 Loading...
Loading...

ATP1A2
 Loading...
Loading...Anti-ATP1A2 Products
-
- Derivation: Phage display library screening
- Species Reactivity: Mouse, Rat, Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB
- Anti-ATP1A2 Immunohistochemistry Kit (VS-0525-XY605)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Target: ATP1A2
- Application: IHC
Can't find the products you're looking for? Try to filter in the left sidebar.Filter By Tag
Our customer service representatives are available 24 hours a day, from Monday to Sunday. Contact Us
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.
Background
Disease related genes, Enzymes, Human disease related genes, Metabolic proteins, Plasma proteins, Potential drug targets, Transporters
Membrane
Cell type enhanced (Astrocytes, Cardiomyocytes, Microglial cells, Oligodendrocyte precursor cells, Sertoli cells, Muller glia cells)
Not detected in immune cells
Cell line enhanced (AF22, HHSteC, RH-30, U-87 MG)
The sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase is composed of a catalytic alpha subunit, an auxiliary non-catalytic beta subunit and an additional regulatory subunit. Interacts with regulatory subunit FXYD1.
Translocase


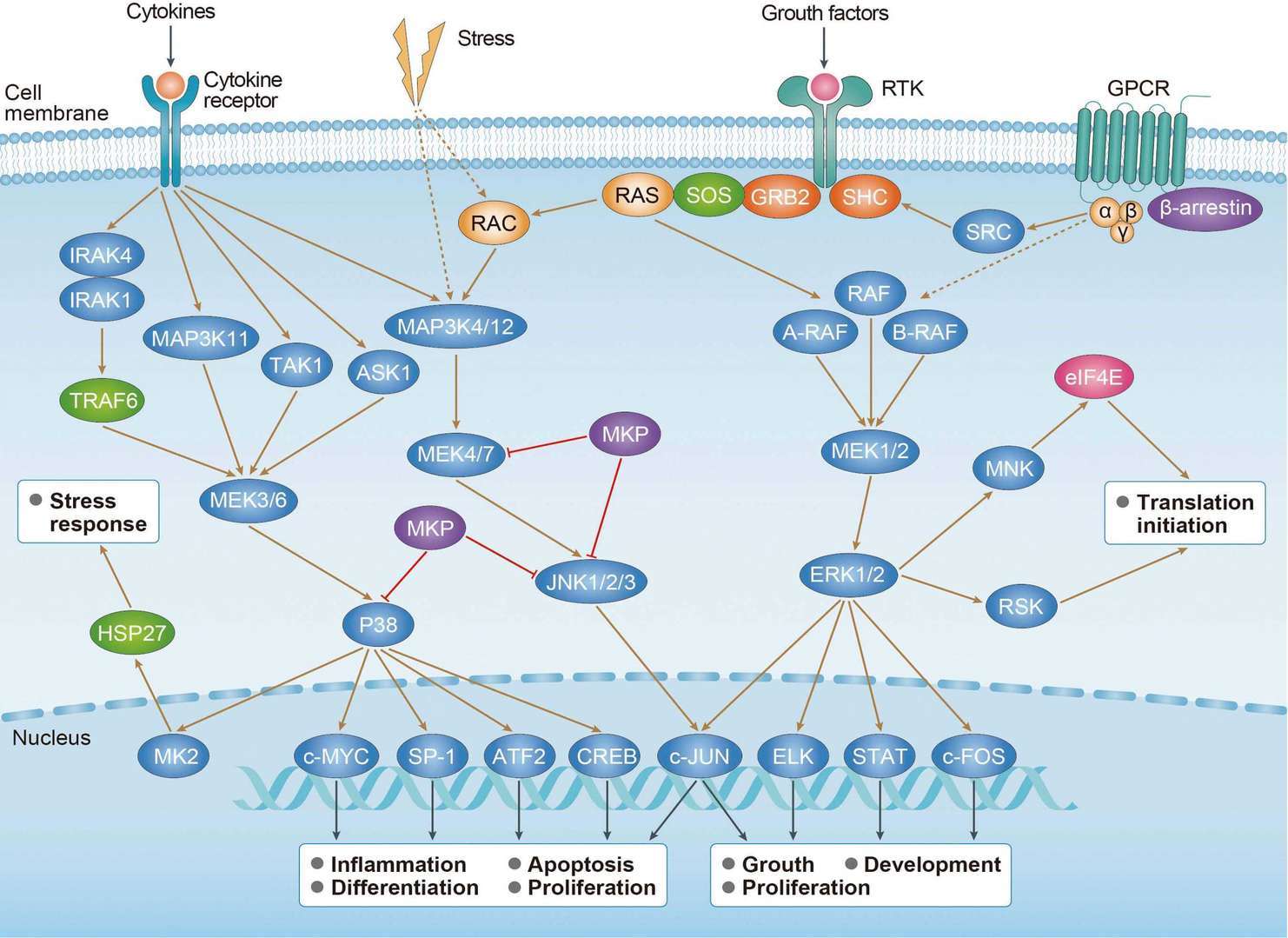 cAMP Signaling Pathway
cAMP Signaling Pathway
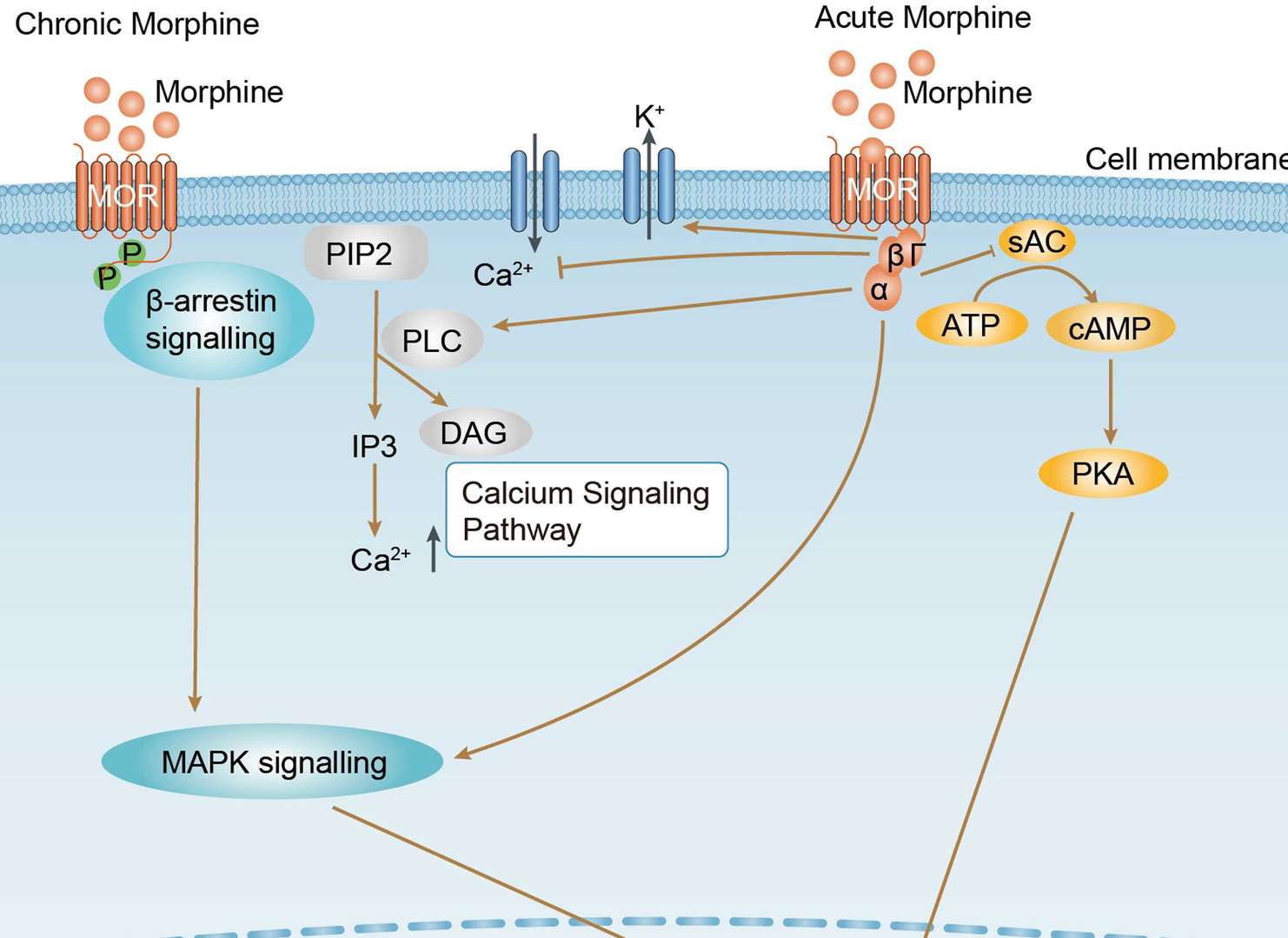 Morphine Addiction
Morphine Addiction

