+ Filter
 Loading...
Loading...

AKT1
 Loading...
Loading...Anti-AKT1 ProductsBackground
Anti-AKT1 Products
- AbPlus™ Anti-AKT1 Magnetic Beads (CBACN-016) (VS-0424-XY10)
-
- Target: AKT1
- Target Species: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
-
- Antibody Host: Mouse
- Antibody Reactivity: Human
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG2b
- Application: WB, ICC, IF, IHC-P, FC
- Anti-AKT1 Immunohistochemistry Kit (VS-0525-XY278)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Target: AKT1
- Application: IHC
- Anti-Mouse AKT1 Immunohistochemistry Kit (VS-0525-XY279)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Target: AKT1
- Application: IHC
- Anti-Zebrafish AKT1 Immunohistochemistry Kit (VS-0525-XY281)
-
- Species Reactivity: Zebrafish
- Target: AKT1
- Application: IHC
- Anti-Rat AKT1 Immunohistochemistry Kit (VS-0525-XY280)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Target: AKT1
- Application: IHC
View More Products
Can't find the products you're looking for? Try to filter in the left sidebar.Filter By Tag
More Infomation
Our customer service representatives are available 24 hours a day, from Monday to Sunday. Contact Us
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.
Background
The serine-threonine protein kinase encoded by the AKT1 gene is catalytically inactive in serum-starved primary and immortalized fibroblasts. AKT1 and the related AKT2 are activated by platelet-derived growth factor. The activation is rapid and specific, and it is abrogated by mutations in the pleckstrin homology domain of AKT1. It was shown that the activation occurs through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. In