CHO Cell-Free based Antibody Production and QC Service
The most popular mammalian system for the in vivo synthesis of therapeutic proteins is CHO cells. There is great promise for the economical and effective synthesis of a wide variety of structurally and functionally varied proteins using CHO-lysate-based cell-free systems. The CHO-lysate-based cell-free system includes translationally active microsomal structures generated from the ER and is created by mildly disrupting cultured CHO cells. Proteins may now be quickly and easily produced using CHO-lysate cell-free processes in the linked transcription–translation mode, which paves the way for practical high-throughput screening applications.
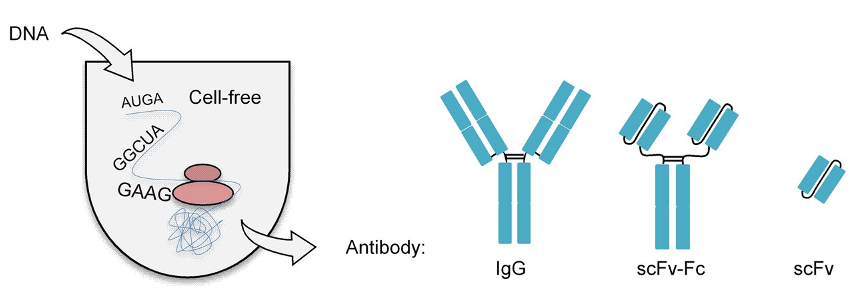 Fig.1. Schematic representation of the antibody production.1
Fig.1. Schematic representation of the antibody production.1
Recombinant Antibody Production in CHO Cell-Free Systems
One component of the CHO cell-free system is endogenous microsomal vesicles, which originate from the ER of the CHO cells used for lysate formation. By connecting antibody gene templates to the appropriate signal sequence, de novo generated proteins can be translocated into ER derived microsomal vesicles. There, they find ideal conditions for folding and assembly, simulating the conditions found in living cells for antibody folding and assembly. One polypeptide chain is used to assemble single-chain antibody fragments, which normally require the creation of no more than two intramolecular disulfide bridges. Full-length antibodies, on the other hand, are considerably more complex and need folding each of the twelve or more unique immunoglobulin domains in addition to the assembly of four distinct polypeptide chains through intermolecular disulfide bonds. DNA templates were linked to the honeybee melittin's ER-specific signal sequence, which has been demonstrated before to provide both effective translation initiation and protein transport into microsomal vesicles, in order to replicate in vivo antibody folding in the cell-free system.
Advantages of CHO Cell-Free Systems
- Well-characterized cell line that is frequently utilized to produce therapeutic in vivo proteins.
- Contain native microsomal structures
- Post-translational modifications
Applications of CHO Cell-Free Systems
Three distinct anti-SMAD2 antibody formats (single chain variable fragment (scFv), scFv-Fc, and IgG) were created in order to evaluate the CHO cell-free system. Circular DNA templates were used with small-scale batch-based processes to achieve protein synthesis reactions. It is possible to achieve total protein yields of 9–18 µg/mL by employing this quick high-throughput method.
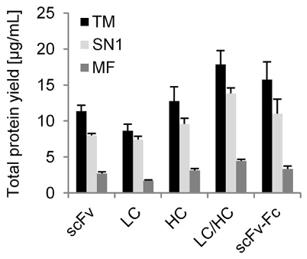 Fig.2. Diagram showing protein yields.1
Fig.2. Diagram showing protein yields.1
Creative Biolabs is one of the leading providers of cell-free antibody production services worldwide. We provide recombinant antibody production services in CHO and other mammalian cell-free systems. Please feel free to contact us for more details.
Reference
- Stech, M et al. “Cell-free synthesis of functional antibodies using a coupled in vitro transcription-translation system based on CHO cell lysates.” Scientific reports vol. 7,1 12030. 20 Sep. 2017, doi:10.1038/s41598-017-12364-w. Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

