+ Filter
 Loading...
Loading...

CD22 & CD19
 Loading...
Loading...Anti-CD22 & CD19 ProductsBackground
Anti-CD22 & CD19 Products
-
- Host Species: Human
- Specificity: Human
- Type: Chimeric antibody (mouse/human)
- Glycosylation site: Asn297 in Fc region
- Glycoform (ratio): GN-GN-M-(M-GN)2
-
- Host Species: Human
- Specificity: Human
- Type: Chimeric antibody (mouse/human)
- Glycosylation site: Asn297 in Fc region
- Glycoform (ratio): GN-GN-M-(M-GN)2
-
- Host Species: Mouse
- Specificity: Human
- Type: Mouse antibody
- Glycosylation site: Fc region
- Glycoform (ratio): G2-NANA
-
- Host Species: Human
- Specificity: Human
- Type: Humanized antibody
- Glycosylation site: Asn297 in Fc region
-
- Host Species: Human
- Specificity: Human
- Type: Humanized antibody
- Glycosylation site: Asn297 in Fc region
-
- Host Species: Mouse
- Specificity: Human
- Type: Mouse antibody
- Glycosylation site: FR1 of VK
-
- Host Species: Human
- Specificity: Human
- Type: Chimeric antibody (mouse/human)
- Glycosylation site: Asn297 in Fc region
View More Products
Can't find the products you're looking for? Try to filter in the left sidebar.Filter By Tag
More Infomation
Our customer service representatives are available 24 hours a day, from Monday to Sunday. Contact Us
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.
Background
CD19 (CD19 Molecule) is a Protein Coding gene. Diseases associated with CD19 include Immunodeficiency, Common Variable, 3 and Common Variable Immunodeficiency. Among its related pathways are RET signaling and Hematopoietic Stem Cell Differentiation Pathways and Lineage-specific Markers. Gene Ontology (GO) annotations related to this gene include signal transducer activity, downstream of receptor.

CD22 or cluster of differentiation-22, is a molecule belonging to the SIGLEC family of lectins. It is found on the surface of mature B cells and to a lesser extent on some immature B cells. Generally speaking, CD22 is a regulatory molecule that prevents the overactivation of the immune system and the development of autoimmune diseases. CD22 is a sugar binding transmembrane protein, which specifically binds sialic acid with an immunoglobulin (Ig) domain located at its N-terminus. The presence of Ig domains makes CD22 a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. CD22 functions as an inhibitory receptor for B cell receptor (BCR) signalling.



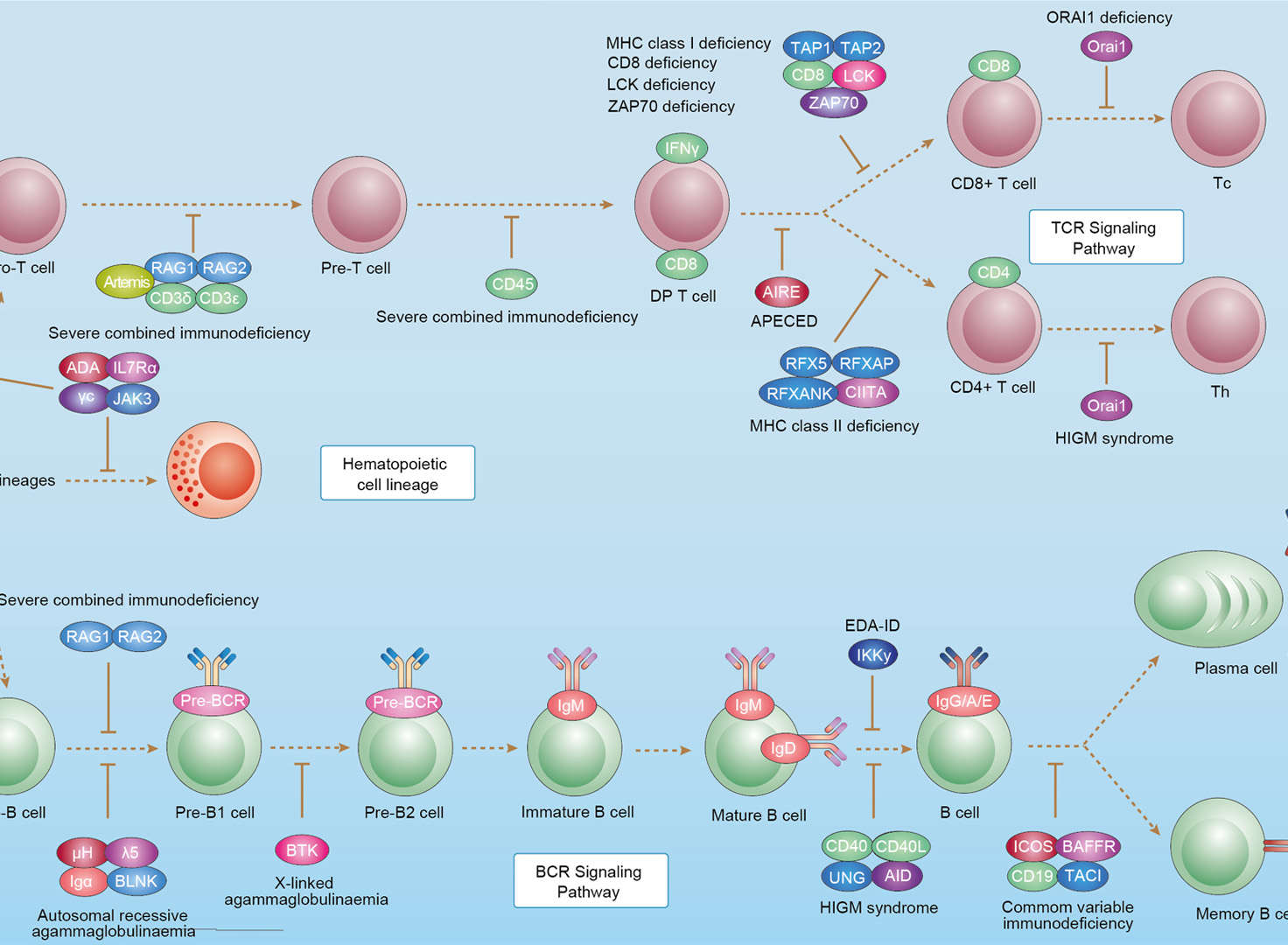 Primary Immunodeficiency
Primary Immunodeficiency