BCR Signal Pathway
About BCR Pathway
The B cell antigen receptor (BCR) signal pathway activation begins at the recognition and binding of membrane immunoglobulin (mIg) molecules to antigens. BCR complex is composed by mIg and associated Igα/Igβ heterodimers (α/β). When the mIg subunit binds to the associated antigens, the receptor aggregation and the tyrosine residues of the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM) of the intracellular segment of α/β heterodimers can be phosphorylated by Lyn kinases or other kinases belonging to the Src family, mediating the intracellular signal transmission. The downstream signal molecule syk is recruited and phosphorylated by BCR complex. Activated sky phosphorylates B cell linker (BLNK) proteins, resulting in varieties of downstream molecules phosphorylated including Bru-tontyrosine kinase (Btk). Subsequently, BLNK protein and Btk binds with phospholipase C-γ2 (PLC-γ2) and phosphorylates it. The activated PLC-γ2 hydrolyzed the cell membrane substrate PIP2 to produce the second messenger inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG). The binding of IP3 to the IP3 receptor on the endoplasmic reticulum can open the membrane Ca2+ channel and intracellular calcium reserve, increase the concentration of Ca2+ in the cytoplasm, activate calcineurin, resulting in the dephosphorylation and activation of transcription factor nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT). DAG can bind protein kinase Cβ (PKCβ) to the inner side of the cell membrane, and PKCβ is phosphorylated by DAG under the synergistic action of phosphatidyl serine. Subsequently, activated PKC phosphorylates the IKK complex and mediates the transmission of NF-κB pathway. Besides, activated PKCβ also induces the activation of ERK, JNK and p38 to mediate gene expression control. Interestingly, ERK regulated by not only PKCβ, but also by RAS. It has been reported that RasGRP3 (a guanine nucleotide–exchange factor) plays an important role in coupling the BCR to RAS activation. Once RasGRP3 activated, the