the developing nervous system AKT is a critical mediator of growth factor-induced neuronal survival. Survival factors can suppress apoptosis in a transcription-independent manner by activating the serine/threonine kinase AKT1, which then phosphorylates and inactivates components of the apoptotic machinery. Mutations in this gene have been associated with the Proteus syndrome. Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2011]


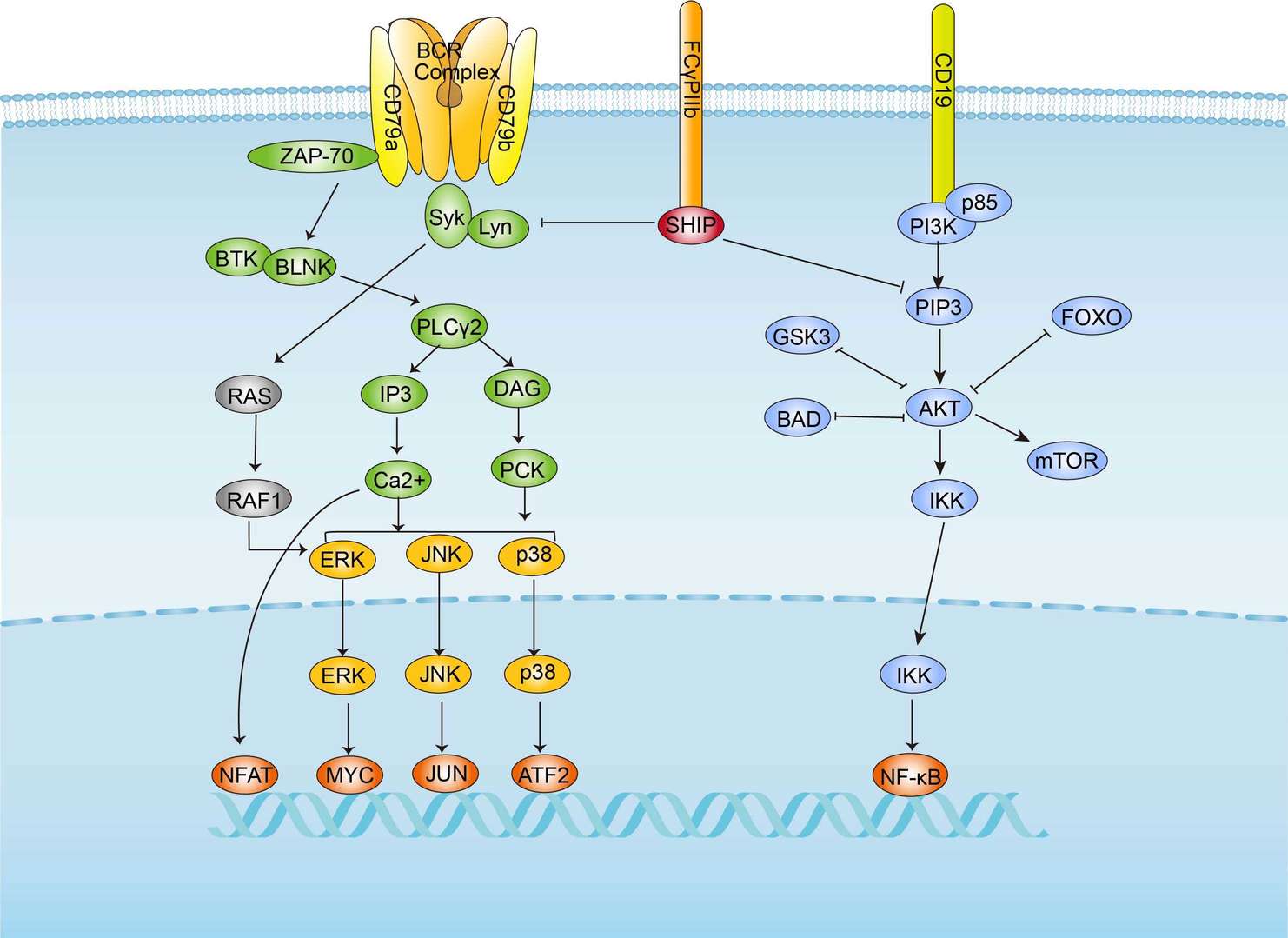 BCR Signaling Pathway
BCR Signaling Pathway
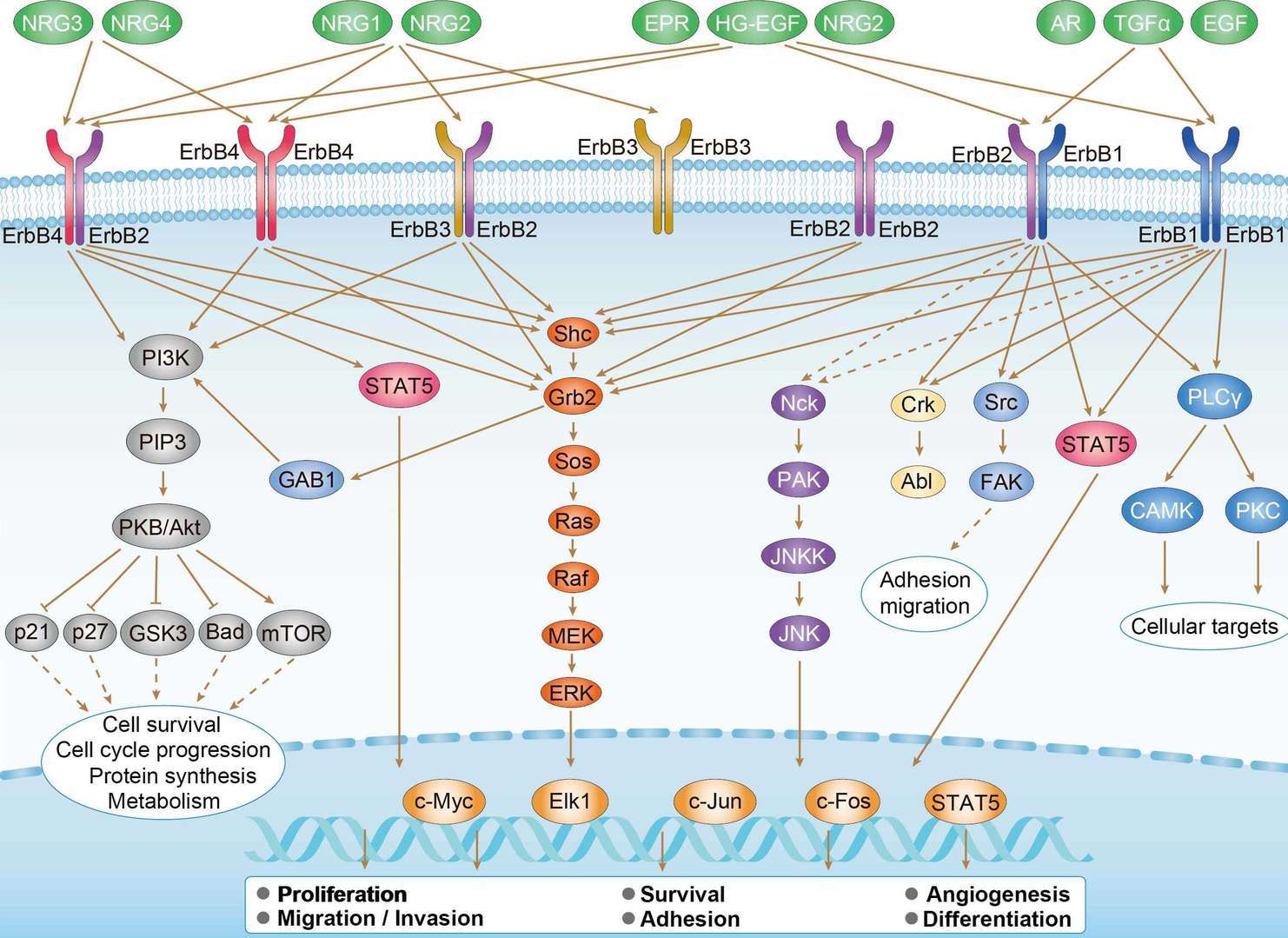 ErbB Signaling Pathway
ErbB Signaling Pathway
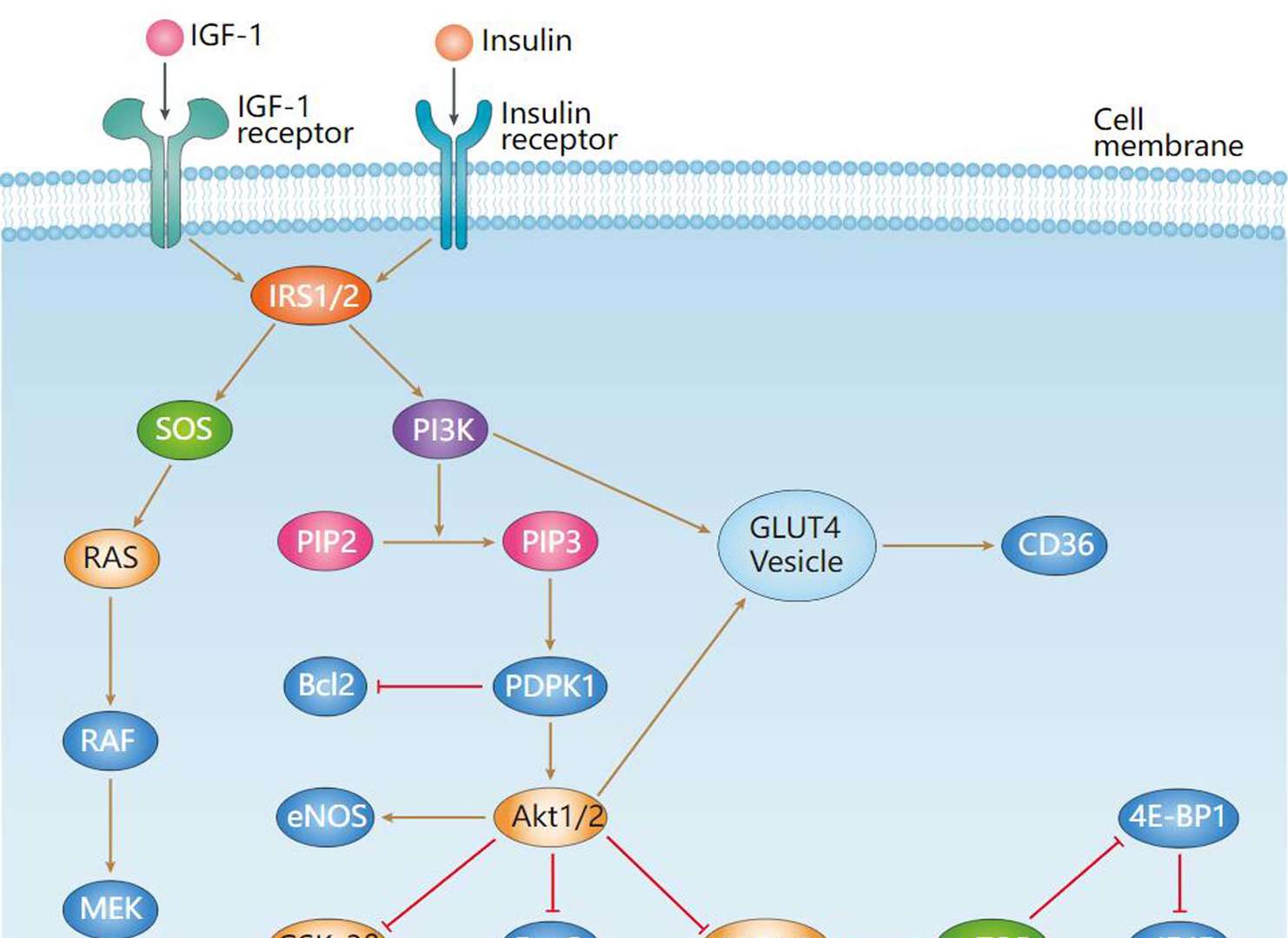 Insulin Signaling Pathway
Insulin Signaling Pathway
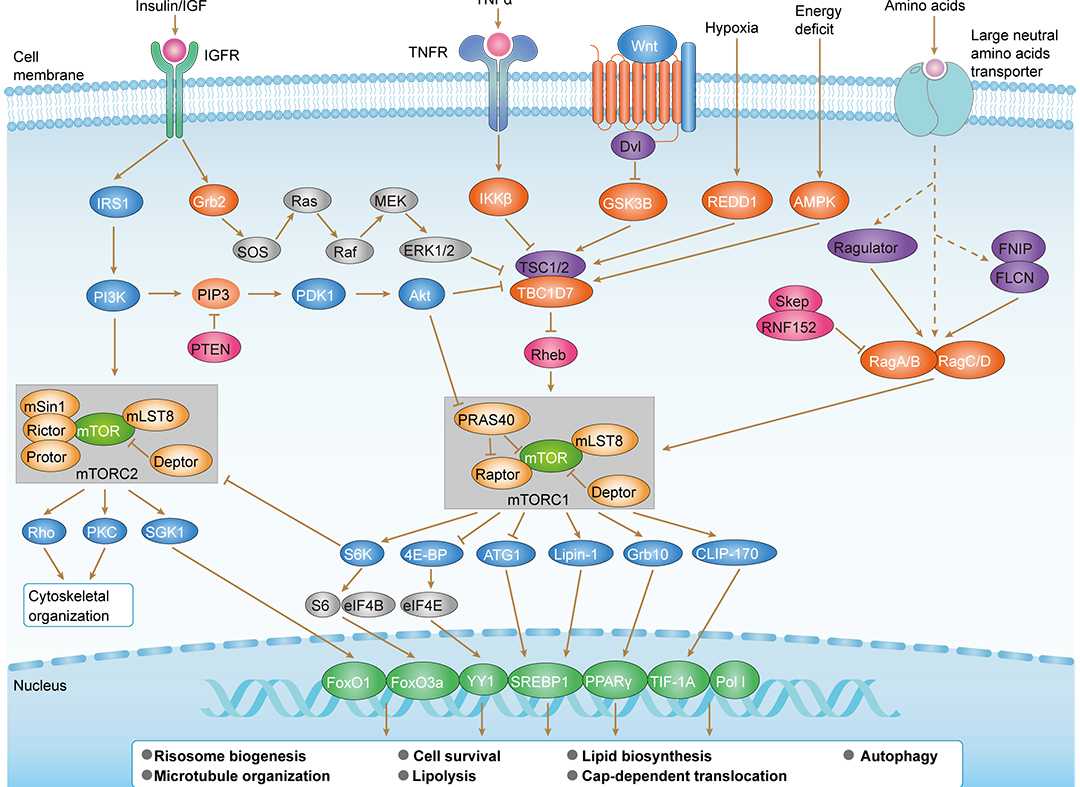 mTOR Signaling Pathway
mTOR Signaling Pathway
