+ Filter
 Loading...
Loading...

CD154
 Loading...
Loading...Anti-CD154 Products
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: FCM
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG2a
- Application: FCM
View More Products
Can't find the products you're looking for? Try to filter in the left sidebar.Filter By Tag
More Infomation
Our customer service representatives are available 24 hours a day, from Monday to Sunday. Contact Us
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.
Background
The cluster of differentiation (CD) system is commonly used as cell markers in immunophynotyping. Different kinds of cells in the immune system can be identified through the surface CD molecules which associating with the immune function of the cell. There are more than 320 CD unique clusters and subclusters have been identified. Some of the CD molecules serve as receptors or ligands important to the cell through initiating a signal cascade which then alter the behavior of the cell. Some CD proteins do not take part in cell signal process but have other functions such as cell adhesion. CD154, also known as CD40 ligand or CD40L, is a member of the TNF superfamily. While CD154 was originally found on T cell surface, its expression has since been found on a wide variety of cells, including platelets, mast cells, macrophages and NK cells. CD154s ability is achieved through binding to the CD40 on antigen- presenting cells (APC). In the macrophage cells, the primary signal for activation is IFN-γ from Th1 type CD4 T cells. The secondary signal is CD40L on the T cell, which interacting with the CD40 molecules, helping increase the level of activation.


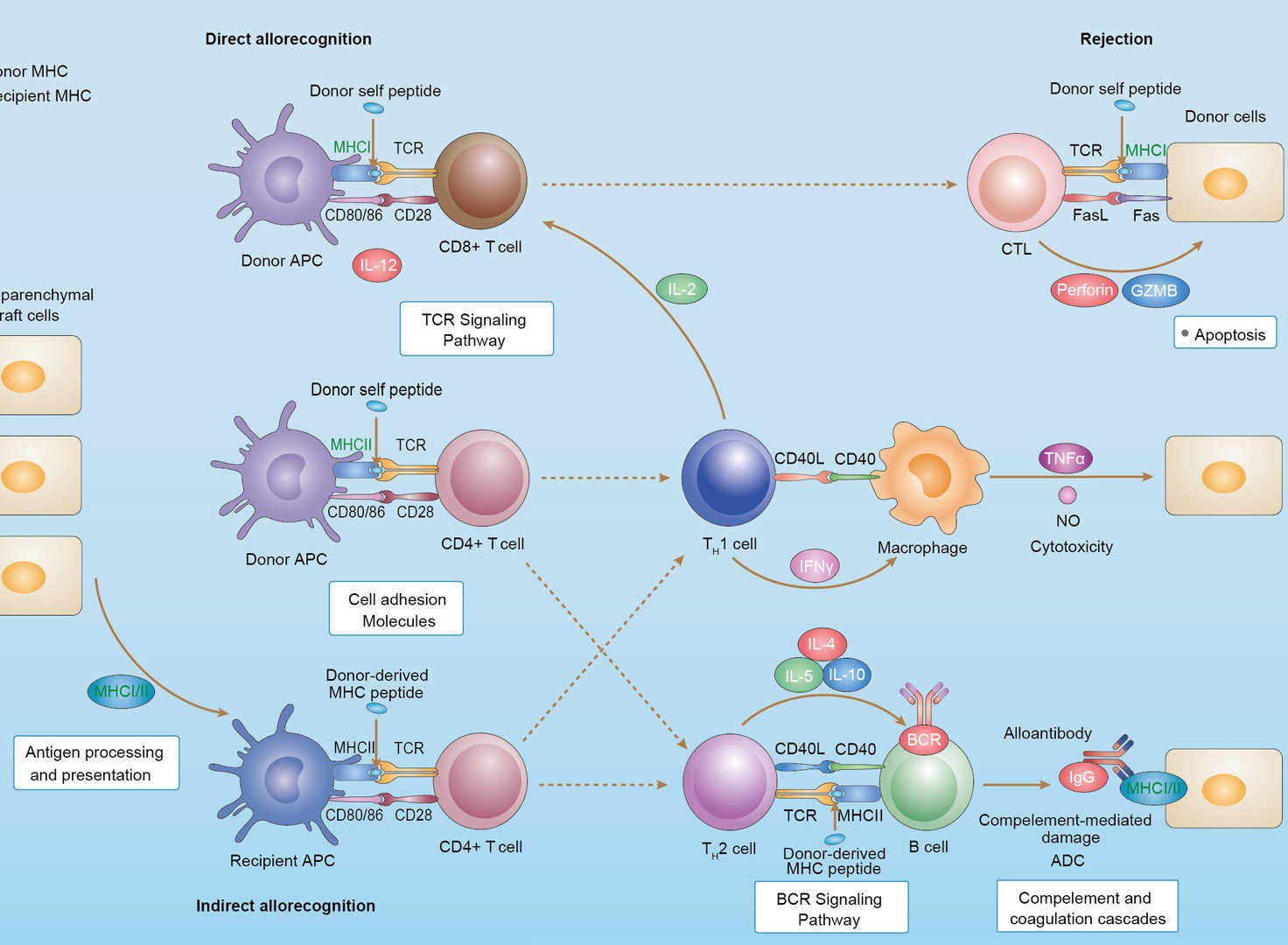 Allograft Rejection
Allograft Rejection
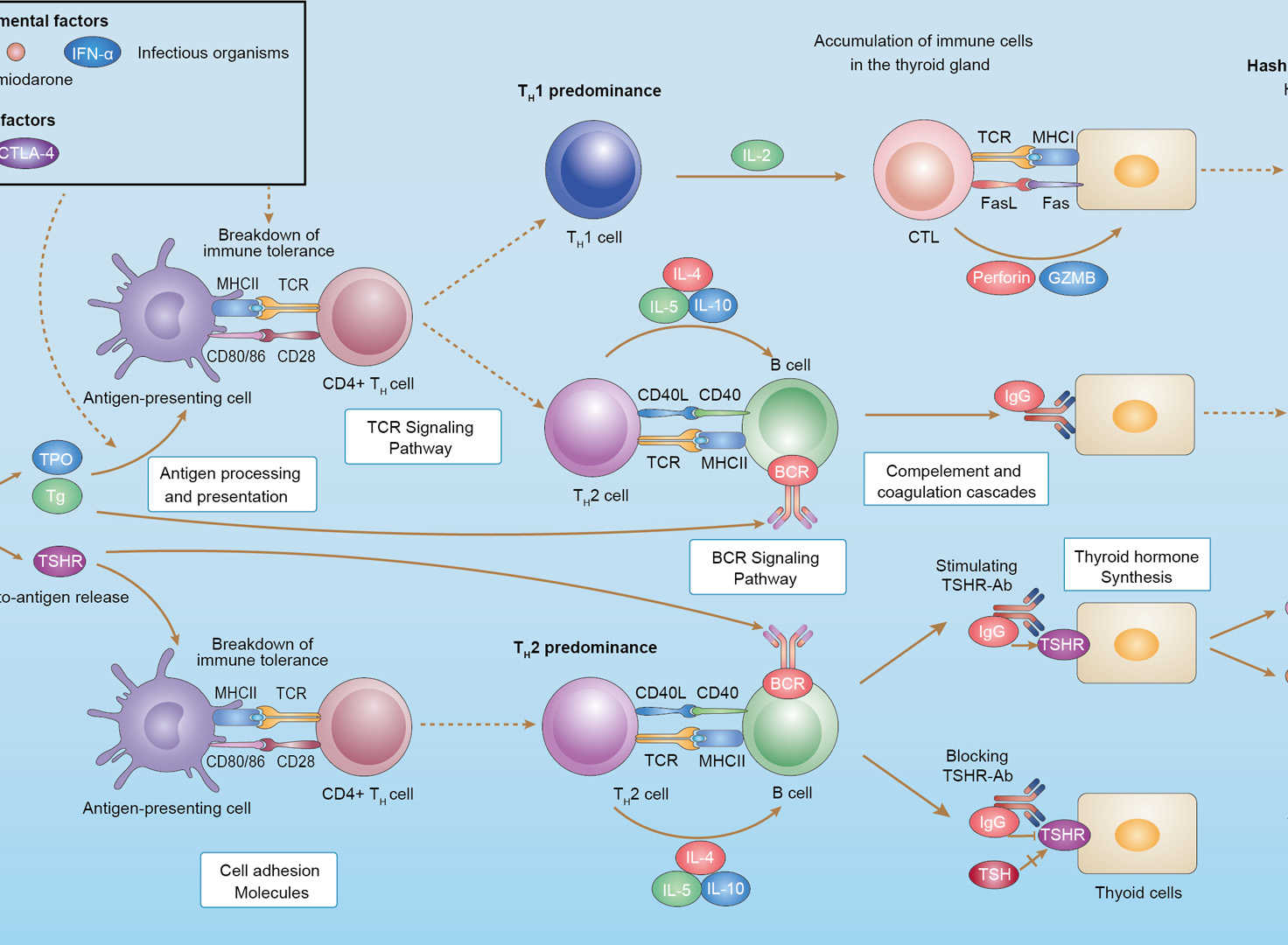 Autoimmune Thyroid Disease
Autoimmune Thyroid Disease

