Anti-ASPH Recombinant Antibody Products
 Loading...
Loading...Anti-ASPH Products
 Loading...
Loading...-
- Derivation: Human
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: IgG
- Application: IF, FACS, FuncS
- Recombinant Anti-human ASPH Antibody (MOB-78)
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: IgG
- Application: WB, FC, FuncS
- Recombinant Anti-human ASPH Antibody Fab Fragment (MOB-78-F(E))
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Fab
- Application: ELISA, Nert, FuncS
- Recombinant Anti-human ASPH Antibody scFv Fragment (MOB-78-S(P))
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: scFv
- Application: ELISA, WB, Neut, FuncS
- Recombinant Human Anti-human ASPH Antibody Fab Fragment (MHH-78-F(E))
-
- Derivation: Human
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Fab
- Application: WB, IHC, FuncS
- Recombinant Human Anti-human ASPH Antibody scFv Fragment (MHH-78-S(P))
-
- Derivation: Human
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: scFv
- Application: ELISA, WB, FC, FuncS
-
- Derivation: Phage display library screening
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IHC-P, IF, FC
- Anti-ASPH Immunohistochemistry Kit (VS-0325-XY189)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Target: ASPH
- Application: IHC
- Human Anti-ASPH scFv-Fc Chimera (VS-0625-FY12) (VS-0625-FY12)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human IgG1, scFv-Fc
- Application: FC
- Anti-Human ASPH Immunohistochemistry Kit (VS-0525-XY564)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Target: ASPH
- Application: IHC
Can't find the products you're looking for? Try to filter in the left sidebar.Filter By Tag
Our customer service representatives are available 24 hours a day, from Monday to Sunday. Contact Us
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.
Creative Biolabs is a trusted provider of anti-Aspartate beta-hydroxylase (ASPH) recombinant antibodies for oncology research and therapeutic development. ASPH is a cell-surface enzyme involved in cancer cell migration and invasion, making it an attractive target for next-generation cancer therapies. Our high-quality recombinant antibodies will be a critical asset to help you better understand ASPH and its role in metastasis, as well as develop targeted antibody-based therapeutics.
ASPH: A Cell-Surface Enzyme Driving Cancer Malignancy
Aspartate beta-hydroxylase (ASPH) is a type II transmembrane protein and enzyme that hydroxylates selected aspartyl and asparaginyl residues in EGF-like domains of a variety of proteins, including the Notch receptor. This post-translational modification is required for the activation of downstream signaling cascades, which in turn promote cellular motility, invasion, and proliferation. ASPH is upregulated in many aggressive cancers, including liver cancer, pancreatic cancer, and lung cancer, and high ASPH expression is associated with poor prognosis and metastasis. ASPH is uniquely accessible as an antibody target as it is highly expressed on the surface of malignant cells.
Alternative Names
ASPH; aspartate beta-hydroxylase; AAH; BAH; HAAH; JCTN; FDLAB; junctin; CASQ2BP1; aspartyl/asparaginyl beta-hydroxylase; humbug; junctate; A beta H-J-J; cardiac junctin; ASP beta-hydroxylase; peptide-aspartate beta-dioxygenase; aspartyl/asparaginyl-beta-h
Background
This gene is thought to play an important role in calcium homeostasis. The gene is expressed from two promoters and undergoes extensive alternative splicing. The encoded set of proteins share varying amounts of overlap near their N-termini but have substantial variations in their C-terminal domains resulting in distinct functional properties. The longest isoforms (a and f) include a C-terminal Aspartyl/Asparaginyl beta-hydroxylase domain that hydroxylates aspartic acid or asparagine residues in the epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like domains of some proteins, including protein C, coagulation factors VII, IX, and X, and the complement factors C1R and C1S. Other isoforms differ primarily in the C-terminal sequence and lack the hydroxylase domain, and some have been localized to the endoplasmic and sarcoplasmic reticulum. Some of these isoforms are found in complexes with calsequestrin, triadin, and the ryanodine receptor, and have been shown to regulate calcium release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Some isoforms have been implicated in metastasis.