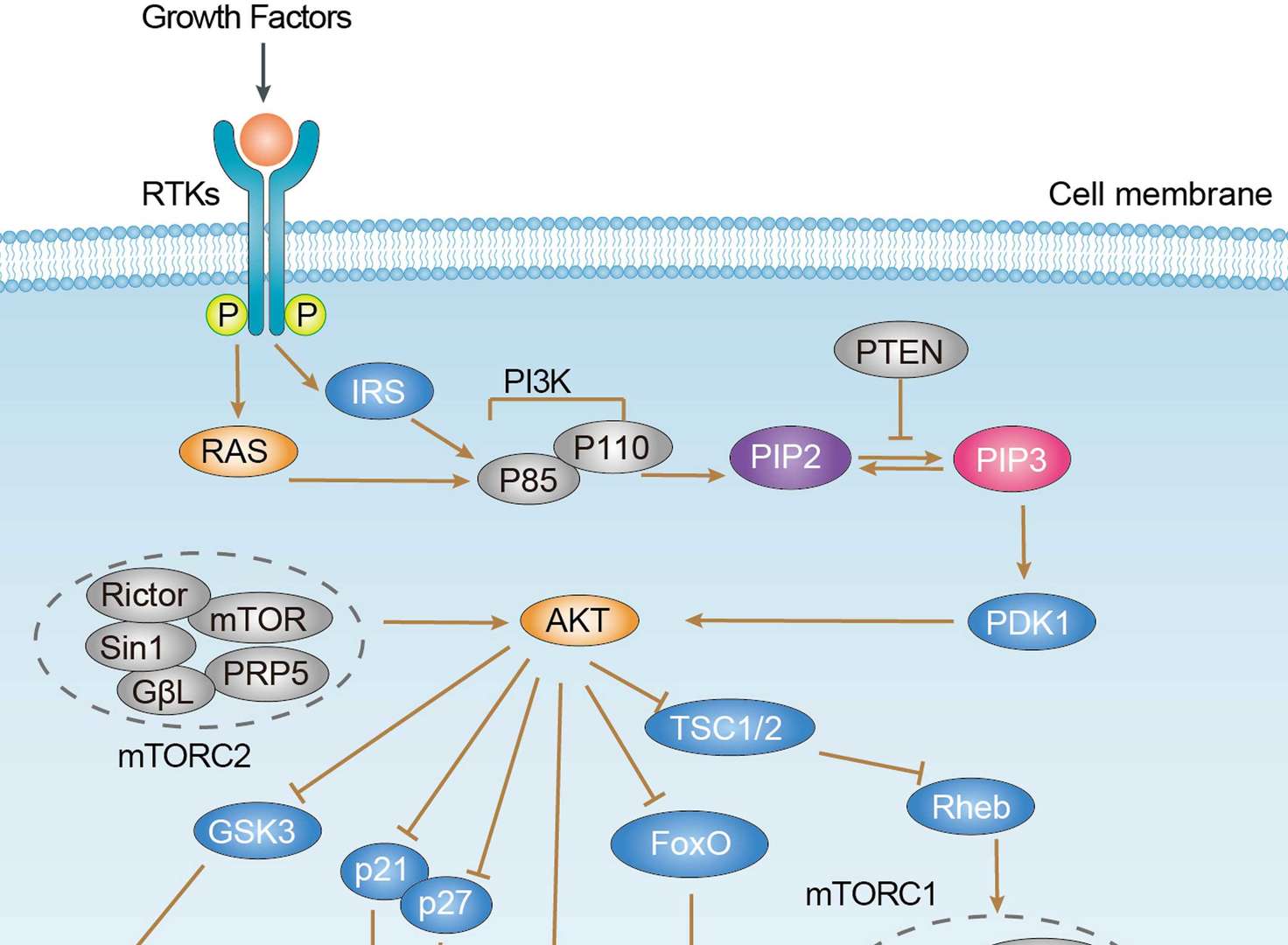 PI3K-Akt Signaling Pathway
PI3K-Akt Signaling Pathway
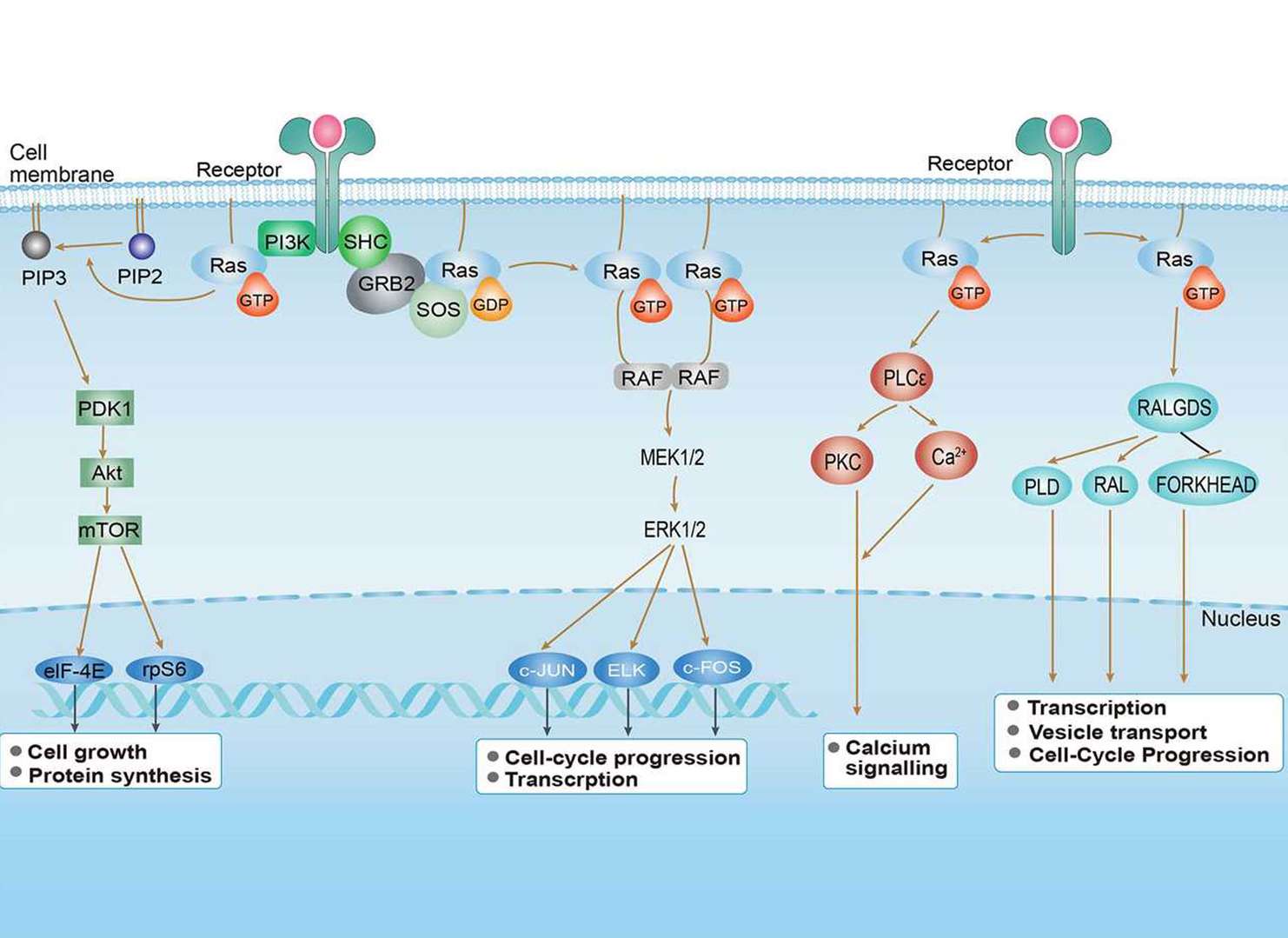 Ras Signaling Pathway
Ras Signaling Pathway
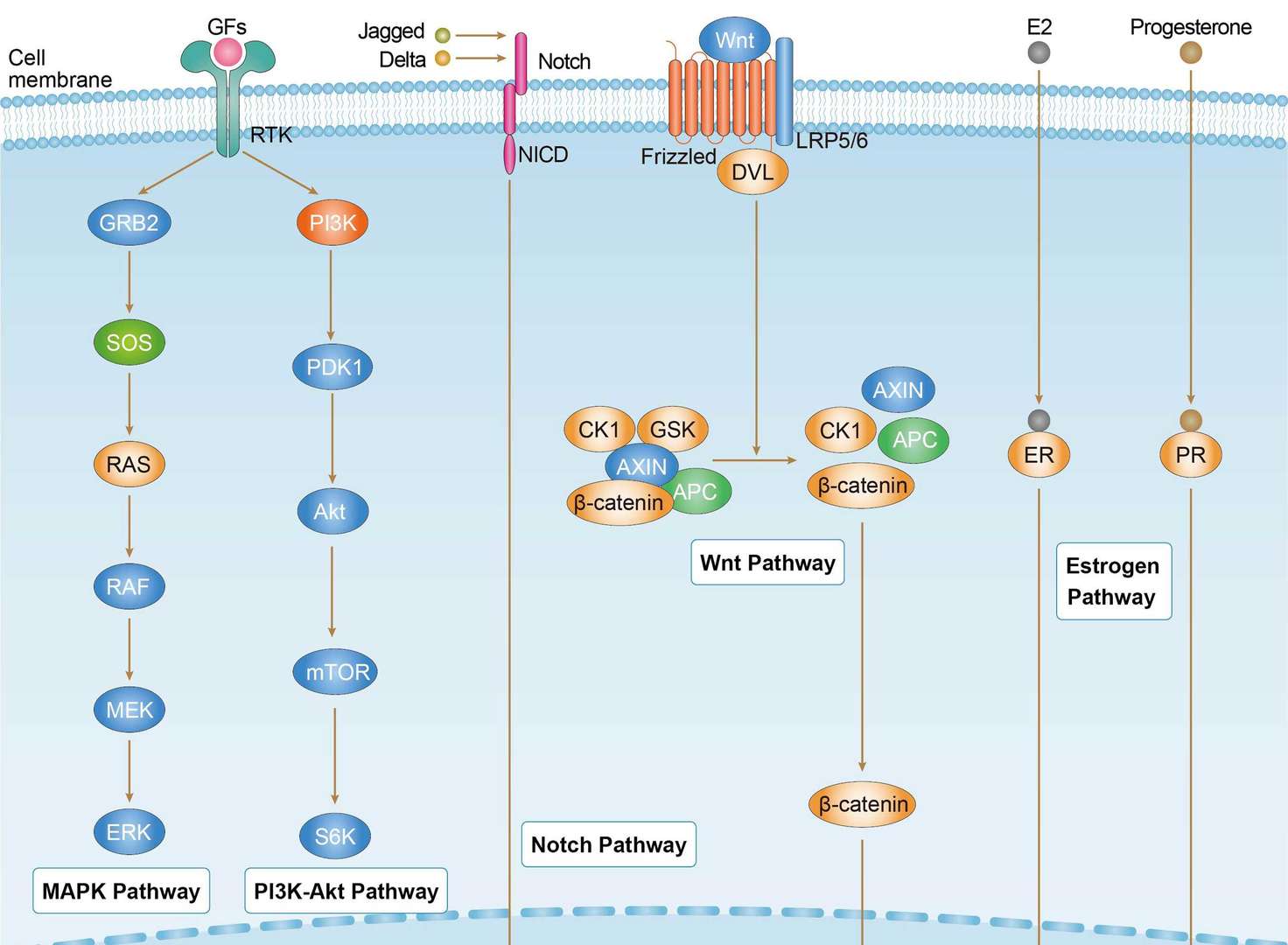 Breast Cancer
Breast Cancer
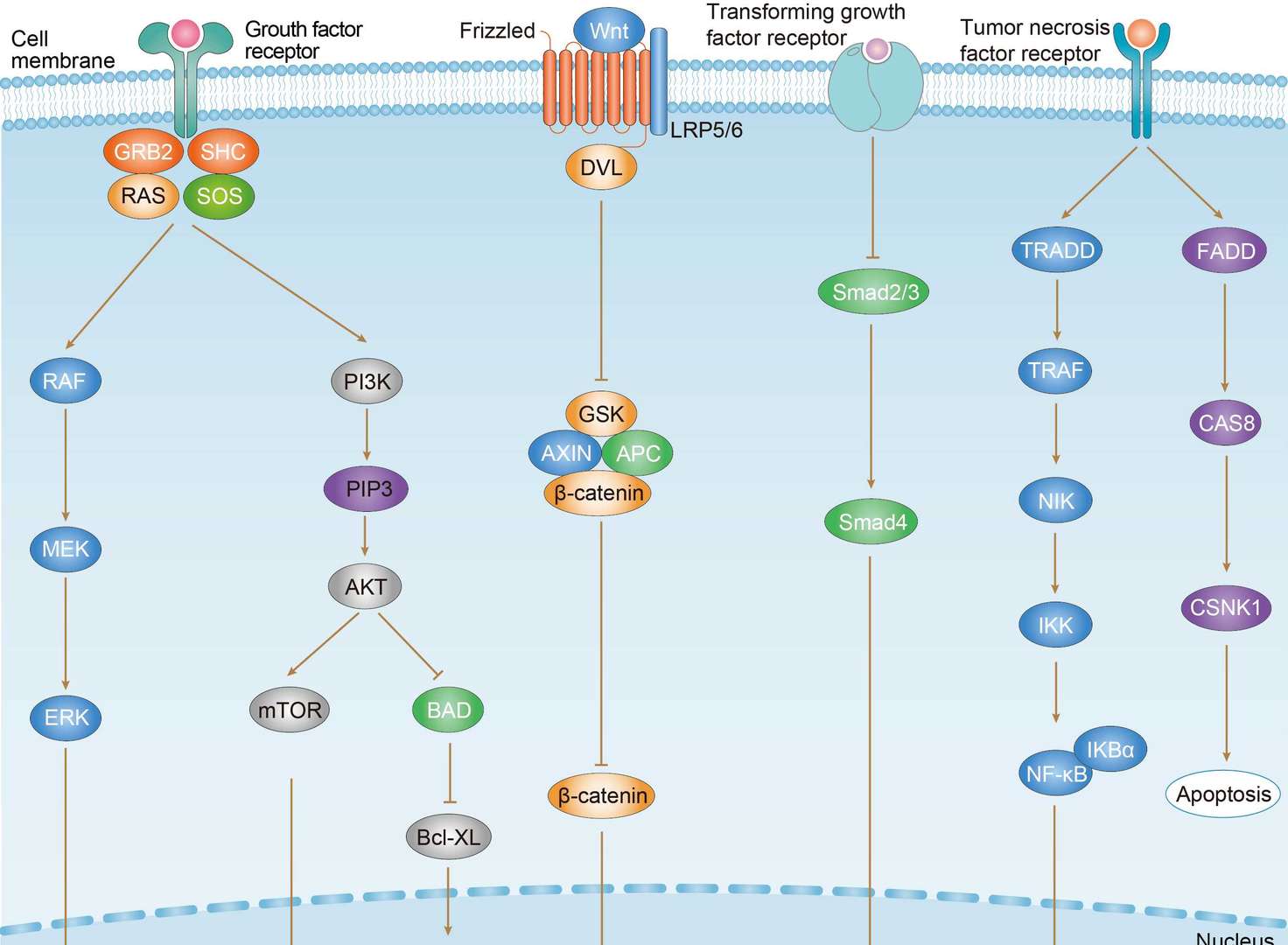 Colorectal Cancer
Colorectal Cancer
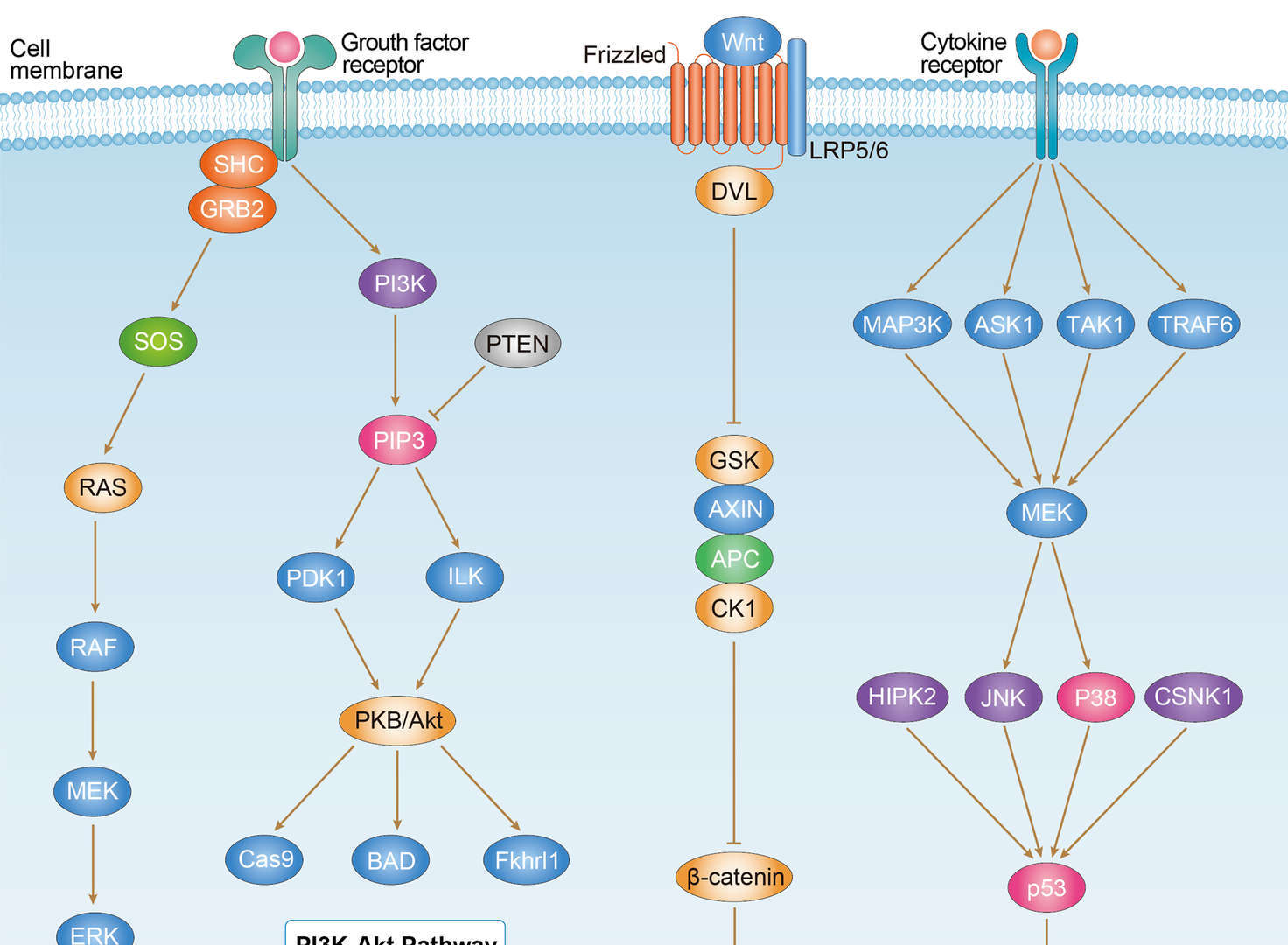 Endometrial Cancer
Endometrial Cancer