downstream molecules as RAF1 and MEK1/MEK2 phosphorylates subsequently, which activate ERK1/ERK2. After BCR activation, CD19 and the B cell adaptor molecule for PI3K are phosphorylated by Lyn and Syk, resulting in the activation of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase (PI3K). PI3K catalyzes the formation of phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate (PIP3) from PIP2, recuiting and activating Akt. Activated Akt phosphorylates IKK complex and finally activates NF-κB, MAPK, NFAT and RAS signal pathways. It has been demonstrated that the BCR signaling plays an important role in the pathogenesis of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and B-cell lymphoma.
Related Pathways
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.


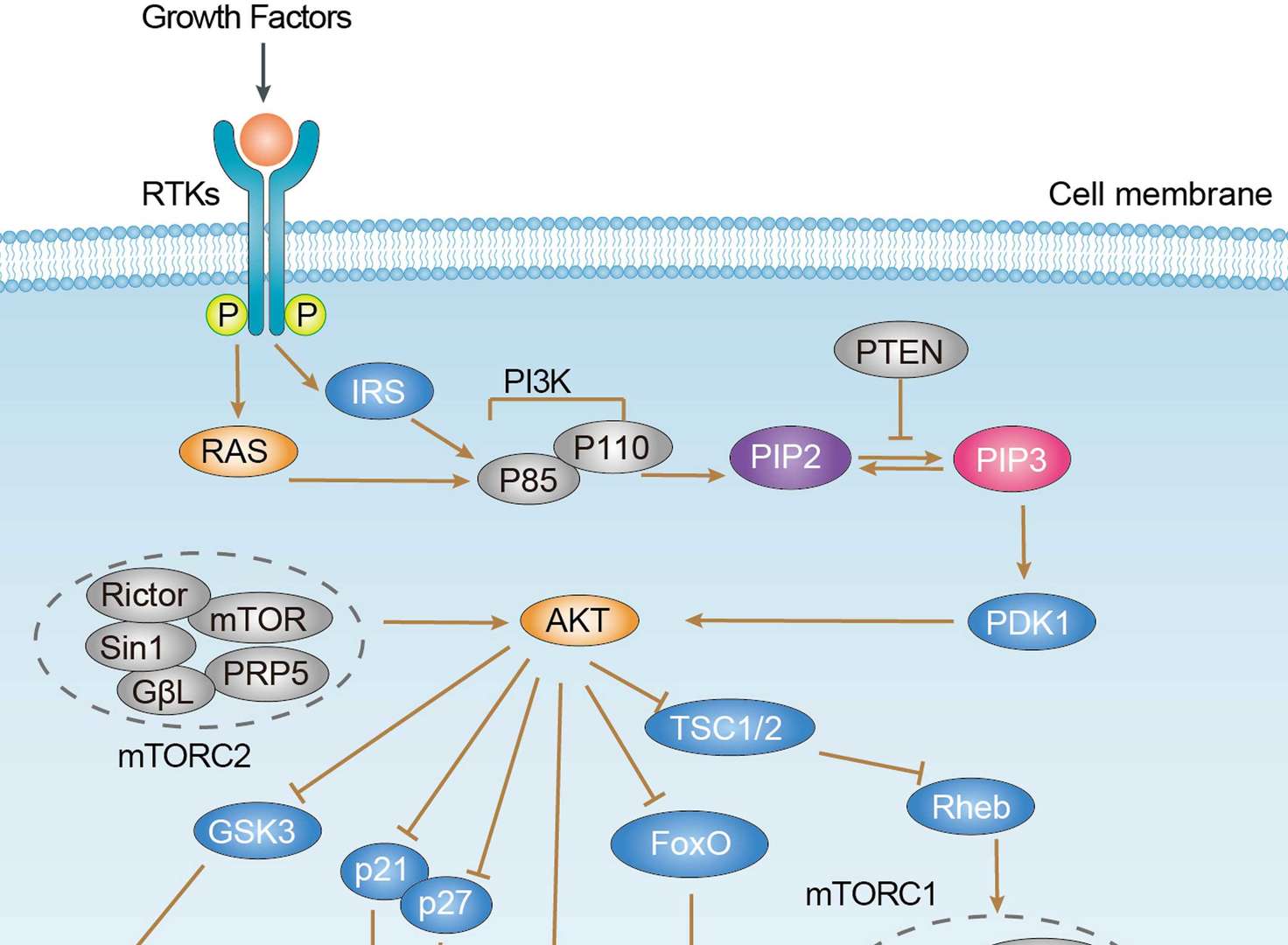 PI3K-Akt Pathway
PI3K-Akt Pathway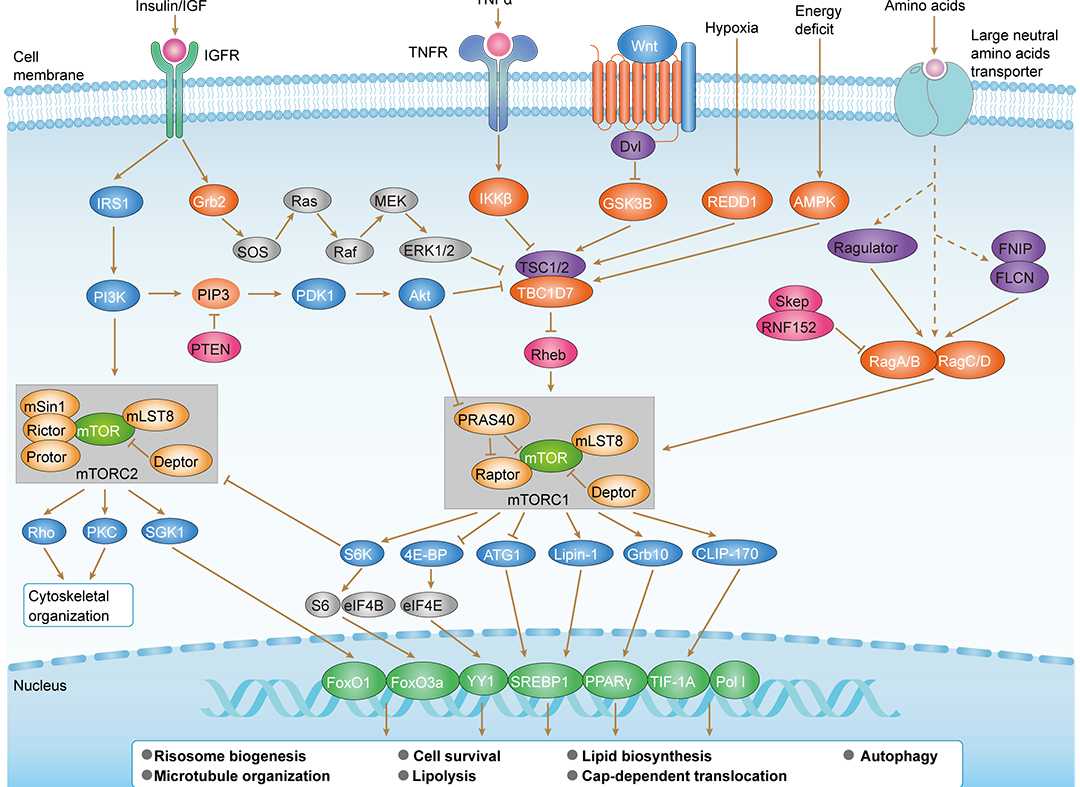 mTOR Signaling Pathway
mTOR Signaling Pathway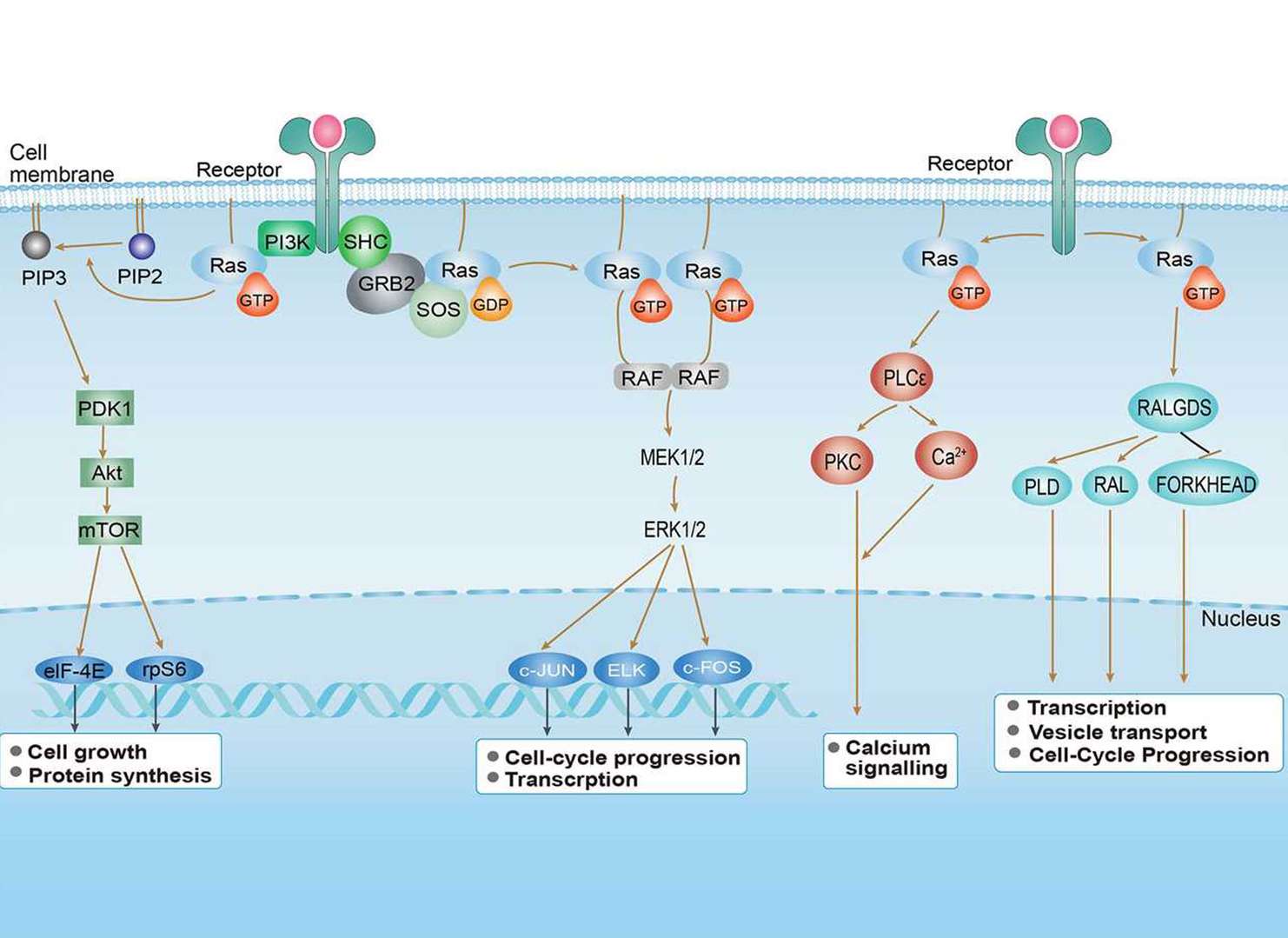 Ras Signaling Pathway
Ras Signaling Pathway