+ Filter
 Loading...
Loading...

DNMT1 & SHH
 Loading...
Loading...Anti-DNMT1 & SHH Products
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human IgG
- Application: ELISA, IP-MS
- Recombinant Anti-human SHH Antibody (MOB-902)
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: IgG
- Application: ELISA, WB, Neut, FuncS
-
- Derivation: Human
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: IgG
- Application: WB, IHC, FuncS
- Anti-Human SHH Recombinant Antibody (MEDI-5304) (TAB-566CL)
-
- Derivation: Human
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody
- Application: Inhib
-
- Derivation: Human
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: ADCC enhanced antibody
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse antibody
- Application: ICC, IF, WB, sELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Application: FC, ICC, IF, IHC-P, WB
- Recombinant Rat Anti-Shh Antibody (6K12) (NEUT-1955CQ)
-
- Species Reactivity: Mouse
- Type: IgG2
- Application: IHC, Neut, WB
- Recombinant Rat Anti-Shh Antibody (CBL167) (NEUT-1956CQ)
-
- Species Reactivity: Mouse
- Type: IgG2
- Application: IHC, Neut, WB
- Recombinant Rat Anti-Shh Antibody (CBL886) (NEUT-1957CQ)
-
- Species Reactivity: Mouse
- Type: IgG2a
- Application: Neut, WB
- Recombinant Mouse Anti-SHH Antibody (171018) (NEUT-1958CQ)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Type: IgG2a
- Application: IHC-FoFr, WB, IHC-Fr, Neut, ELISA, ICC, IF
- PE-A2/Human DNMT1 (GLIEKNIEL) MHC Tetramer (MHC-LC1940)
-
- Class: Class I
- Antigen: DNMT1
- Antigen Species: Human
- Peptide: GLIEKNIEL
- Conjugate: PE
- APC-A2/Human DNMT1 (GLIEKNIEL) MHC Tetramer (MHC-LC1955)
-
- Class: Class I
- Antigen: DNMT1
- Antigen Species: Human
- Peptide: GLIEKNIEL
- Conjugate: APC
- PE-A*02:01/Human DNMT1 (GLIEKNIEL) MHC Tetramer (MHC-LC1982)
-
- Class: Class I
- Antigen: DNMT1
- Antigen Species: Human
- Peptide: GLIEKNIEL
- Conjugate: PE
- APC-A*01:01/Human DNMT1 (YLDDPDLKY) MHC Tetramer (MHC-LC4421)
-
- Class: Class I
- Antigen: DNMT1
- Antigen Species: Human
- Peptide: YLDDPDLKY
- Conjugate: APC
- PE-A*01:01/Human DNMT1 (YLDDPDLKY) MHC Tetramer (MHC-LC2374)
-
- Class: Class I
- Antigen: DNMT1
- Antigen Species: Human
- Peptide: YLDDPDLKY
- Conjugate: PE
- PE-A*02:01/Human DNMT1 (YLDDPDLKY) MHC Tetramer (MHC-LC4422)
-
- Class: Class I
- Antigen: DNMT1
- Antigen Species: Human
- Peptide: YLDDPDLKY
- Conjugate: PE
- PE-B*15:01/Human DNMT1 (YLDDPDLKY) MHC Tetramer (MHC-LC4423)
-
- Class: Class I
- Antigen: DNMT1
- Antigen Species: Human
- Peptide: YLDDPDLKY
- Conjugate: PE
- Human Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (clone 3H8) (HPAB-0710-CN)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human IgG2
- Application: ELISA, FC
- Human Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (clone 6D7OP) (HPAB-0711-CN)
-
- Species Reactivity: Mouse
- Type: Human IgG1
- Application: ELISA, FC, Neut
- Human Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (clone 3H8OP) (HPAB-0712-CN)
-
- Species Reactivity: Mouse
- Type: Human IgG1
- Application: ELISA, FC
- Human Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (clone 1A12) (HPAB-AP788-YC)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human IgG
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (clone 1G12) (HPAB-AP789-YC)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human IgG
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (clone 1H10) (HPAB-AP790-YC)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human IgG
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (clone 4B6) (HPAB-AP791-YC)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human IgG
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (clone 1G1) (HPAB-AP792-YC)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Type: Human IgG2
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (clone 1H8) (HPAB-AP793-YC)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human IgG2
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (clone 1A5) (HPAB-AP794-YC)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human IgG
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (clone 1G1OP) (HPAB-AP795-YC)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human IgG
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Mouse Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (clone 5E1) (FAMAB-1549CQ)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Rat
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: Block, WB, ELISA, IHC
- Mouse Anti-DNMT1 Recombinant Antibody (clone CBS388) (MRO-A1926-YJ)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Zebrafish
- Type: Mouse IgG2b
- Application: WB, ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA, IHC, IF
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: ELISA, WB, IHC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Mouse Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (clone 5H4) (VS3-XY1420)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: ELISA, WB, FC, IHC
- Mouse Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (clone 8G3) (VS3-XY1421)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: ELISA, WB
- Rabbit Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (VS3-WK985) (VS3-WK985)
-
- Derivation: Rabbit
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, ICC, IF, IHC, FC
