 Loading...
Loading...

Anti-GCAT Recombinant Antibody Products
 Loading...
Loading...Anti-GCAT Products
-
- Derivation: Phage display library
- Species Reactivity: Mouse, Rat, Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, ICC, IF, IP, IHC-P
Can't find the products you're looking for? Try to filter in the left sidebar.Filter By Tag
Our customer service representatives are available 24 hours a day, from Monday to Sunday. Contact Us
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.
Creative Biolabs is committed to delivering high-quality, innovative recombinant antibodies engineered to target GCAT, actively driving forward advancements in biomedical research through cutting-edge solutions. By leveraging state-of-the-art technological platforms, we ensure our products consistently adhere to rigorous standards for performance and reliability, providing researchers with robust tools to advance their work. Our extensive antibody portfolio is thoughtfully designed to deliver both scientific excellence and dependable results, catering to a wide spectrum of research needs. Beyond our top-tier reagents, we offer expert, collaborative technical support tailored to assist researchers at every stage of their projects, fostering a partnership focused on overcoming challenges. Partnering with Creative Biolabs means gaining access to advanced research solutions and a dedicated team fully committed to your research success, combining innovation in product development with unwavering support to empower your scientific journey.
GCAT: A Potential Biomarker in Mitochondrial Dysfunction Cancer and Metabolic Disorders
GCAT is a mitochondrial enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of glycine, an amino acid essential for various cellular processes including nucleotide synthesis, redox balance, and mitochondrial function. Disruption of GCAT activity has been linked to mitochondrial dysfunction, which can contribute to neurological and metabolic disorders. Altered expression or mutations in GCAT may impair glycine metabolism, leading to developmental delays, neuromuscular symptoms, or broader mitochondrial pathologies. In cancer research, GCAT has gained attention for its potential role in supporting abnormal metabolic demands in tumor cells, particularly through its influence on amino acid availability and mitochondrial activity. Dysregulation of GCAT may also be involved in aging-related conditions, where mitochondrial decline plays a central role. As studies continue to explore the metabolic underpinnings of disease, GCAT is emerging as a potential biomarker and therapeutic target in both rare genetic syndromes and more common disorders involving mitochondrial and cellular energy imbalances.
Alternative Names
Complement Glycine C-Acetyltransferase; Glycine Acetyltransferase; Aminoacetone Synthase; EC 2.3.1.29; AKB Ligase; KBL; Glycine C-Acetyltransferase (2-Amino-3-Ketobutyrate Coenzyme A Ligase);-Amino-3-Ketobutyrate Coenzyme A Ligase; 2-Amino-3-Ketobutyrate-CoA Ligase; EC 2.3.1
Background
The degradation of L-threonine to glycine consists of a two-step biochemical pathway involving the enzymes L-threonine dehydrogenase and 2-amino-3-ketobutyrate coenzyme A ligase. L-Threonine is first converted into 2-amino-3-ketobutyrate by L-threonine dehydrogenase. This gene encodes the second enzyme in this pathway, which then catalyzes the reaction between 2-amino-3-ketobutyrate and coenzyme A to form glycine and acetyl-CoA. The encoded enzyme is considered a class II pyridoxal-phosphate-dependent aminotransferase. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants. A pseudogene of this gene is found on chromosome 14.
Enzymes, Metabolic proteins, Plasma proteins
Intracellular
Cell type enhanced (Proximal tubular cells, Distal tubular cells, Hepatocytes)
Low immune cell specificity
Low cell line specificity
Acyltransferase, Transferase
Anti-GCAT rAb Products
Our goal is to expedite scientific discovery by providing high-quality anti-GCAT recombinant antibodies that not only offer strong value but also come with dependable technical support, designed to assist researchers at every phase of their experimental processes and ensure seamless progress toward their objectives.
Table 1. Featured anti-GCAT recombinant antibody products at Creative Biolabs.
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Target Species | Host Species | Applications |
| MOR-1413 | Hi-Affi™ Rabbit Anti-GCAT Recombinant Antibody (clone DS1413AB) | Mouse; Rat; Human | Rabbit | WB; ICC; IF; IP; IHC-P |
Customer Reviews

Hi-Affi™ Rabbit Anti-GCAT Recombinant Antibody (clone DS1413AB) (CAT#: MOR-1413)

Hi-Affi™ Rabbit Anti-GCAT Recombinant Antibody (clone DS1413AB) (CAT#: MOR-1413)
rAb Production
Drawing on years of expertise in the development and refinement of recombinant antibodies, we are dedicated to delivering high-quality products with efficiency as a core priority. Our unwavering commitment to exceptional service ensures that researchers obtain reliable antibody solutions accompanied by a rapid turnaround, empowering their workflows with both precision and speed.
