS3-CJ869) (VS3-CJ869)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: WB, IHC
- Mouse Anti-VAV1 Recombinant Antibody (VS3-CJ674) (VS3-CJ674)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1, κ
- Application: WB
- Rabbit Anti-SRC Recombinant Antibody (VS3-CJ623) (VS3-CJ623)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, ICC, IF, IHC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, FC
- Mouse Anti-SRC Recombinant Antibody (VS3-CJ621) (VS3-CJ621)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG2b, κ
- Application: WB
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, ICC, IF, IHC
- Mouse Anti-YES1 Recombinant Antibody (VS3-CJ477) (VS3-CJ477)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: WB
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, ICC, IF
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IHC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat, Zebrafish
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IP, FC
- Mouse Anti-NRAS Recombinant Antibody (VS3-CJ234) (VS3-CJ234)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: WB
Our customer service representatives are available 24 hours a day, from Monday to Sunday. Contact Us
Can't find the products you're looking for? Try to filter in the left sidebar.Filter By Tag
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.































