- Recombinant Rabbit Anti-SHH Antibody (clone R06-9H9) (VS3-FY1333)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IHC-Fr, IHC-P, ICC, IF
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IHC-P, ICC, IF
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: WB, ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, ICC, IF, IP
- Rabbit Anti-DNMT1 Recombinant Antibody (clone JF09-89) (MRO-0486-CN)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IF, IHC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IF, IHC, FC
- Mouse Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (HPAB-N0236-YC) (HPAB-N0236-YC)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: ELISA, FC, WB, FuncS, Inhib, IF
- Mouse Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody; scFv Fragment (HPAB-N0236-YC-S(P)) (HPAB-N0236-YC-S(P))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse scFv
- Application: ELISA, FC, WB, FuncS
- Mouse Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody; Fab Fragment (HPAB-N0236-YC-F(E)) (HPAB-N0236-YC-F(E))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse Fab
- Application: ELISA, FC, WB, FuncS
- Human Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (clone 1G1OP); scFv Fragment (HPAB-AP795-YC-S(P))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human scFv
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Mouse Anti-NHP SHH Recombinant Antibody (clone 5H4) (VS-1024-XY476)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Non-human primate
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: WB, IHC, FC, ELISA
- Human Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (clone 1A12); scFv Fragment (HPAB-AP788-YC-S(P))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human scFv
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (clone 1G12); scFv Fragment (HPAB-AP789-YC-S(P))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human scFv
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (clone 1H10); scFv Fragment (HPAB-AP790-YC-S(P))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human scFv
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (clone 4B6); scFv Fragment (HPAB-AP791-YC-S(P))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human scFv
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (clone 1G1); scFv Fragment (HPAB-AP792-YC-S(P))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Type: Human scFv
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (clone 1H8); scFv Fragment (HPAB-AP793-YC-S(P))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human scFv
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (clone 1A5); scFv Fragment (HPAB-AP794-YC-S(P))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human scFv
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (clone 1A12); Fab Fragment (HPAB-AP788-YC-F(E))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human Fab
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (clone 1G12); Fab Fragment (HPAB-AP789-YC-F(E))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human Fab
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (clone 1H10); Fab Fragment (HPAB-AP790-YC-F(E))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human Fab
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (clone 4B6); Fab Fragment (HPAB-AP791-YC-F(E))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human Fab
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (clone 1G1); Fab Fragment (HPAB-AP792-YC-F(E))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Type: Human Fab
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (clone 1H8); Fab Fragment (HPAB-AP793-YC-F(E))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human Fab
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (clone 1A5); Fab Fragment (HPAB-AP794-YC-F(E))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human Fab
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (clone 1G1OP); Fab Fragment (HPAB-AP795-YC-F(E))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human Fab
- Application: ELISA, Inhib
- Human Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (clone 3H8); scFv Fragment (HPAB-0710-CN-S(P))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human scFv
- Application: ELISA, FC
- Human Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (clone 6D7OP); scFv Fragment (HPAB-0711-CN-S(P))
-
- Species Reactivity: Mouse
- Type: Human scFv
- Application: ELISA, FC, Neut
- Human Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (clone 3H8OP); scFv Fragment (HPAB-0712-CN-S(P))
-
- Species Reactivity: Mouse
- Type: Human scFv
- Application: ELISA, FC
- Human Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (clone 3H8); Fab Fragment (HPAB-0710-CN-F(E))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human Fab
- Application: ELISA, FC
- Human Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (clone 6D7OP); Fab Fragment (HPAB-0711-CN-F(E))
-
- Species Reactivity: Mouse
- Type: Human Fab
- Application: ELISA, FC, Neut
- Human Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (clone 3H8OP); Fab Fragment (HPAB-0712-CN-F(E))
-
- Species Reactivity: Mouse
- Type: Human Fab
- Application: ELISA, FC
- Human Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (clone 6D7); scFv Fragment (NS-082CN-S(P))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Type: Human scFv
- Application: ELISA, FC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Type: Human IgG2
- Application: ELISA, FC
