Rabbit Anti-RHOA Recombinant Antibody (VS3-CJ1078)
CAT#: VS3-CJ1078
This product is a rabbit antibody that recognizes human, mouse, and rat RHOA.








Specifications
- Immunogen
- Recombinant protein
- Host Species
- Rabbit
- Type
- Rabbit IgG
- Specificity
- Human, Mouse, Rat RHOA
- Species Reactivity
- Human, Mouse, Rat
- Applications
- WB, ICC, IF, FC
- Conjugate
- Unconjugated
Product Property
- Purification
- Protein A affinity purified
- Purity
- >95% as determined by SDS-PAGE
- Format
- Liquid
- Buffer
- 40% Glycerol, 1% BSA, TBS, pH7.4.
- Preservative
- 0.05% Sodium Azide
- Storage
- Store at 4°C for short term. Aliquot and store at -20°C for long term. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles.
Applications
- Application Notes
- This antibody has been tested for use in Western Blot, Immunocytochemistry, Immunofluorescence, Flow Cytometry.
Target
- Alternative Names
- ARHA; ARH12; RHO12; EDFAOB; RHOH12
- Gene ID
- 387
- UniProt ID
- P61586
- Sequence Similarities
- Belongs to the small GTPase superfamily. Rho family.
- Cellular Localization
- Cell membrane, Cell projection, Cytoplasm, Cytoskeleton, Membrane, Nucleus
- Post Translation Modifications
- (Microbial infection) Substrate for botulinum ADP-ribosyltransferas
(Microbial infection) Cleaved by yopT protease when the cell is infected by some Yersinia pathogens. This removes the lipid attachment, and leads to its displacement from plasma membrane and to subsequent cytoskeleton cleavage.
(Microbial infection) AMPylation at Tyr-34 and Thr-37 are mediated by bacterial enzymes in case of infection by H.somnus and V.parahaemolyticus, respectively. AMPylation occurs in the effector region and leads to inactivation of the GTPase activity by preventing the interaction with downstream effectors, thereby inhibiting actin assembly in infected cells. It is unclear whether some human enzyme mediates AMPylation; FICD has such ability in vitro but additional experiments remain to be done to confirm results in vivo.
(Microbial infection) Glycosylated at Tyr-34 by Photorhabdus asymbiotica toxin PAU_02230. Mono-O-GlcNAcylation by PAU_02230 inhibits downstream signaling by an impaired interaction with diverse regulator and effector proteins of Rho and leads to actin disassembly.
(Microbial infection) Glucosylated at Thr-37 by C.difficile toxins TcdA and TcdB in the colonic epithelium (PubMed:7777059, PubMed:7775453, PubMed:24905543).
Monoglucosylation completely prevents the recognition of the downstream effector, blocking the GTPases in their inactive form, leading to actin cytoskeleton disruption and cell death, resulting in the loss of colonic epithelial barrier function (PubMed:7777059, PubMed:7775453).
(Microbial infection) Glycosylated (O-GlcNAcylated) at Thr-37 by C.novyi toxin TcdA (PubMed:8810274).
O-GlcNAcylation completely prevents the recognition of the downstream effector, blocking the GTPases in their inactive form, leading to actin cytoskeleton disruption (PubMed:8810274).
(Microbial infection) Stearoylated By S.flexneri N-epsilon-fatty acyltransferase IcsB, thereby disrupting the host actin cytoskeleton.
Phosphorylation by PRKG1 at Ser-188 inactivates RHOA signaling (PubMed:11162591).
Phosphorylation by SLK at Ser-188 in response to AGTR2 activation (By similarity).
Ubiquitinated by the BCR(KCTD13) and BCR(TNFAIP1) E3 ubiquitin ligase complexes, leading to its degradation by the proteasome, thereby regulating the actin cytoskeleton and synaptic transmission in neurons.
Serotonylation of Gln-63 by TGM2 during activation and aggregation of platelets leads to constitutive activation of GTPase activity.
- Protein Refseq
- NP_001300870.1; NP_001655.1
- Function
- Small GTPase which cycles between an active GTP-bound and an inactive GDP-bound state. Mainly associated with cytoskeleton organization, in active state binds to a variety of effector proteins to regulate cellular responses such as cytoskeletal dynamics, cell migration and cell cycle. Regulates a signal transduction pathway linking plasma membrane receptors to the assembly of focal adhesions and actin stress fibers (PubMed:8910519, PubMed:9121475, PubMed:31570889).
Involved in a microtubule-dependent signal that is required for the myosin contractile ring formation during cell cycle cytokinesis (PubMed:16236794, PubMed:12900402).
Plays an essential role in cleavage furrow formation. Required for the apical junction formation of keratinocyte cell-cell adhesion (PubMed:20974804, PubMed:23940119).
Essential for the SPATA13-mediated regulation of cell migration and adhesion assembly and disassembly (PubMed:19934221).
The MEMO1-RHOA-DIAPH1 signaling pathway plays an important role in ERBB2-dependent stabilization of microtubules at the cell cortex. It controls the localization of APC and CLASP2 to the cell membrane, via the regulation of GSK3B activity. In turn, membrane-bound APC allows the localization of the MACF1 to the cell membrane, which is required for microtubule capture and stabilization (PubMed:20937854).
Regulates KCNA2 potassium channel activity by reducing its location at the cell surface in response to CHRM1 activation; promotes KCNA2 endocytosis (PubMed:9635436, PubMed:19403695).