Cancer-related genes, Disease related genes, Enzymes, Human disease related genes, Metabolic proteins, Plasma proteins, Potential drug targets, Transporters
Intracellular, Membrane (different isoforms)
Cell type enhanced (Muller glia cells)
Immune cell enhanced (plasmacytoid DC)
Cell line enhanced (U-87 MG)
Monomer (By similarity). Isoform 8 interacts with ORAI1 and STIM1. Isoform 4 interacts with CASQ2.
Dioxygenase, Oxidoreductase
Anti-ASPH rAb Products
Our anti-ASPH recombinant antibodies (rAbs) were designed to bind with high affinity and specificity to ASPH to enable its detection on the surface of cancer cells. They are also extensively validated for use in challenging applications such as flow cytometry, IHC, and functional blocking assays. Our recombinant anti-ASPH antibodies will provide the specificity and functional activity you need to better understand ASPH's role in cancer and for antibody-based therapeutic development.
Table 1. Featured anti-ASPH recombinant antibody products at Creative Biolabs.
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Target Species | Host Species | Applications |
| MHH-78 | Recombinant Human Anti-human ASPH Antibody | Human | Human IgG1 | IF, FACS, FuncS |
| MOB-78 | Recombinant Anti-human ASPH Antibody | Human | Mouse IgG | WB, FC, FuncS |
| MOR-0269 | Affi™ Rabbit Anti-ASPH Recombinant Antibody (clone DS269AB) | Human | Rabbit IgG | WB, IHC-P, IF, FC |
Customer Reviews

Recombinant Human Anti-human ASPH Antibody
rAb Production
Creative Biolabs utilizes advanced production platforms to help accelerate the development of new cancer therapies. Our anti-ASPH recombinant antibodies are produced in highly-optimized mammalian cell lines to ensure that they specifically recognize the native, extracellular, catalytic domain of the enzyme so you can be assured of a product with high functional activity.
Featured Anti-ASPH Recombinant Antibody Production Platforms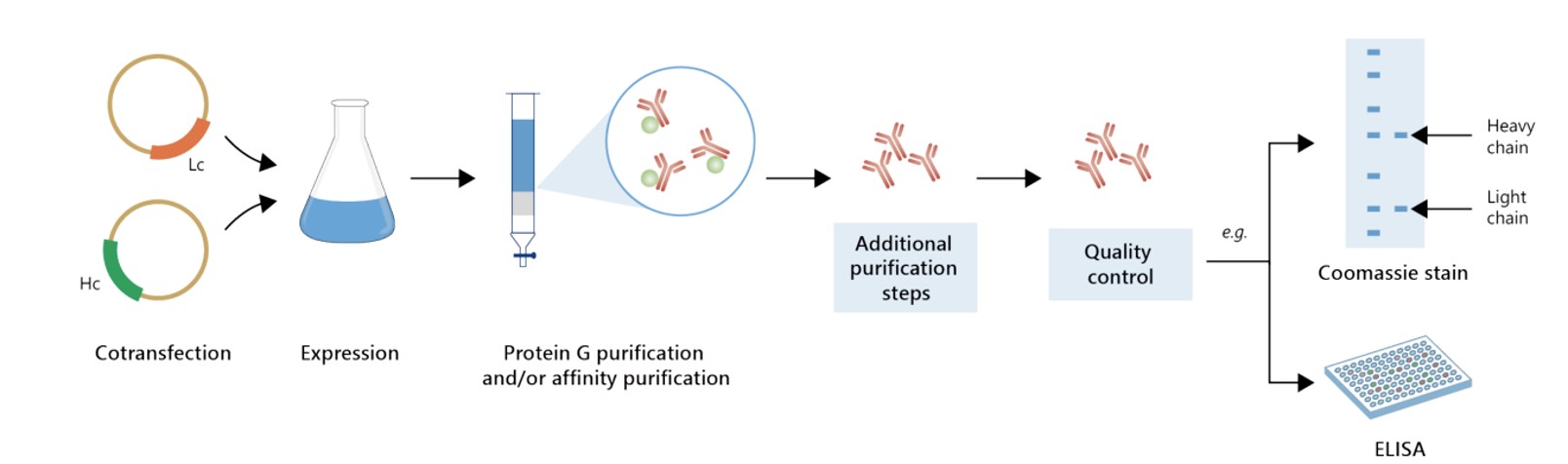
Fig.1 Milligram-scale anti-ASPH recombinant antibody production.
