J-Chain Dependent IgA Dimerization Service
Introduction: The Pivotal Role of the J-Chain in Polymeric Immunoglobulin Function
IgA exists in both monomeric and polymeric forms, its efficacy in mucosal immunity is largely contingent upon its dimerization. The significance of J-chain-mediated dimerization extends beyond mere structural assembly. Dimeric IgA is the primary form recognized by the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor (pIgR) expressed on epithelial cells. This recognition is fundamental for the efficient transcytosis of IgA across mucosal barriers, such as the intestinal and respiratory epithelia, into the lumen. Without the J-chain, IgA predominantly exists as a monomer, a form that exhibits significantly reduced binding affinity for pIgR and is consequently less effective in providing localized mucosal protection. Structural analyses, including cryo-electron microscopy (CryoEM) studies, have revealed the intricate architecture of dIgA, where the two IgA copies, along with the J-chain, form a bent and tilted arrangement, further emphasizing the J-chain's role in shaping the functional conformation of the antibody. This unique conformation influences the positioning of antigen-binding fragments (Fabs) while preserving access to critical receptor-binding sites. At Creative Biolabs, our deep understanding of these intricate molecular mechanisms, honed over two decades of specialized biological research, positions us uniquely to offer advanced solutions for J-chain dependent IgA dimerization.
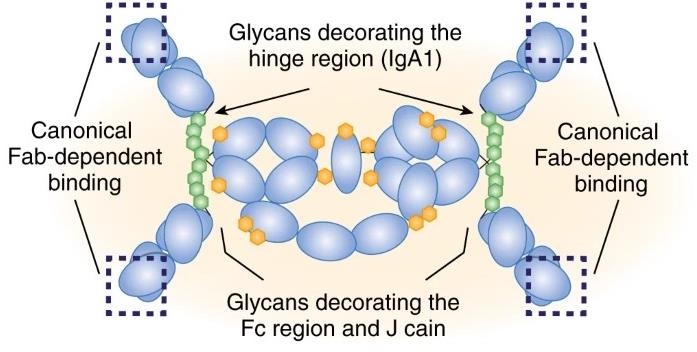 Fig.1 Schematic of secretory IgA interacts with the microbiota.1
Fig.1 Schematic of secretory IgA interacts with the microbiota.1
J-Chain Dependent IgA Dimerization Service at Creative Biolabs
Creative Biolabs is proud to introduce its specialized J-Chain Dependent IgA Dimerization Service, designed to meet the rigorous demands of researchers and therapeutic developers working on mucosal immunity, infectious diseases, and autoimmune conditions. Leveraging our extensive expertise and cutting-edge methodologies, we provide precisely engineered dimeric IgA constructs. This service is underpinned by Creative Biolabs' commitment to scientific excellence, ensuring that the IgA constructs delivered are functionally robust and structurally accurate, mimicking the native dimeric form essential for pIgR binding and transepithelial transport.
The generation of stable and functional dimeric IgA is a complex process requiring meticulous control over protein expression, purification, and assembly conditions. Our service directly addresses this challenge by providing a reliable platform for producing J-chain-incorporated dIgA, thereby enabling researchers to bypass the inherent difficulties associated with generating these complex polymeric antibodies. This capability is paramount for studies investigating IgA's role in immune exclusion, neutralization of toxins and pathogens, and its interaction with the gut microbiota.
Service Content
The Creative Biolabs J-Chain Dependent IgA Dimerization Service encompasses a comprehensive workflow designed to deliver high-quality, functionally validated dimeric IgA. Our service content includes:
- Recombinant J-Chain Production: High-purity recombinant human or species-specific J-chain is produced using optimized expression systems. This ensures the availability of a critical component for efficient IgA dimerization. Our processes ensure the J-chain maintains its native conformation, crucial for its interaction with IgA heavy chains.
- IgA Monomer Preparation: We provide highly purified IgA monomers (e.g., IgA1, IgA2, or specific mutant variants) ready for dimerization. These monomers are rigorously characterized for purity and integrity, ensuring optimal starting material for the dimerization process.