Acts as an allosteric activator of guanine nucleotide exchange factor ECT2 by binding in its activated GTP-bound form to the PH domain of ECT2 which stimulates the release of PH inhibition and promotes the binding of substrate RHOA to the ECT2 catalytic center (PubMed:31888991).
May be an activator of PLCE1 (PubMed:16103226).
In neurons, involved in the inhibition of the initial spine growth. Upon activation by CaMKII, modulates dendritic spine structural plasticity by relaying CaMKII transient activation to synapse-specific, long-term signaling (By similarity).
Acts as a regulator of platelet alpha-granule release during activation and aggregation of platelets (By similarity).
(Microbial infection) Serves as a target for the yopT cysteine peptidase from Yersinia pestis, vector of the plague.
Customer Review
There are currently no Customer reviews or questions for VS3-CJ1078. Click the button above to contact us or submit your feedback about this product.
Submit Your Publication
Published with our product? Submit your paper and receive a 10% discount on your next order! Share your research to earn exclusive rewards.
Related Signaling Pathways
Downloadable Resources
Download resources about recombinant antibody development and antibody engineering to boost your research.
Product Notes
This is a product of Creative Biolabs' Hi-Affi™ recombinant antibody portfolio, which has several benefits including:
• Increased sensitivity
• Confirmed specificity
• High repeatability
• Excellent batch-to-batch consistency
• Sustainable supply
• Animal-free production
See more details about Hi-Affi™ recombinant antibody benefits.
Datasheet
MSDS
COA
Certificate of Analysis LookupTo download a Certificate of Analysis, please enter a lot number in the search box below. Note: Certificate of Analysis not available for kit components.
Protocol & Troubleshooting
We have outlined the assay protocols, covering reagents, solutions, procedures, and troubleshooting tips for common issues in order to better assist clients in conducting experiments with our products. View the full list of Protocol & Troubleshooting.
Isotype Control
- CAT
- Product Name
Secondary Antibody
- CAT
- Product Name
See other products for "RHOA"
Select a product category from the dropdown menu below to view related products.
| CAT | Product Name | Application | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| BRD-0510MZ | Chicken Anti-RhoA Polyclonal IgY | WB | Chicken antibody |
| CAT | Product Name | Application | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| MOR-3067 | Hi-Affi™ Recombinant Rabbit Anti-RHOA Monoclonal Antibody (DS3067AB) | WB, IHC | IgG |
| MOR-3068 | Hi-Affi™ Recombinant Rabbit Anti-RHOA Monoclonal Antibody (DS3068AB) | ELISA, FC | IgG |
| CAT | Product Name | Application | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| FAMAB-0306WJ | Human Anti-RHOA Recombinant Antibody (clone C1) | ELISA, WB | Human IgG |
| FAMAB-0307WJ | Human Anti-RHOA Recombinant Antibody (clone F7) | ELISA, WB | Human IgG |
| FAMAB-0308WJ | Human Anti-RHOA Recombinant Antibody (clone D10) | ELISA, WB | Human IgG |
| VS3-FY2110 | Rabbit Anti-RHOA Recombinant Antibody (clone R58-4S-7) | WB, IHC-P, IF, FC | Rabbit IgG |
| VS7-0425-WR780 | Mouse Anti-RHOA Recombinant Antibody (clone 7E7H4) | WB, IHC, ICC, FC | Mouse IgG2b |
| CAT | Product Name | Application | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| FAMAB-0306WJ-S(P) | Human Anti-RHOA Recombinant Antibody (clone C1); scFv Fragment | ELISA, WB | Human scFv |
| FAMAB-0307WJ-S(P) | Human Anti-RHOA Recombinant Antibody (clone F7); scFv Fragment | ELISA, WB | Human scFv |
| FAMAB-0308WJ-S(P) | Human Anti-RHOA Recombinant Antibody (clone D10); scFv Fragment | ELISA, WB | Human scFv |
| FAMAB-0309WJ-S(P) | Human Anti-RHOA Recombinant Antibody (clone A5); scFv Fragment | ELISA, WB | Human scFv |
| CAT | Product Name | Application | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| FAMAB-0306WJ-F(E) | Human Anti-RHOA Recombinant Antibody (clone C1); Fab Fragment | ELISA, WB | Human Fab |
| FAMAB-0307WJ-F(E) | Human Anti-RHOA Recombinant Antibody (clone F7); Fab Fragment | ELISA, WB | Human Fab |
| FAMAB-0308WJ-F(E) | Human Anti-RHOA Recombinant Antibody (clone D10); Fab Fragment | ELISA, WB | Human Fab |
| FAMAB-0309WJ-F(E) | Human Anti-RHOA Recombinant Antibody (clone A5); Fab Fragment | ELISA, WB | Human Fab |
| CAT | Product Name | Application | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| VS-0724-YC730 | AbPlus™ Anti-RHOA Magnetic Beads (VS-0724-YC730) | IP, Protein Purification |
| CAT | Product Name | Application | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| VS13-YC1003 | CytoStream™ Rabbit Anti-RHOA Recombinant Antibody (VS13-YC1003) | WB, ICC, IF, FC | Rabbit IgG |
| CAT | Product Name | Application | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| VS-0325-XY1916 | Anti-RHOA Immunohistochemistry Kit | IHC | |
| VS-0525-XY6112 | Anti-Mouse RHOA Immunohistochemistry Kit | IHC | |
| VS-0525-XY6111 | Anti-Human RHOA Immunohistochemistry Kit | IHC |
Popular Products

