Anti-CPS1 Recombinant Antibody Products
 Loading...
Loading...Anti-CPS1 Products
 Loading...
Loading...- Rabbit Anti-CPS1 Recombinant Antibody (clone JB40-33) (MRO-0385-CN)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IF, IHC, IP
- AbPlus™ Anti-CPS1 Magnetic Beads (VS-0724-YC117) (VS-0724-YC117)
-
- Target: CPS1
- Target Species: Human
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1, κ
- Application: WB, IP, IF, IHC, ELISA
- Recombinant Mouse Anti-Human CPS1 Antibody (MOB-0728MZ)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse antibody
- Application: IHC-P
-
- Derivation: Phage display library
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IHC, ICC, IP
- Anti-CPS1 Immunohistochemistry Kit (VS-0325-XY526)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Target: CPS1
- Application: IHC
- Anti-Mouse CPS1 Immunohistochemistry Kit (VS-0525-XY1641)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Target: CPS1
- Application: IHC
- Anti-Human CPS1 Immunohistochemistry Kit (VS-0525-XY1640)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Target: CPS1
- Application: IHC
- Anti-Rat CPS1 Immunohistochemistry Kit (VS-0525-XY1642)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Target: CPS1
- Application: IHC
Can't find the products you're looking for? Try to filter in the left sidebar.Filter By Tag
Our customer service representatives are available 24 hours a day, from Monday to Sunday. Contact Us
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.
Pioneering research in metabolic diseases? Here at Creative Biolabs, we provide top-tier, elite anti-CPS1 recombinant antibodies. Carbamoyl Phosphate Synthetase 1 (CPS1) is the first and rate-limiting enzyme of the urea cycle and is thus absolutely critical for detoxification of ammonia. Our high-quality antibodies are essential diagnostic tools for CPS1 deficiency as well as novel therapies like gene and mRNA-based therapeutics for this tragic disorder.
CPS1: The Gatekeeper of the Urea Cycle
Carbamoyl Phosphate Synthetase 1 (CPS1) is a large enzyme in the mitochondrial matrix of hepatocytes and intestinal epithelial cells. It catalyzes the first committed step of the urea cycle: the ATP-dependent conversion of ammonia and bicarbonate to carbamoyl phosphate. This reaction is the primary pathway by which the body disposes of toxic ammonia produced from protein metabolism. Genetic deficiency of CPS1 causes a severe neonatal-onset inborn error of metabolism that is characterized by life-threatening hyperammonemia that can lead to irreversible neurological injury if not promptly treated.
Alternative Names
Carbamoyl-Phosphate Synthase 1; Carbamoyl-Phosphate Synthase 1, Mitochondrial; Carbamoyl-Phosphate Synthase (Ammonia); EC 6.3.4.16; Carbamoyl-Phosphate Synthase [Ammonia], Mitochondrial; Carbamoyl-Phosphate Synthetase 1, Mitochondrial;
Background
CPS1 (Carbamoyl-Phosphate Synthase 1) is a Protein Coding gene. Diseases associated with this gene include Carbamoyl Phosphate Synthetase I Deficiency, Hyperammonemia Due To and Pulmonary Hypertension, Neonatal. Pathways associated with this gene include CDK-mediated phosphorylation and removal of Cdc6 and Arginine biosynthesis. GO annotations associated with this gene include calcium ion binding and phospholipid binding. Notable paralogs of this gene include CAD.
Disease related genes, Enzymes, FDA approved drug targets, Human disease related genes, Metabolic proteins, Plasma proteins
Intracellular
Cell type enriched (Hepatocytes)
Not detected in immune cells
Cell line enhanced (HeLa, SiHa, SK-BR-3)
Can form homooligomers (monomers as predominant form and dimers).
Allosteric enzyme, Ligase
Anti-CPS1 rAb Products
Our anti-CPS1 recombinant antibodies are engineered for unparalleled specificity and performance. They are fully validated for use in the clinical diagnostic setting, primarily Western Blot of liver biopsy lysates to confirm the absence of CPS1 protein in affected patients. They are also optimized for IHC to study its distribution in the liver lobule.
Table 1. Featured anti-CPS1 recombinant antibody products at Creative Biolabs.
| Cat. No. | Product Name | Target Species | Host Species | Applications |
| MRO-0385-CN | Rabbit Anti-CPS1 Recombinant Antibody (clone JB40-33) | Human, Mouse, Rat | Rabbit IgG | WB, IF, IHC, IP |
| MOB-3273z | Mouse Anti-CPS1 Recombinant Antibody (clone 29D7) | Human | Mouse IgG1, κ | WB, IP, IF, IHC, ELISA |
| MOR-0785 | Hi-Affi™ Rabbit Anti-CPS1 Recombinant Antibody (clone DS785AB) | Human | Rabbit IgG | WB, IHC, ICC, IP |
Customer Reviews

Mouse Anti-CPS1 Recombinant Antibody (clone 29D7)
rAb Production
In our work at Creative Biolabs to speed development of new therapeutics for metabolic diseases, we leverage the most advanced production technologies. Our anti-CPS1 recombinant antibodies are expressed in systems optimized to ensure the highest possible affinity and specificity for this large mitochondrial protein.