- Human Anti-SHH Recombinant Antibody (clone 6D7); Fab Fragment (NS-082CN-F(E))
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Type: Human Fab
- Application: ELISA, FC
-
- Derivation: Chimeric (mouse/human)
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Fab
- Application: Neut
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse scFv
- Application: Neut
- Recombinant Human Anti-human SHH Antibody Fab Fragment (MHH-902-F(E))
-
- Derivation: Human
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Fab
- Application: WB, FC, FuncS
- Recombinant Human Anti-human SHH Antibody scFv Fragment (MHH-902-S(P))
-
- Derivation: Human
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: scFv
- Application: ELISA, WB, IF, FuncS
- Recombinant Anti-human SHH Antibody Fab Fragment (MOB-902-F(E))
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Fab
- Application: IF, FC, FuncS
- Recombinant Anti-human SHH Antibody scFv Fragment (MOB-902-S(P))
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: scFv
- Application: IP, IF, Biosensors, FuncS
-
- Targets: DNMT1 & SHH
- Type: Bi-Single Domain Antibody
- Application: FuncS, Promising therapeutic agent
- Chicken Anti-DNMT1 Polyclonal IgY (BRD-0164MZ)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Chicken antibody
- Application: WB
-
- Derivation: Phage display library
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: FC, ICC, IF, IP, WB
-
- Derivation: Phage display library screening
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: IgG
- Application: FC, IHC-P, IP, WB
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: IgG
- Application: WB, IF, ICC, FC
- Anti-SHH Immunohistochemistry Kit (VS-0325-XY2063)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Target: SHH
- Application: IHC
- Anti-DNMT1 Immunohistochemistry Kit (VS-0525-XY2045)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Target: DNMT1
- Application: IHC
- Anti-Monkey SHH Immunohistochemistry Kit (VS-0525-XY6567)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Monkey
- Target: SHH
- Application: IHC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human IgG
- Application: Inhibition
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: WB, IHC-P, FC
- Rabbit Anti-DNMT1 Recombinant Antibody (VS13-YC315) (VS13-YC315)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, ICC, IF, IHC-P
- Anti-Mouse DNMT1 Immunohistochemistry Kit (VS-0525-XY2046)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat, Porcine, Bovine, Sheep
- Target: DNMT1
- Application: IHC
- Anti-Mouse SHH Immunohistochemistry Kit (VS-0525-XY6566)
-
- Species Reactivity: Mouse
- Target: SHH
- Application: IHC
- Mouse Anti-DNMT1 Recombinant Antibody (clone 60B1220.1) (VS-0725-FY209)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: ChIP, IHC, IP, WB
- Rat Anti-DNMT1 Recombinant Antibody (clone 2C1) (VS-0725-FY212)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rat IgG2b
- Application: ChIP, IP, WB
View More Products
Can't find the products you're looking for? Try to filter in the left sidebar.Filter By Tag
More Infomation
Our customer service representatives are available 24 hours a day, from Monday to Sunday. Contact Us
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.
Background
This gene encodes an enzyme that transfers methyl groups to cytosine nucleotides of genomic DNA. This protein is the major enzyme responsible for maintaining methylation patterns following DNA replication and shows a preference for hemi-methylated DNA. Methylation of DNA is an important component of mammalian epigenetic gene regulation. Aberrant methylation patterns are found in human tumors and associated with developmental abnormalities. Variation in this gene has been associated with cerebellar ataxia, deafness, and narcolepsy, and neuropathy, hereditary sensory, type IE. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants.
This gene encodes a protein that is instrumental in patterning the early embryo. It has been implicated as the key inductive signal in patterning of the ventral neural tube, the anterior-posterior limb axis, and the ventral somites. Of three human proteins showing sequence and functional similarity to the sonic hedgehog protein of Drosophila, this protein is the most similar. The protein is made as a precursor that is autocatalytically cleaved; the N-terminal portion is soluble and contains the signalling activity while the C-terminal portion is involved in precursor processing. More importantly, the C-terminal product covalently attaches a cholesterol moiety to the N-terminal product, restricting the N-terminal product to the cell surface and preventing it from freely diffusing throughout the developing embryo. Defects in this protein or in its signalling pathway are a cause of holoprosencephaly (HPE), a disorder in which the developing forebrain fails to correctly separate into right and left hemispheres. HPE is manifested by facial deformities. It is also thought that mutations in this gene or in its signalling pathway may be responsible for VACTERL syndrome, which is characterized by vertebral defects, anal atresia, tracheoesophageal fistula with esophageal atresia, radial and renal dysplasia, cardiac anomalies, and limb abnormalities. Additionally, mutations in a long range enhancer located approximately 1 megabase upstream of this gene disrupt limb patterning and can result in preaxial polydactyly.


