 Loading...
Loading...

RXRA
 Loading...
Loading...Anti-RXRA Products
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: ELISA, WB
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IF, IHC, IP
-
- Derivation: Rabbit
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, ELISA
- Anti-Human RXRA Immunohistochemistry Kit (VS-0525-XY6284)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Target: RXRA
- Application: IHC
-
- Derivation: Phage display library screening
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: IgG
- Application: WB, ICC, IP
- Anti-RXRA Immunohistochemistry Kit (VS-0325-XY1983)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Target: RXRA
- Application: IHC
- Rabbit Anti-RXRA Recombinant Antibody (VS13-YC1025) (VS13-YC1025)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, ICC, IF, IHC-P, IP
Can't find the products you're looking for? Try to filter in the left sidebar.Filter By Tag
Our customer service representatives are available 24 hours a day, from Monday to Sunday. Contact Us
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.
Background

Cancer-related genes, FDA approved drug targets, Metabolic proteins, Nuclear receptors, Transcription factors
Intracellular
Cell type enhanced (Hepatocytes, Kupffer cells)
Immune cell enhanced (neutrophil)
Cell line enhanced (HaCaT)
Homodimer (PubMed:10669605, PubMed:17761950). Heterodimer (via C-terminus) with RARA; required for ligand-dependent retinoic acid receptor transcriptional activity; association with RARA is enhanced by pulsatile shear stress (PubMed:28167758, PubMed:10698945, PubMed:15509776). Heterodimer with PPARA (via the leucine-like zipper in the LBD); the interaction is required for PPARA transcriptional activity (PubMed:10195690, PubMed:11915042, PubMed:11698662). Heterodimerizes with PPARG (PubMed:10882139, PubMed:11698662). Heterodimerizes (via NR LBD) with RARB (PubMed:29021580). Heterodimerizes with NR1H4; the heterodimerization enhances the binding affinity for LXXLL motifs from coactivators (PubMed:30275017). Interacts with NCOA3 and NCOA6 coactivators (PubMed:9267036, PubMed:10567404). Interacts with coactivator FAM120B (By similarity). Interacts with coactivator PELP1, SENP6, SFPQ, DNTTIP2 and RNF8 (PubMed:16574651, PubMed:16912044, PubMed:11259580, PubMed:15047147, PubMed:14981089). Interacts with PRMT2 (PubMed:12039952). Interacts with ASXL1 (By similarity). Interacts with BHLHE40/DEC1, BHLHE41/DEC2, NCOR1 and NCOR2 (PubMed:19786558). Interacts in a ligand-dependent fashion with MED1 and NCOA1 (PubMed:19786558, PubMed:10882139, PubMed:11698662). Interacts with VDR (PubMed:28698609). Interacts with EP300; the interaction is decreased by 9-cis retinoic acid (PubMed:17761950). Heterodimer (via C-terminus) with NR4A1 (via DNA-binding domain); DNA-binding of the heterodimer is enhanced by 9-cis retinoic acid (PubMed:17761950, PubMed:15509776). NR4A1 competes with EP300 for interaction with RXRA and thereby attenuates EP300 mediated acetylation of RXRA (PubMed:17761950). In the absence of hormonal ligand, interacts with TACC1 (PubMed:20078863). (Microbial infection) Interacts (via the DNA binding domain) with HCV core protein; the interaction enhances the transcriptional activities of the RXRA/RARA and the RXRA/PPARA heterodimers.
DNA-binding, Receptor