Featured Anti-CPS1 Recombinant Antibody Production Platforms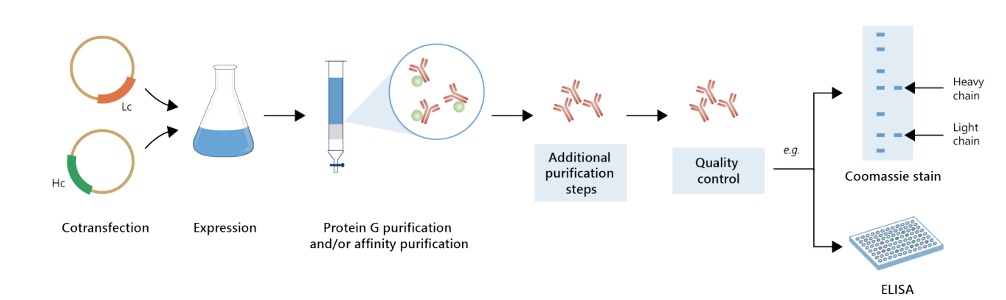
Fig.1 Milligram-scale anti-CPS1 recombinant antibody production.
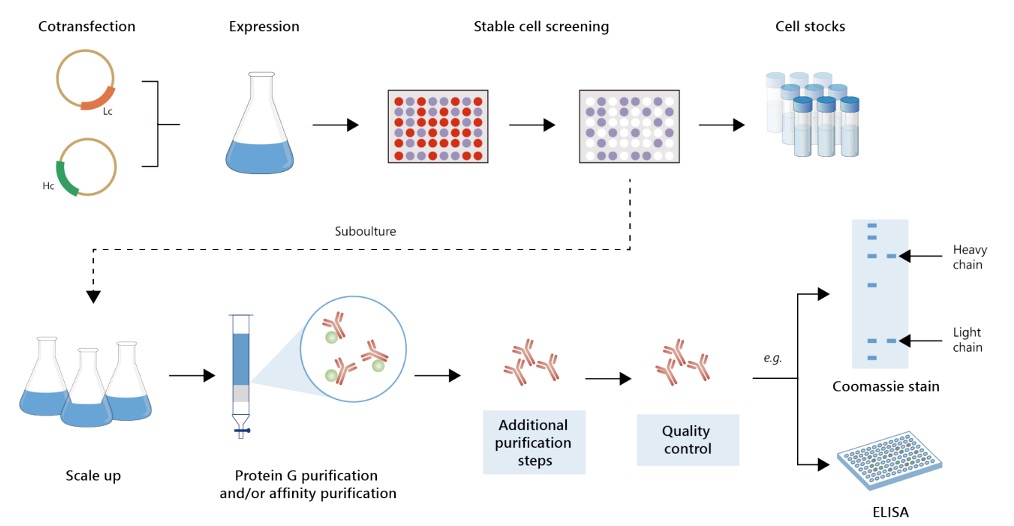 Fig.2 Gram-scale anti-CPS1 recombinant antibody production.
Fig.2 Gram-scale anti-CPS1 recombinant antibody production.
rAb Modalities
At Creative Biolabs, we are committed to giving researchers the flexible and innovative tools they need. Our anti-CPS1 recombinant antibodies are available in modalities optimized for the unique needs of diagnostic labs as well as the needs of researchers developing next-generation therapeutics.
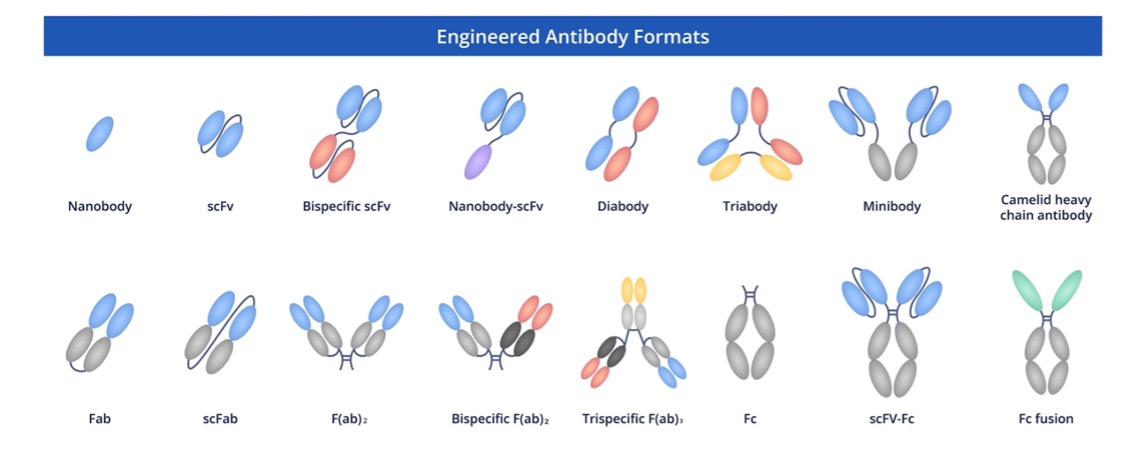 Fig.3 Full-length anti-CPS1 recombinant antibody production and modalities.
Fig.3 Full-length anti-CPS1 recombinant antibody production and modalities.
Accelerate your work in the diagnosis and treatment of urea cycle disorders with Creative Biolabs' elite, anti-CPS1 recombinant antibodies. Our entire portfolio is defined by our commitment to high specificity and stringent validation so that you are provided with the ideal tools for both diagnostics and therapeutic development. Trust our experts to support your critical work. Contact one of our specialists today.