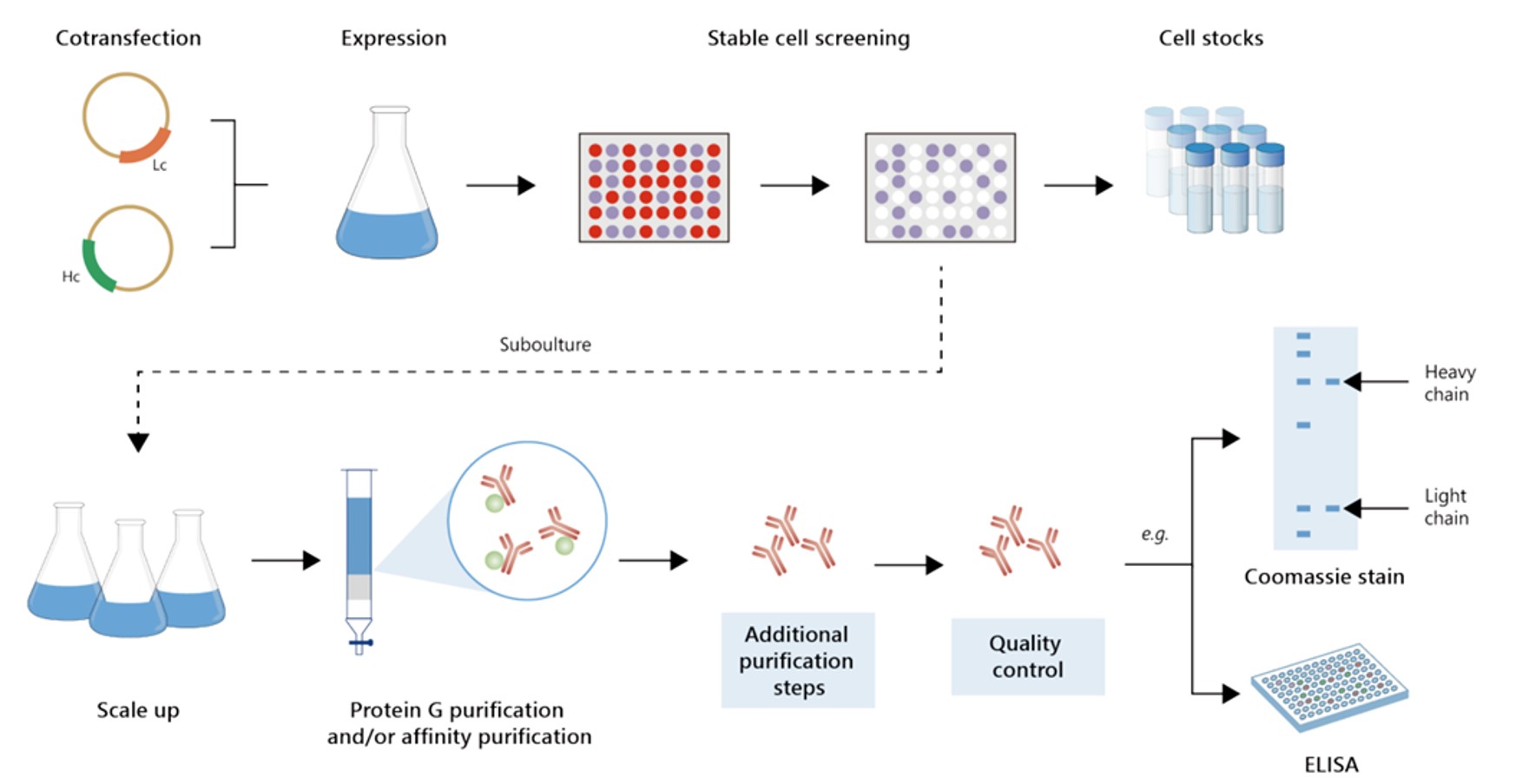 Fig.2 Gram-scale anti-ASPH recombinant antibody production.
Fig.2 Gram-scale anti-ASPH recombinant antibody production.
rAb Modalities
Creative Biolabs is committed to providing novel solutions for oncology research and drug development. Our anti-ASPH recombinant antibodies are available in a variety of customizable modalities to suit your specific application, including full-length IgGs for therapeutic development, Fab fragments for structural studies, or formats designed for CAR-T cell or ADC development.