Application: ELISA, IP, FC, FuncS, Neut, IF, ICC

Application: IF, IP, Neut, FuncS, ELISA, FC, WB

Application: ELISA, WB, BLI, SPR
![Figure 2 Anti-Human CD19 Recombinant Antibody Fab Fragment [TAB-1611CL-F(E)] in HPLC](https://img.creativebiolabs.net/productimages/COA-TAB-1611CL-F(E)-2.png)
Application: Depletion, FuncS

Application: WB, ELISA, FuncS, Inhib, PK, IP, SPR

Application: ELISA, IHC, FC, IP, IF, FuncS

Application: ELISA, IHC, FC, IP, IF, Inhib

Application: ELISA, IHC, FC, IP, IF, Inhib

Application: ELISA, PD, Activ, PK, Stim
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use. No products from Creative Biolabs may be resold, modified for resale or used to manufacture commercial products without prior written approval from Creative Biolabs.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.











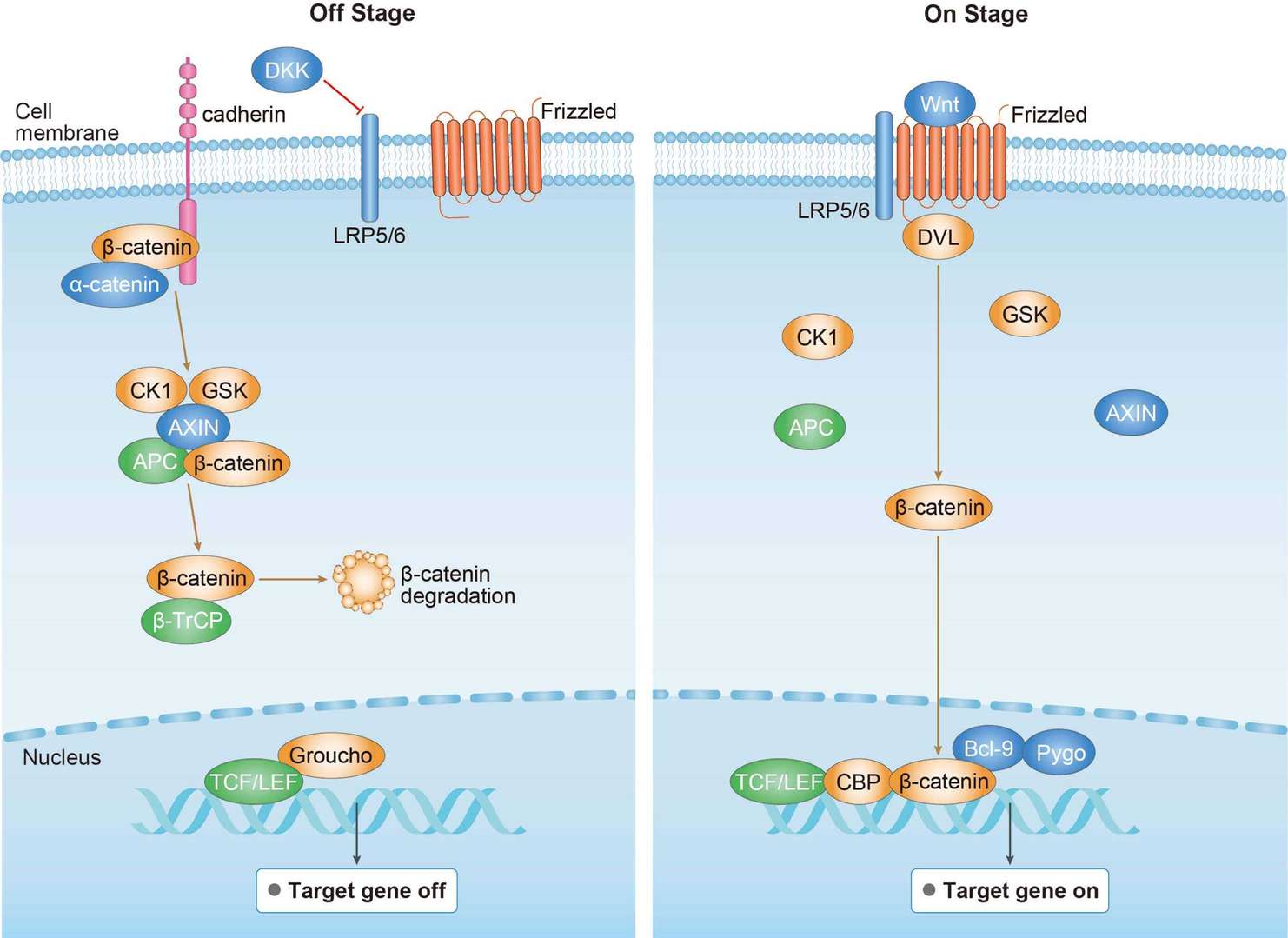 Canonical Wnt Signaling Pathway
Canonical Wnt Signaling Pathway
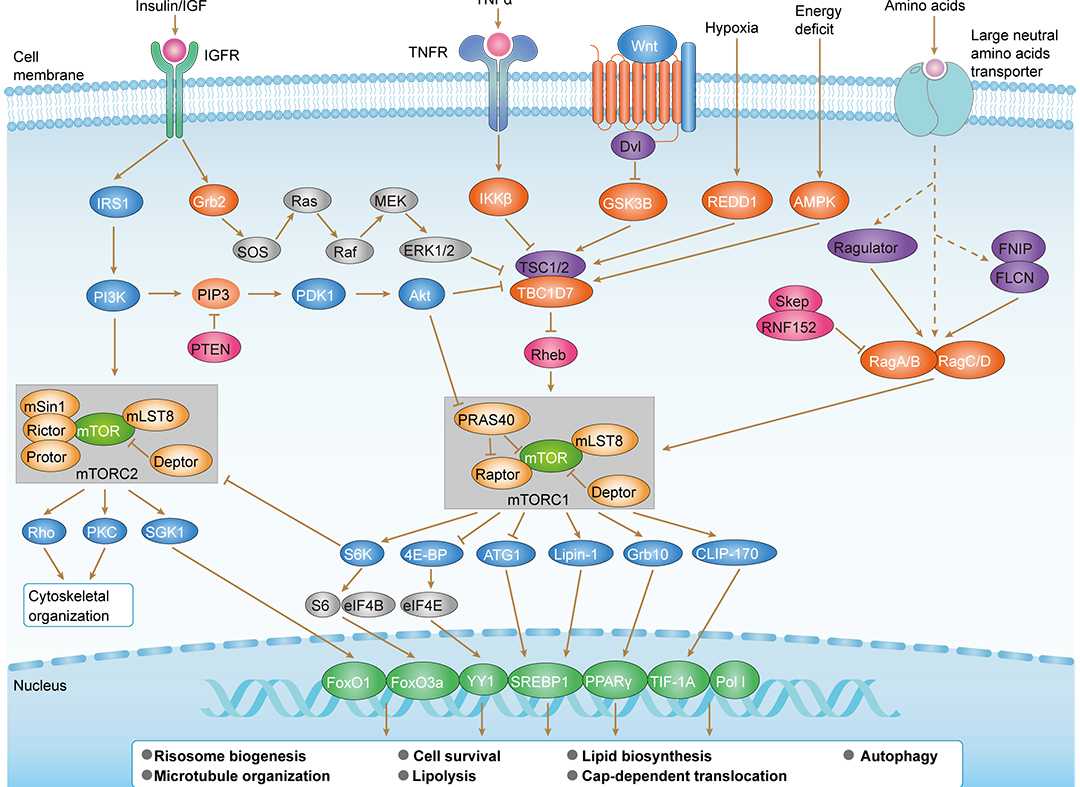 mTOR Signaling Pathway
mTOR Signaling Pathway
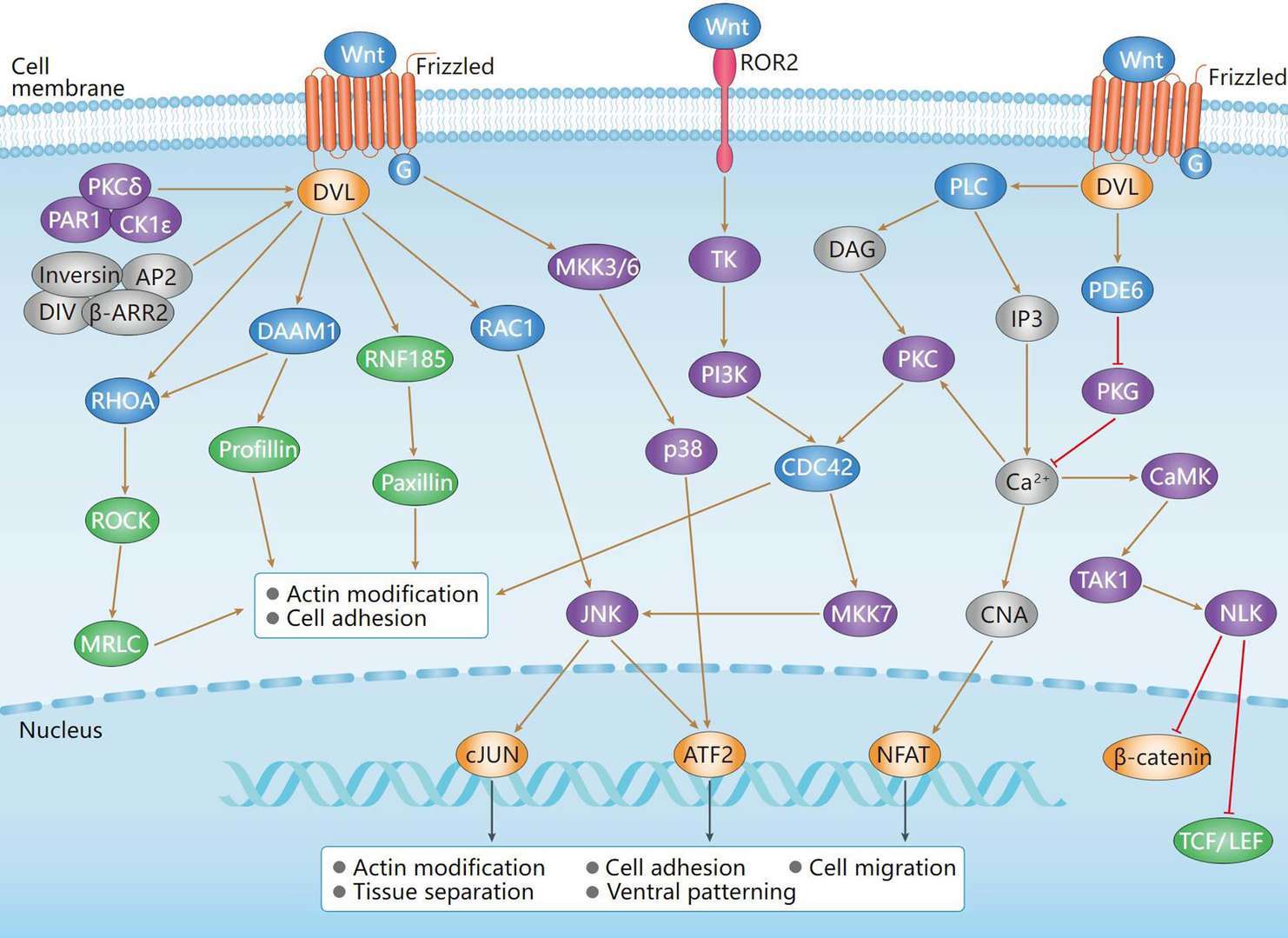 Non-Canonical Wnt Signaling Pathway
Non-Canonical Wnt Signaling Pathway