Featured Anti-GCAT Recombinant Antibody Production Platforms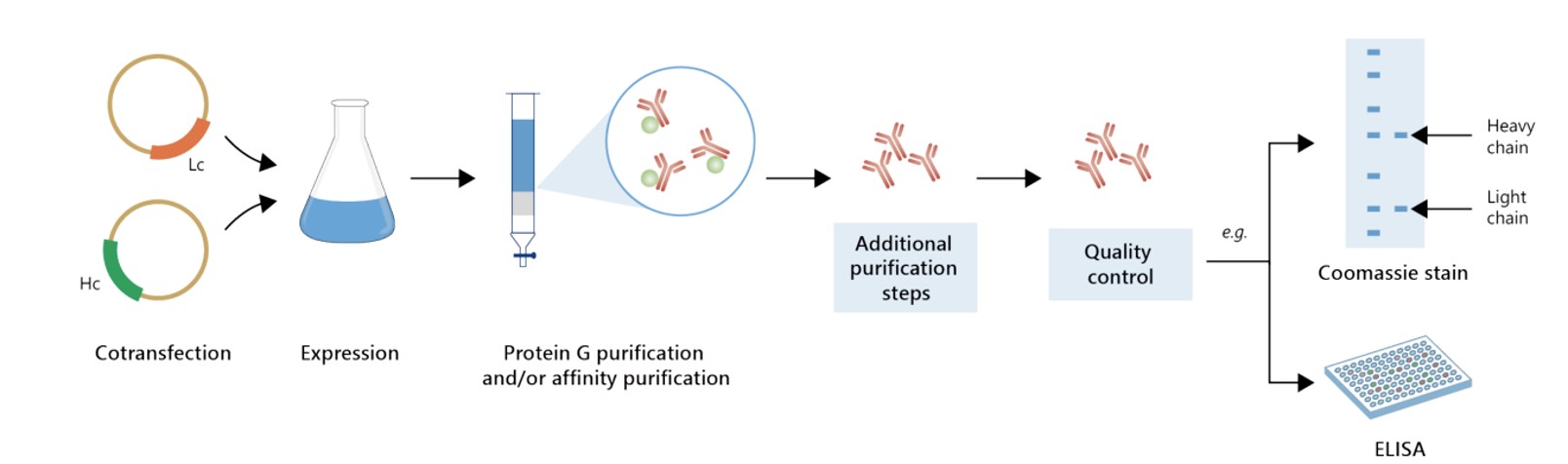
Fig.1 Milligram-scale recombinant antibody production.
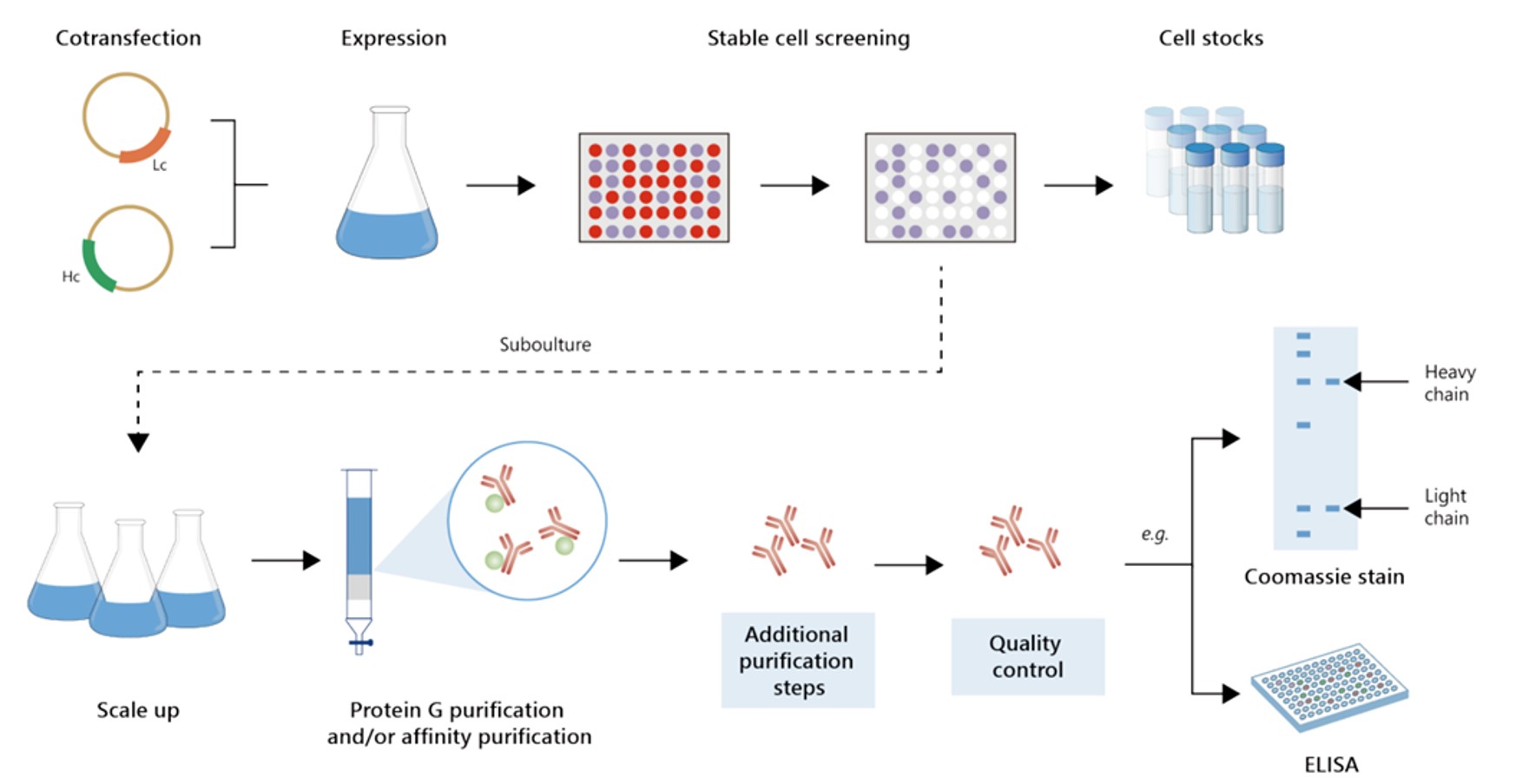 Fig.2 Gram-scale recombinant antibody production.
