 Loading...
Loading...

CD36
Anti-CD36 Recombinant Antibody Products
- Mouse Anti-CD36 Recombinant Antibody (clone FA6-152) (NEUT-343CQ)
-
- Species Reactivity: Rat, Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: Block, FuncS, IHC-Fr, FC
- Mouse Anti-CD36 Recombinant Antibody (clone JC63.1) (NEUT-344CQ)
-
- Species Reactivity: Mouse, Rat, Human
- Type: Mouse IgA
- Application: FC, Block, IF
- Mouse Anti-CD36 Recombinant Antibody (clone SMϕ) (NEUT-346CQ)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgM, κ
- Application: FC, IHC-Fr, IHC-P, ICC, WB, Block, ELISA
- Mouse Anti-CD36 Recombinant Antibody (clone 185-1G2) (NEUT-347CQ)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG2a, κ
- Application: Block, IHC-Fr, FC, IF
- Mouse Anti-CD36 Recombinant Antibody (clone CBL248) (NEUT-348CQ)
-
- Species Reactivity: Rat
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: ELISA, IP, FC, IHC, Neut
Can't find the products you're looking for? Try to filter in the left sidebar.Filter By Tag
Our customer service representatives are available 24 hours a day, from Monday to Sunday. Contact Us
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.
Cancer-related genes, CD markers, Disease related genes, Human disease related genes, Metabolic proteins, Plasma proteins, Potential drug targets, Transporters
Membrane
Cell type enhanced (Adipocytes, Hofbauer cells, Sertoli cells, Cardiomyocytes)
Group enriched (classical monocyte, myeloid DC, intermediate monocyte)
Group enriched (ASC diff, HEL)
Interacts with THBS1 and THBS2; the interactions mediate the THBS antiangiogenic activity (PubMed:1371676). Upon interaction with a ligand, such as oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL) or amyloid-beta 42, rapidly forms a complex with TLR4 and TLR6; the complex is internalized and triggers an inflammatory signal. Through its C-terminus, interacts with PTK2, PXN and LYN, but not with SRC. LYN kinase activity is required for facilitating TLR4:TLR6 heterodimerization and signal initiation (PubMed:1371676, 20037584). Upon interaction with ligands such as diacylated lipopeptides, interacts with the TLR2:TLR6 heterodimer (PubMed:16880211). Interacts with CD9, CD81, FCER1G, ITGB2 and/or ITGB2; forming a membrane heteromeric complex required for the internalization of CD36 and its ligands (By similarity). (Microbial infection) Binds to Plasmodium falciparum EMP1.
Receptor

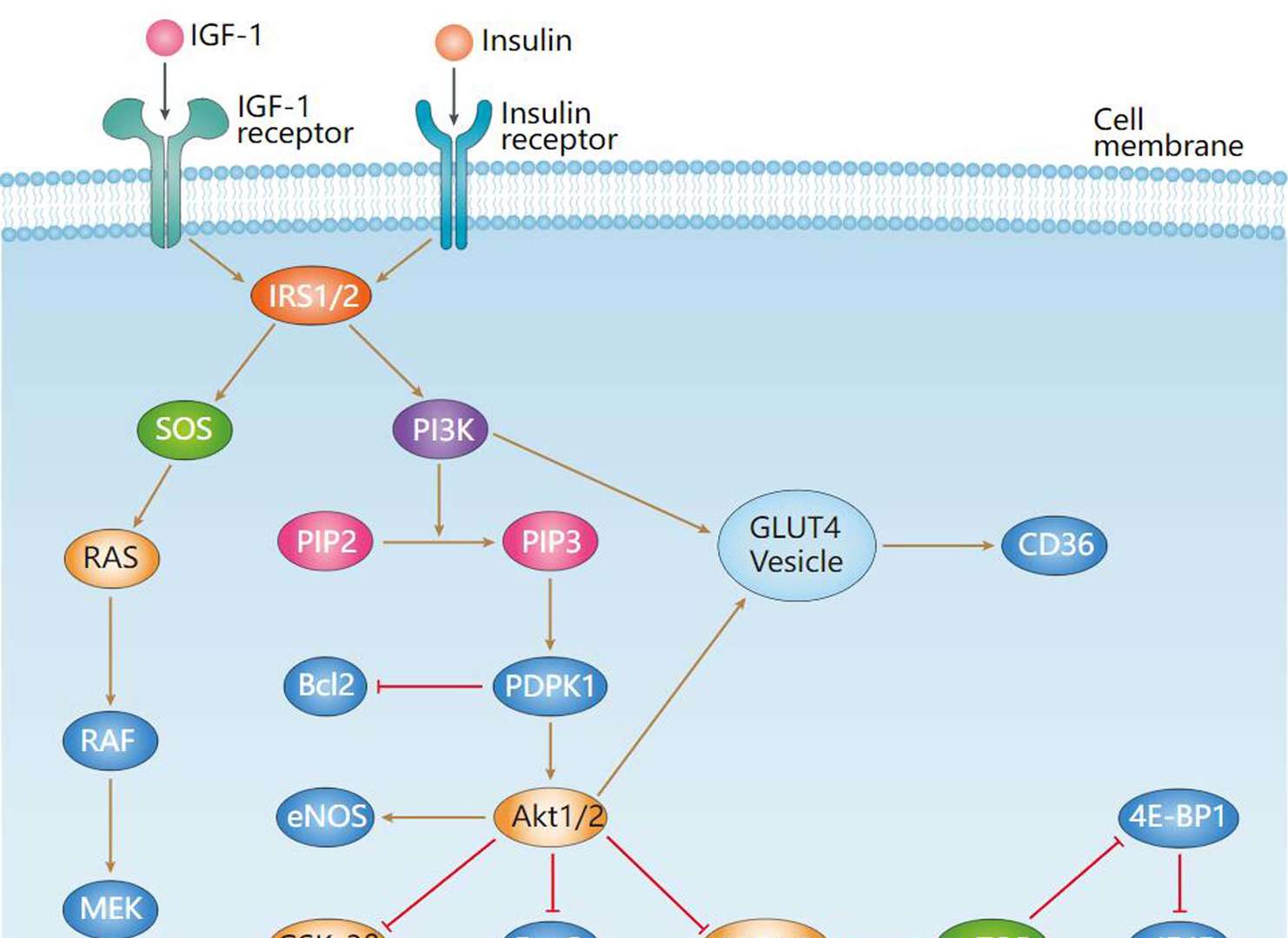 Insulin Signaling Pathway
Insulin Signaling Pathway