Anti-ABCC4 Recombinant Antibody Products
 Loading...
Loading...Anti-ABCC4 Products
 Loading...
Loading...-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: WB, ELISA, FC, ICC, IF, IHC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: WB
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: WB, ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: ELISA, WB, IHC, FC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: ELISA, WB, IHC, FC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: IHC-P
- Anti-ABCC4 Immunohistochemistry Kit (VS-0525-XY26)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Target: ABCC4
- Application: IHC
- Anti-Mouse ABCC4 Immunohistochemistry Kit (VS-0525-XY27)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Target: ABCC4
- Application: IHC
Can't find the products you're looking for? Try to filter in the left sidebar.Filter By Tag
Our customer service representatives are available 24 hours a day, from Monday to Sunday. Contact Us
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.
Creative Biolabs supports research in pharmacology, virology, and cardiovascular medicine with world-class anti-ABCC4 recombinant antibodies. ABCC4 is a widely expressed transporter of cyclic nucleotides (cAMP and cGMP) and many different drugs. Our top-quality antibodies help you explore its functions in platelet activation, viral replication, and response to chemotherapy.
ABCC4: A Versatile Efflux Pump for Signal Molecules and Drugs
ABCC4 is ATP-binding cassette subfamily C member 4, also known as Multidrug Resistance-Associated Protein 4 (MRP4). ABCC4 is a physiologically relevant efflux transporter that pumps out cyclic nucleotides cAMP and cGMP to turn off their signaling activity. It is especially important in platelets to limit aggregation. The protein can also efflux prostaglandins, bile acids, and a large variety of drugs such as the antiviral drug tenofovir, anticancer drugs (methotrexate, doxorubicin), or cardiovascular drugs (atenolol). In particular, it is often overexpressed in cancer as a drug resistance mechanism that can also impact antiviral treatment efficacy.
Alternative Names
ABCC4; Multidrug Resistance-Associated Protein 4; Member 4); Multispecific Organic Anion Transporter B; MRP/CMOAT-Related ABC Transporter; MRP4; Canalicular Multispecific Organic Anion Transporter (ABC Superfamily); MOATB; Multi-Specific Organic Anion Tra
Background
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the superfamily of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters. ABC proteins transport various molecules across extra- and intra-cellular membranes. ABC genes are divided into seven distinct subfamilies (ABC1, MDR/TAP, MRP, ALD, OABP, GCN20, White). This protein is a member of the MRP subfamily which is involved in multi-drug resistance. This family member plays a role in cellular detoxification as a pump for its substrate, organic anions. It may also function in prostaglandin-mediated cAMP signaling in ciliogenesis. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants.
Enzymes, Metabolic proteins, Plasma proteins, Transporters
Membrane
Cell type enhanced (Microglial cells, granulocytes, Erythroid cells)
Low immune cell specificity
Group enriched (HEL, HMC-1, RPTEC TERT1)
Interacts (via PDZ-binding motif) with SNX27 (via PDZ domain); this interaction accelerates MRP4 internalization.
Translocase
Anti-ABCC4 rAb Products
Creative Biolabs' recombinant anti-ABCC4 antibodies are produced for optimal specificity and performance. They are thoroughly validated to specifically detect the ABCC4 transporter in cell lines, tissue, and primary cells such as platelets. Tailored for FACS, Western Blot, and IHC, these rAbs have been optimized for a robust, reliable signal that accurately reflects the expression of this clinically relevant transporter.
Table 1. Featured anti-ABCC4 recombinant antibody products at Creative Biolabs.
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Target Species | Host Species | Applications |
| MOB-2633z | Mouse Anti-ABCC4 Recombinant Antibody (clone 32G6) | Human | Mouse IgG1 | WB, ELISA, FC, ICC, IF, IHC |
| VS3-WK167 | Mouse Anti-ABCC4 Recombinant Antibody (clone H3-A7) | Human | Mouse IgG1 | WB, ELISA |
| VS13-YC3 | Rabbit Anti-ABCC4 Recombinant Antibody (VS13-YC3) | Human | Rabbit IgG | IHC-P |
Customer Reviews

Mouse Anti-ABCC4 Recombinant Antibody (clone 32G6)
rAb Production
Creative Biolabs employs industry-leading production platforms to support these niche clinical pharmacology and cell signaling applications. Our recombinant anti-ABCC4 antibodies are expressed in systems optimized to make sure they recognize the native transporter. This provides you with the most specific and active antibody for your ABCC4 research.