Fig.2 Gram-scale recombinant antibody production.
rAb Modalities
At Creative Biolabs, we empower scientists with an expansive collection of cutting-edge recombinant antibodies available in diverse configurations. Our team's proficiency in state-of-the-art antibody modification techniques enables us to create adaptable and groundbreaking research tools. Every antibody offering is enhanced by premium tailored services that precisely address your study's unique biological questions and experimental needs.
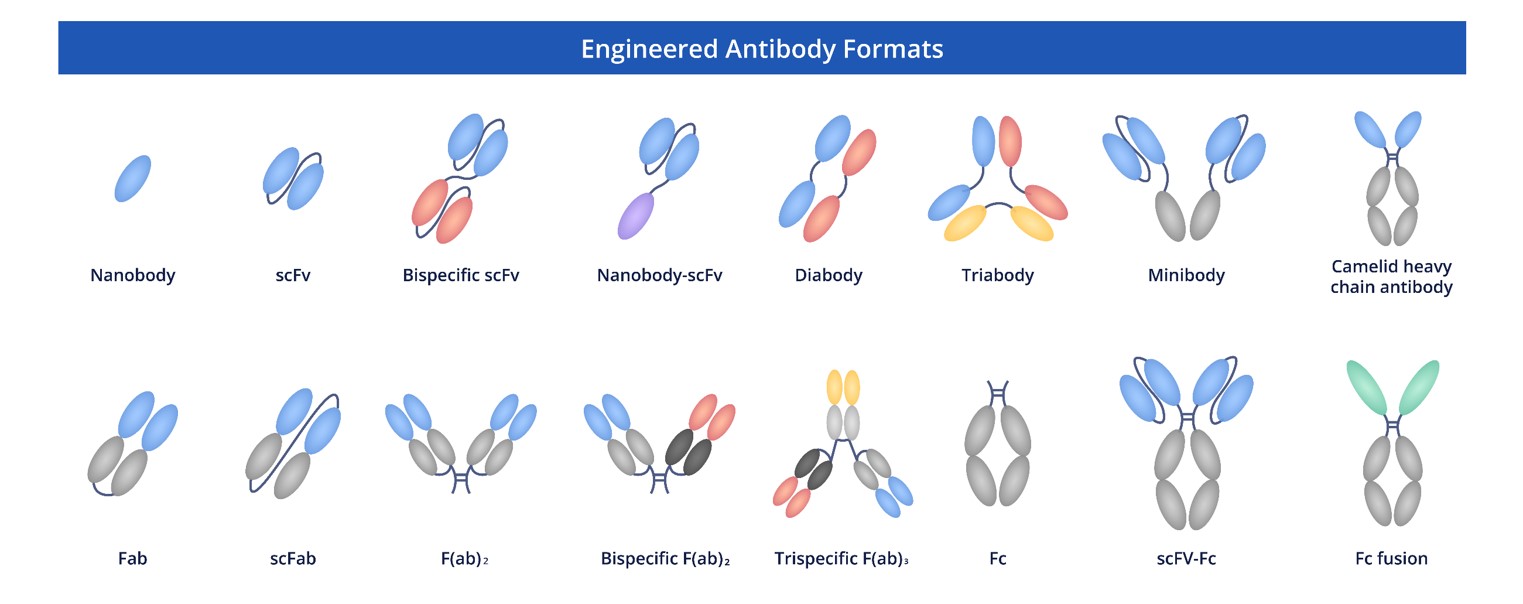 Fig.3 Full Length Anti-GCAT Recombinant Antibody Production and Modalities.
Fig.3 Full Length Anti-GCAT Recombinant Antibody Production and Modalities.
If you need further information about the GCAT target, please don't hesitate to contact us by phone or email. Our experienced team is always ready to help with any questions or experimental issues you may encounter, ensuring you receive the support necessary for smooth and effective research.