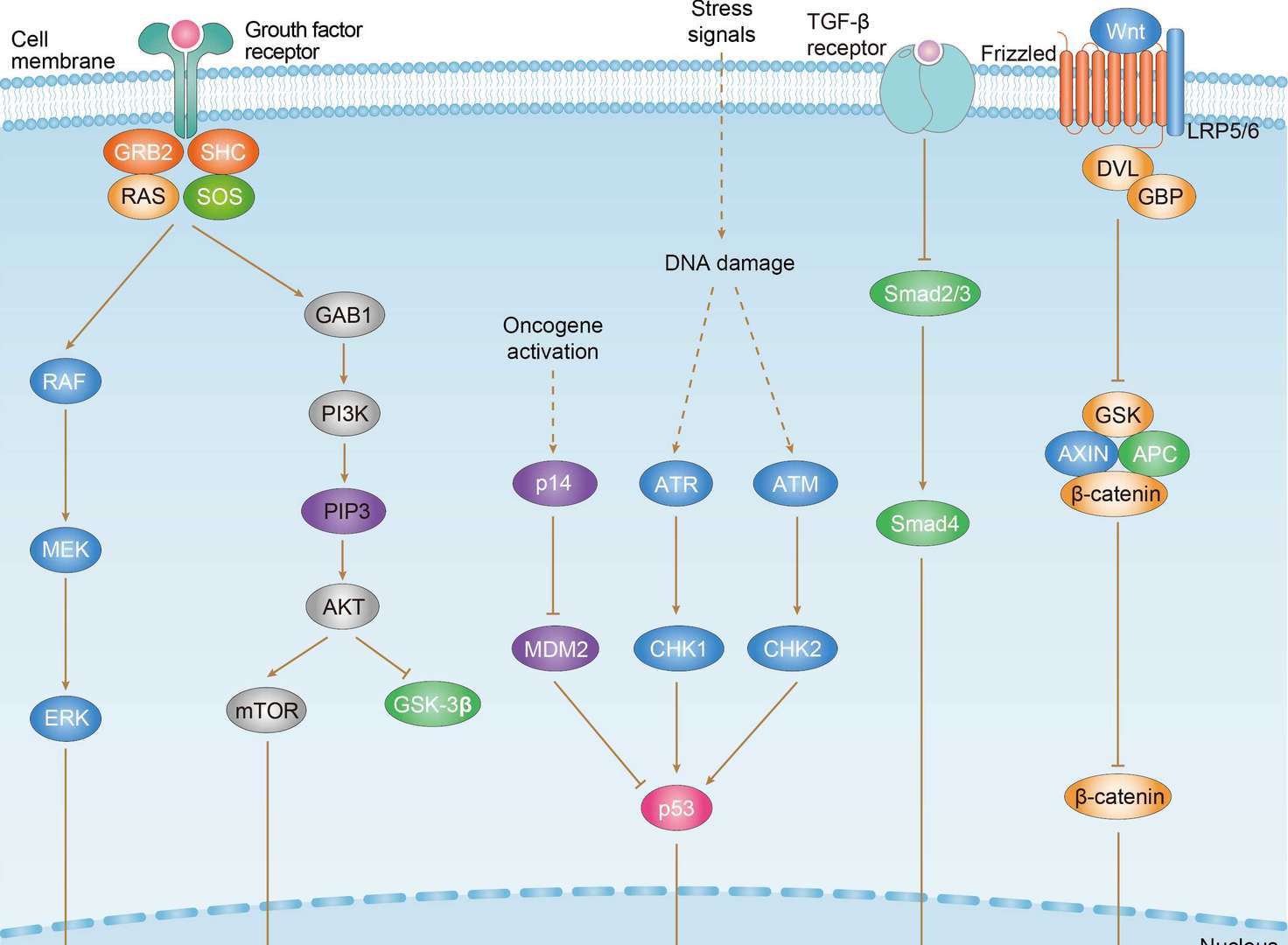 Gastric Cancer
Gastric Cancer
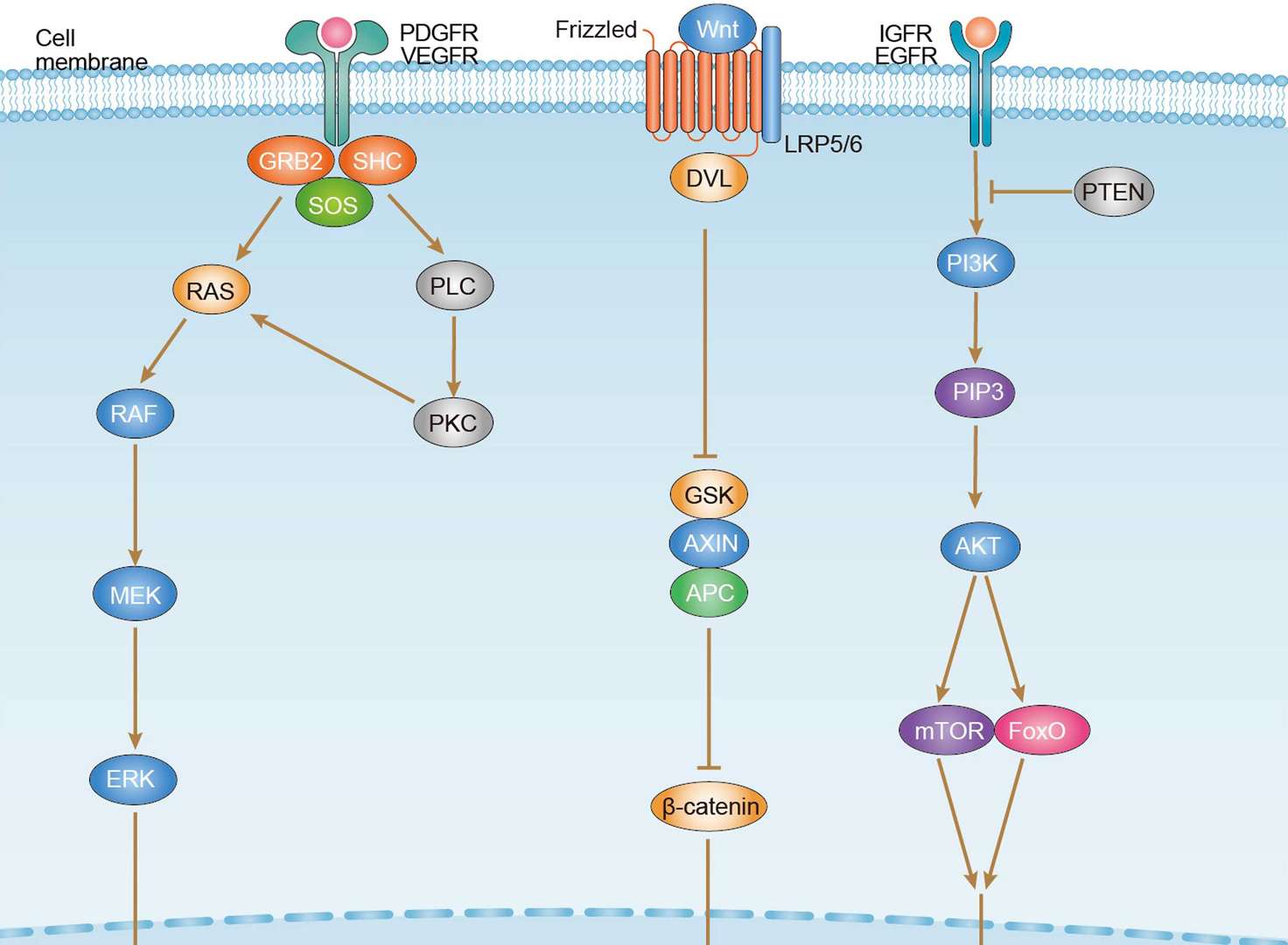 Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Hepatocellular Carcinoma
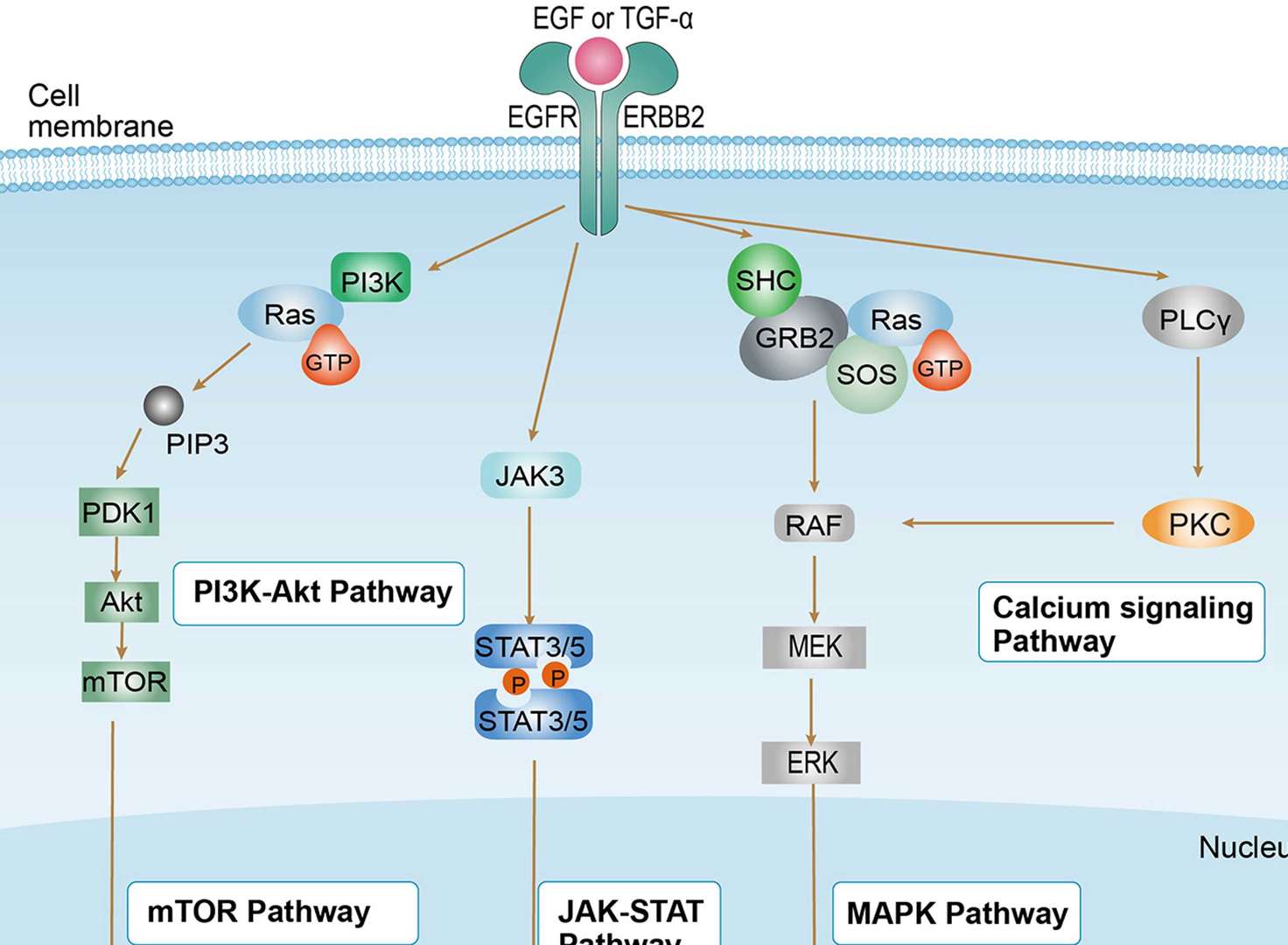 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
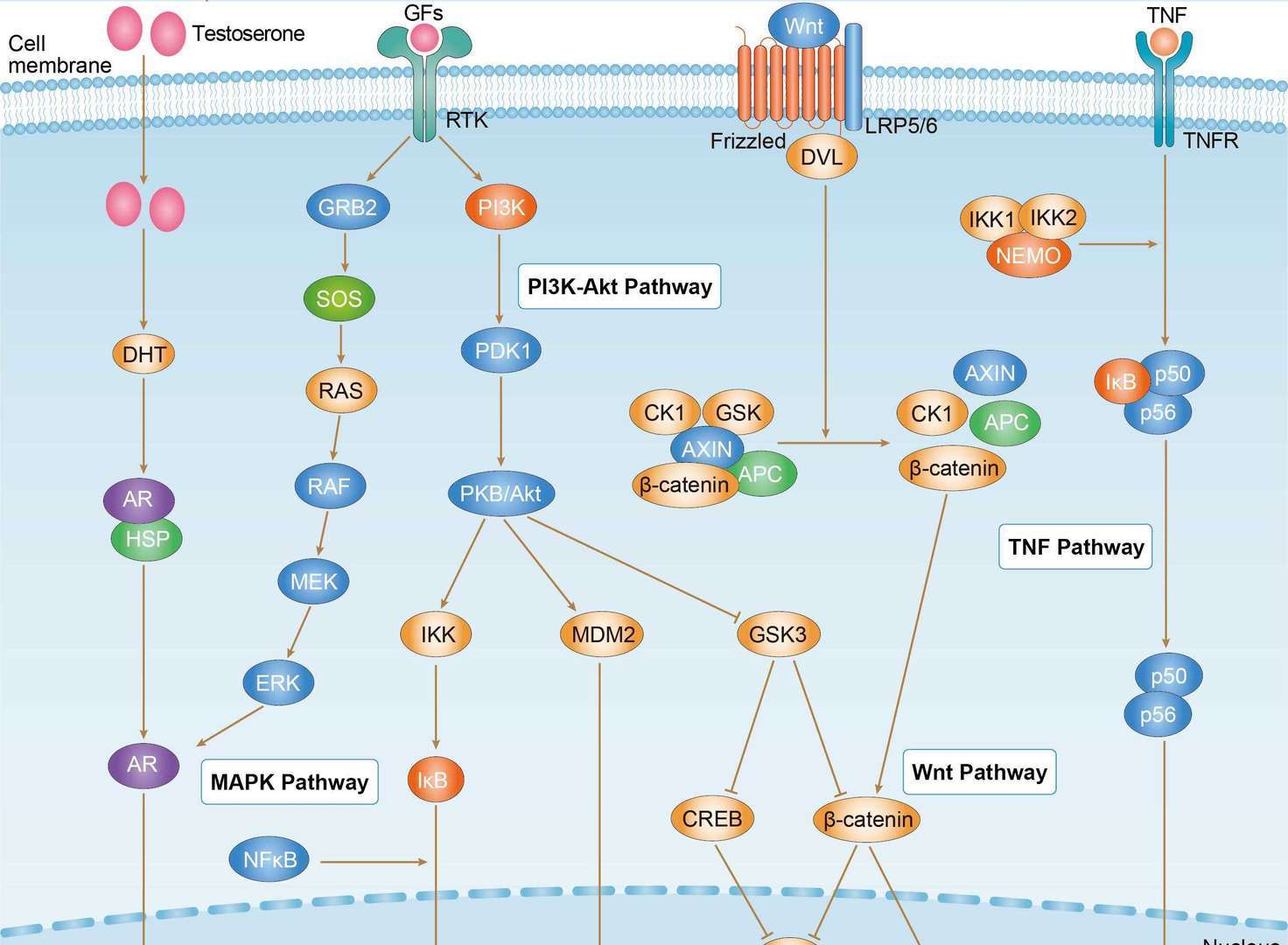 Prostate Cancer
Prostate Cancer
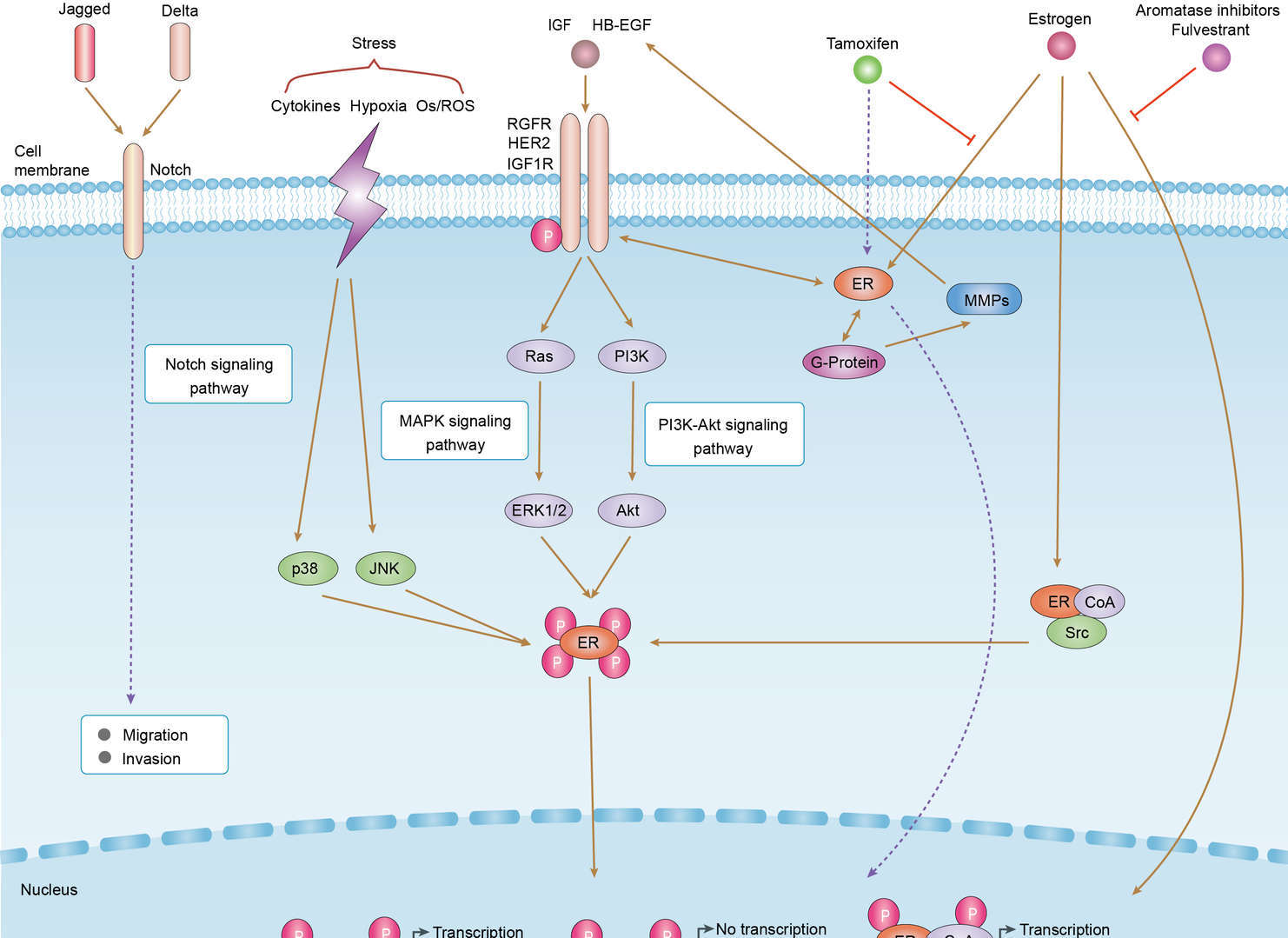 Endocrine Resistance
Endocrine Resistance