Featured Anti-ABCC4 Recombinant Antibody Production Platforms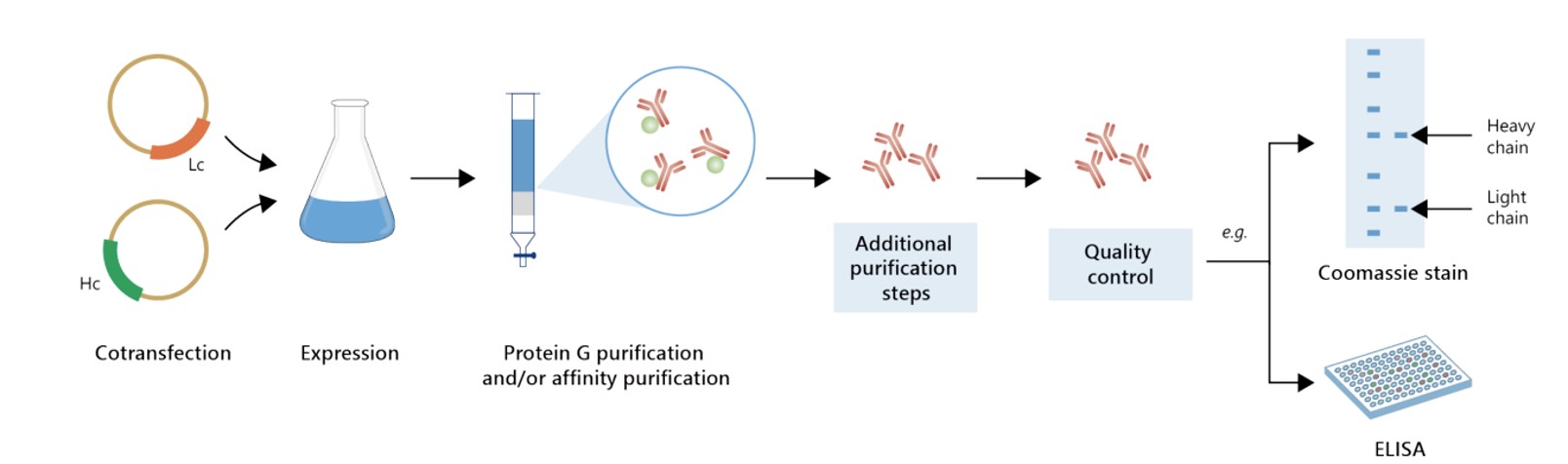
Fig.1 Milligram-scale anti-ABCC4 recombinant antibody production.
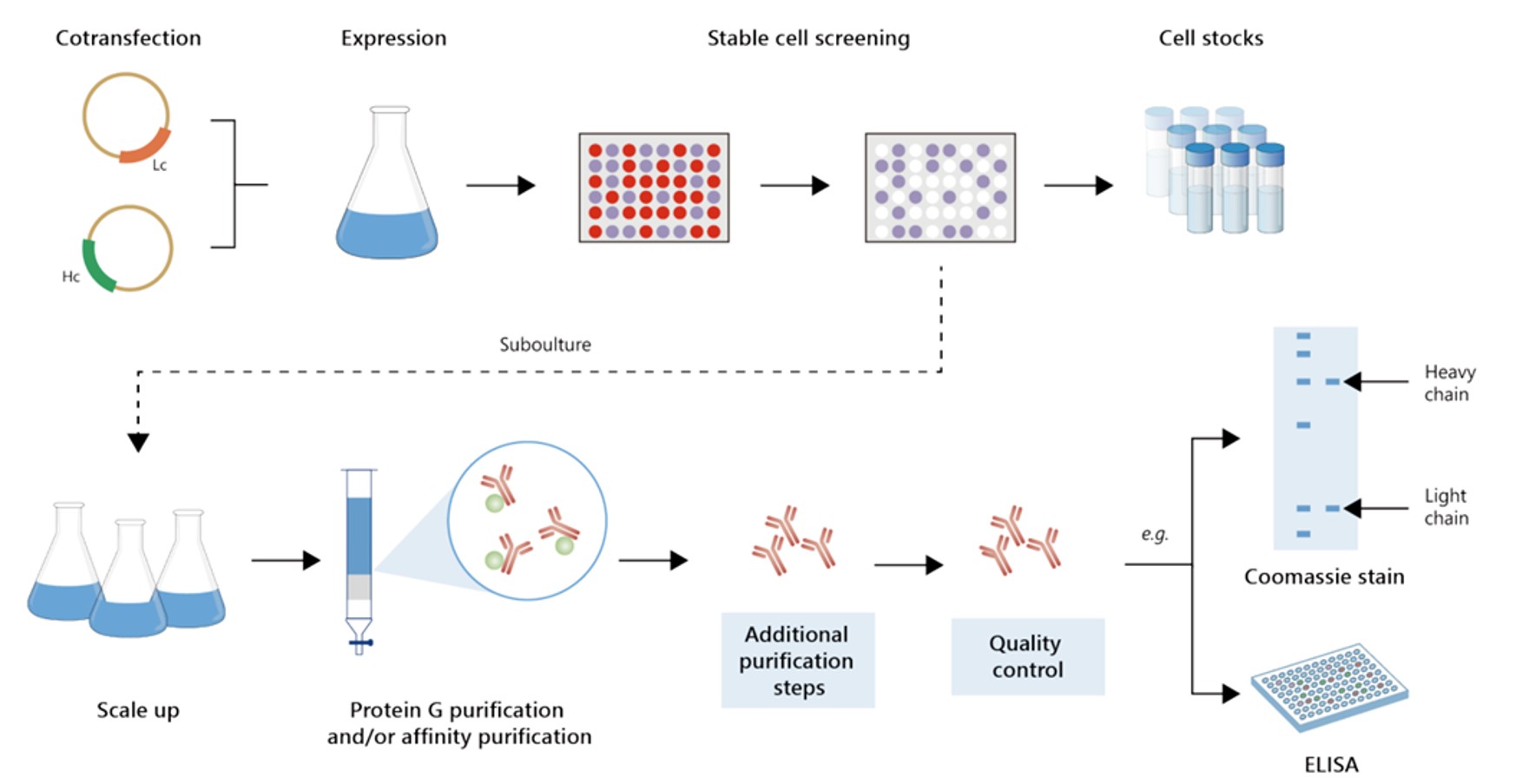 Fig.2 Gram-scale anti-ABCC4 recombinant antibody production.