- Optimized Dimerization Protocol: Utilizing proprietary protocols developed over 20 years of experience, Creative Biolabs facilitates the efficient and controlled assembly of IgA monomers with the J-chain. This involves precise control over buffer conditions, temperature, and incubation times to maximize the yield of stable dIgA.
- Purification of Dimeric IgA: Following the dimerization reaction, the dIgA complexes are purified to remove any unreacted monomers, J-chain, or aggregates. Our purification strategies ensure the isolation of homogeneous dimeric IgA suitable for downstream applications.
- Rigorous Quality Control and Characterization: Every batch of dimeric IgA produced through our service undergoes extensive quality control. This includes:
- Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC): To confirm the dimeric state and assess purity.
- SDS-PAGE (reducing and non-reducing): To verify J-chain incorporation and disulfide bond formation.
- Functional Assays (upon request): Including pIgR binding assays to confirm functional integrity and transcytosis potential, mimicking the in vivo transport mechanism across epithelial cells.
Our Advantages
Creative Biolabs' J-Chain Dependent IgA Dimerization Service is distinguished by several key advantages, reflecting our deep expertise and commitment to scientific rigor:
- Two Decades of Specialized Experience
- In-depth Structural Understanding
- Tailored Solutions
- Functional Validation
FAQs
Q1: Why is J-chain dependent IgA dimerization critical for mucosal immunity research?
A1: J-chain dependent IgA dimerization is crucial because only dimeric IgA (dIgA) is efficiently transported across epithelial barriers into mucosal secretions via the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor (pIgR). This transport mechanism is essential for dIgA to perform its primary function of immune exclusion, neutralizing pathogens and toxins at mucosal surfaces, and maintaining gut homeostasis. Without the J-chain, IgA largely remains monomeric, which is significantly less effective in mucosal protection.
Q2: What are the primary applications of Creative Biolabs' J-Chain Dependent IgA Dimerization Service?
A2: Our service supports a wide range of applications, including:
- Vaccine Development: Designing and testing mucosal vaccines that elicit effective dimeric IgA responses.
- Infectious Disease Research: Studying the mechanisms by which dIgA neutralizes specific pathogens at mucosal sites.
- Autoimmune Disease Research: Investigating the role of IgA in autoimmune conditions affecting mucosal tissues.
- Gut Microbiome Studies: Analyzing the interaction between dIgA and commensal bacteria, and its role in maintaining gut barrier function.
- Therapeutic Antibody Development: Developing novel therapeutic antibodies that leverage the unique properties of dimeric IgA for targeted delivery to mucosal sites.
Q3: How does Creative Biolabs ensure the quality and functional integrity of the dimeric IgA?
A3: Creative Biolabs employs a multi-faceted quality control approach. We perform comprehensive structural characterization using techniques such as Size Exclusion Chromatography (SEC) and SDS-PAGE to confirm the dimeric state and J-chain incorporation. For functional integrity, we offer optional pIgR binding assays to validate the biological activity and transcytosis potential of the dIgA, ensuring it meets the stringent requirements for in vivo relevance. Our two decades of experience allow us to anticipate and mitigate potential issues in the dimerization process.
Q4: Can Creative Biolabs produce dimeric IgA from different species or with specific modifications?
A4: Yes, Creative Biolabs offers customizable solutions. We can produce J-chain dependent dimeric IgA from various species and incorporate specific modifications to the IgA heavy chains or J-chain as required for your research.
Contact Us
For more information about Creative Biolabs' J-Chain Dependent IgA Dimerization Service or to discuss your specific project requirements, please contact our expert team. We are committed to supporting your research endeavors with high-quality, functionally validated dimeric IgA constructs.
Reference
- Pabst, Oliver, and Emma Slack. "IgA and the intestinal microbiota: the importance of being specific." Mucosal immunology vol. 13,1 (2020): 12-21. DOI: 10.1038/s41385-019-0227-4. Distributed under Open Access License CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