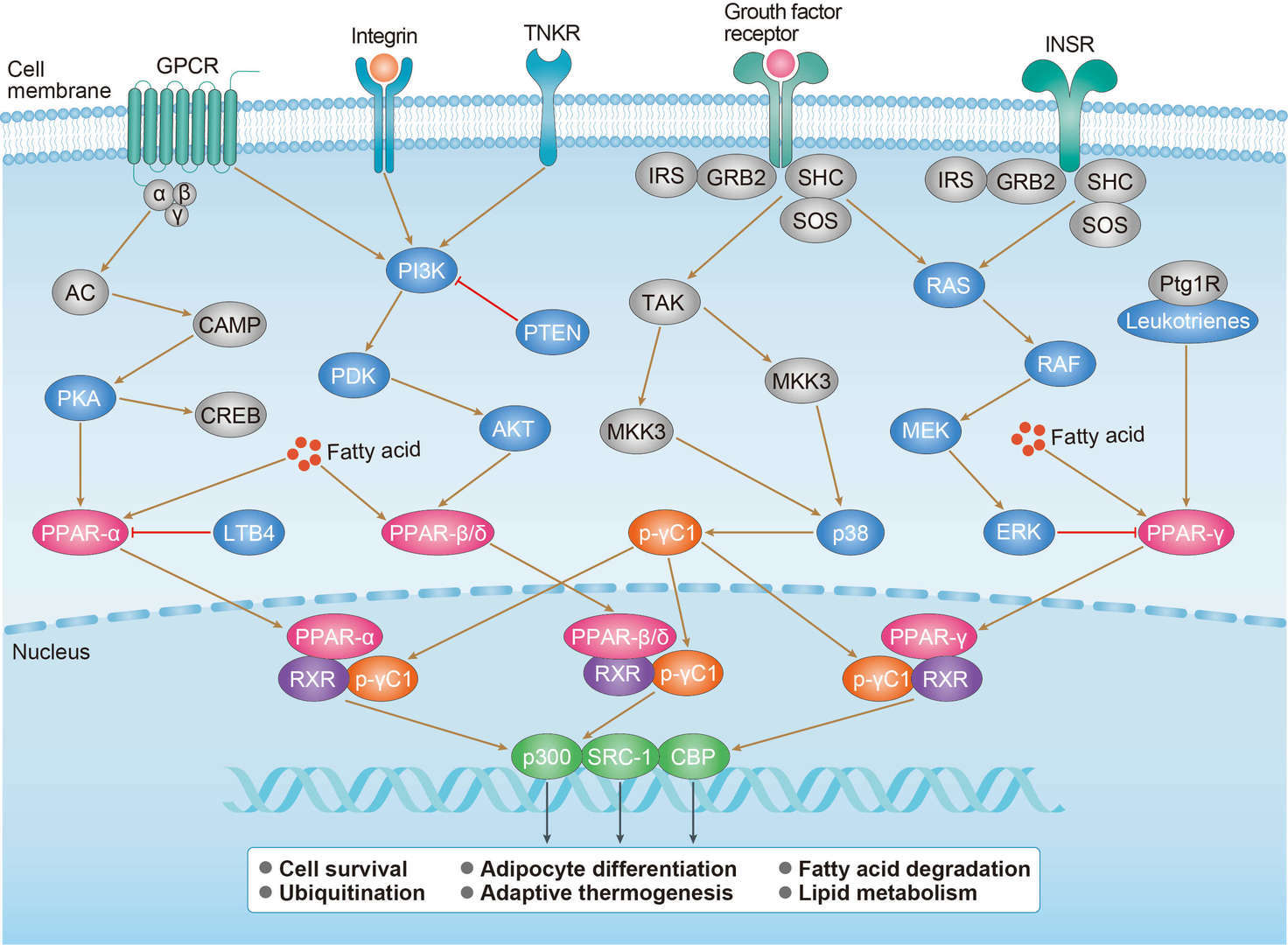 PPAR Signaling Pathway
PPAR Signaling Pathway
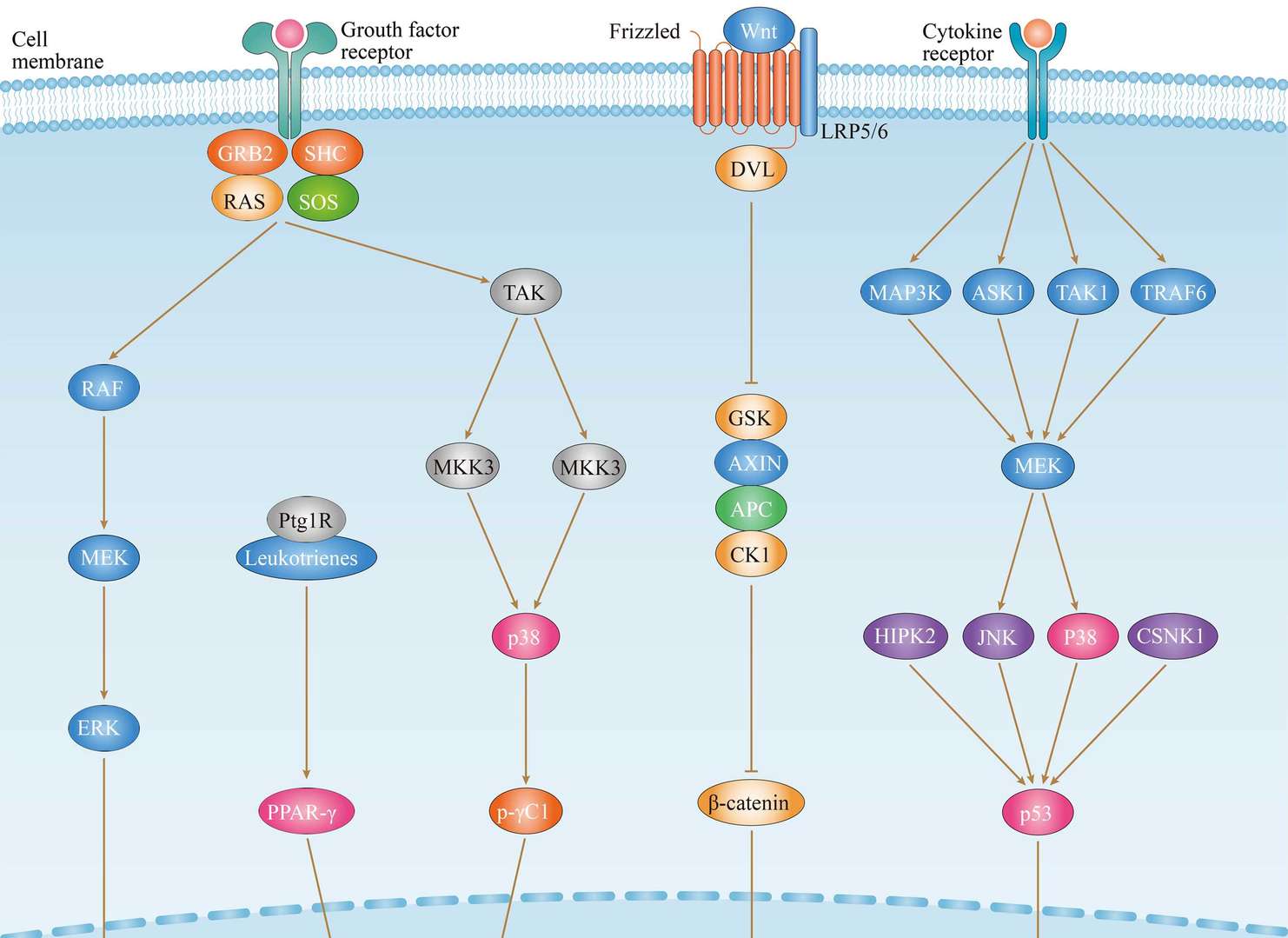 Throid Cancer
Throid Cancer