Fig.2 Gram-scale anti-ABCC4 recombinant antibody production.
rAb Modalities
Creative Biolabs is committed to enabling scientific discovery through a flexible antibody portfolio. Our anti-ABCC4 recombinant antibodies can be provided in a range of modalities and can be customized to fit your experimental requirements. No matter where you are in the world or what stage of development your research is at, we want you to have the tools you need to investigate this diverse transporter.
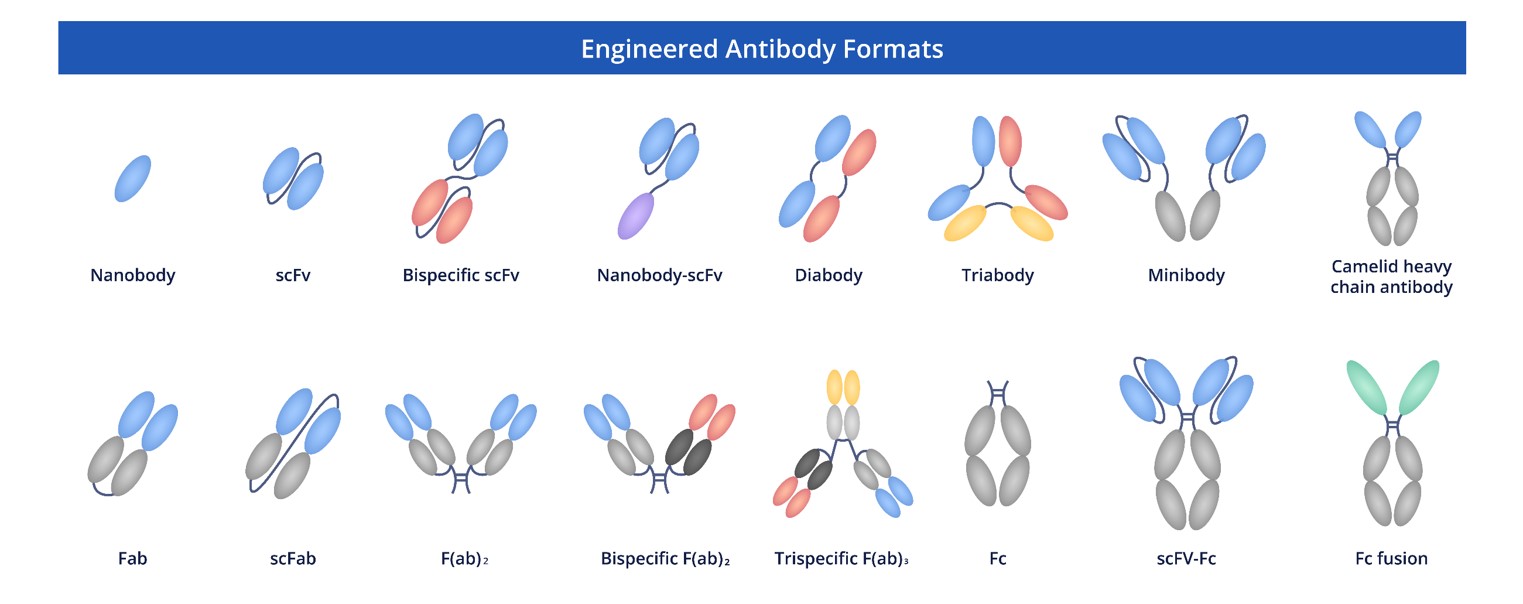 Fig.3 Full-length anti-ABCC4 recombinant antibody production and modalities.
Fig.3 Full-length anti-ABCC4 recombinant antibody production and modalities.
Creative Biolabs recombinant antibodies are the optimal research tools for exploring the multiple roles of ABCC4. Defined by their high specificity and extensive validation, our product portfolio includes the right solution for your research into cancer, virology, and cardiovascular disease. Quality from Creative Biolabs, where customer service and scientific rigor partner to deliver antibodies that speed progress. Reach out to one of our scientists today.