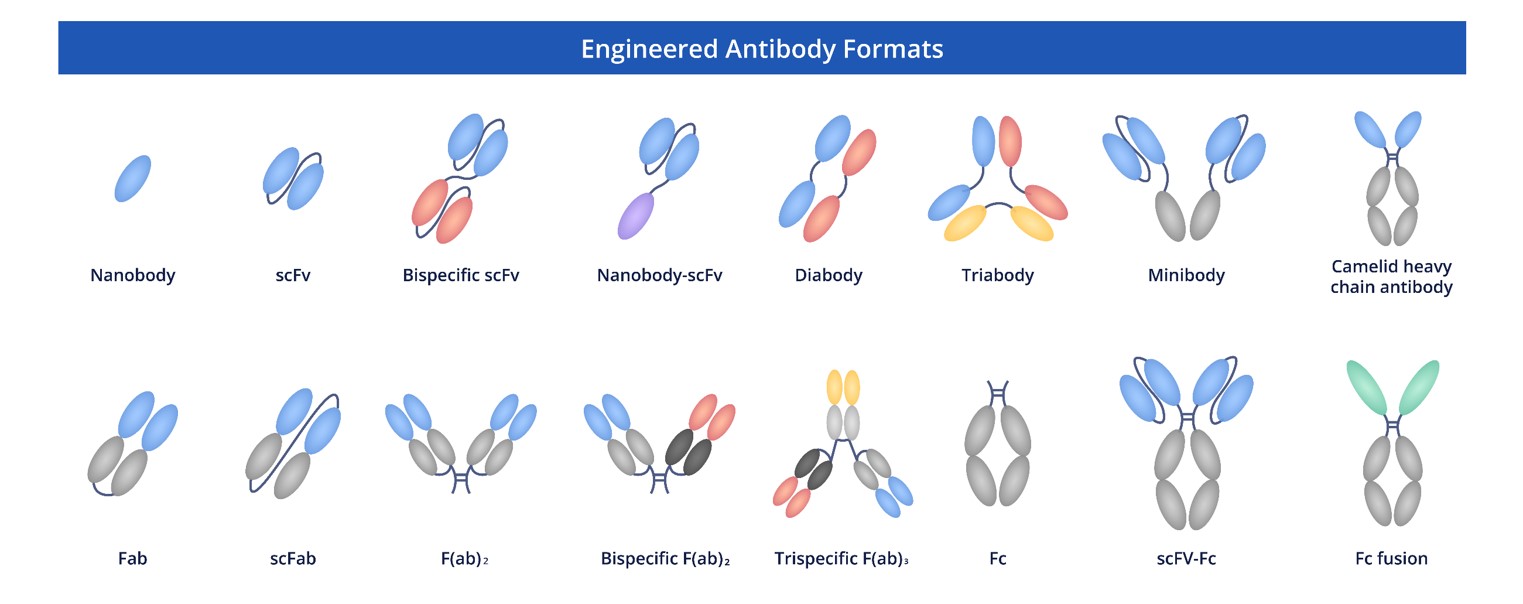 Fig.3 Full-length anti-ASPH recombinant antibody production and modalities.
Fig.3 Full-length anti-ASPH recombinant antibody production and modalities.
ASPH-Targeted Drug Information
Table 2. Public drug targeting ASPH.
| Company | Research phase | Classification | Condition |
| Dicerna (acquired by Novo Nordisk) | Terminated | RNAi therapeutic (not an antibody) | Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) |
| Various Academic/Biotech | Preclinical / Research | Monoclonal Antibody, ADC, CAR-T | Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Cholangiocarcinoma, Pancreatic Cancer |
(Disclaimer: The information in this table is just for knowledge sharing and not for marketing or sales purposes.)
Target cancer cell motility and invasion with Creative Biolabs' premium anti-Aspartate beta-hydroxylase (ASPH) recombinant antibodies. Our catalog of ASPH-specific rAbs offer the specificity and functional activity required to investigate this important cell-surface enzyme. Place your confidence in our experience to provide you with the best starting material for your next generation of cancer therapeutics. Contact our team of scientists today.