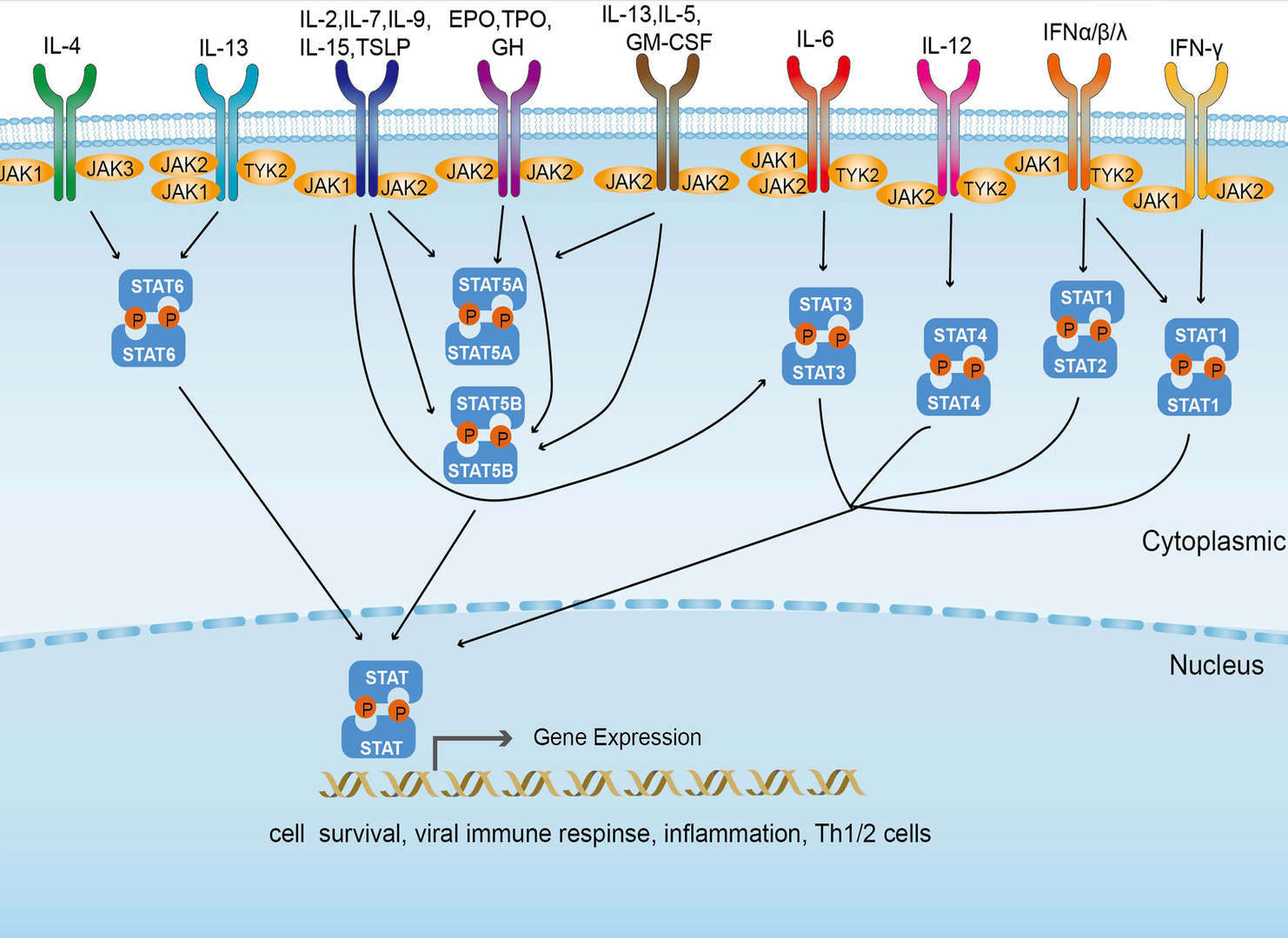 JAK-STAT Signaling Pathway
JAK-STAT Signaling Pathway
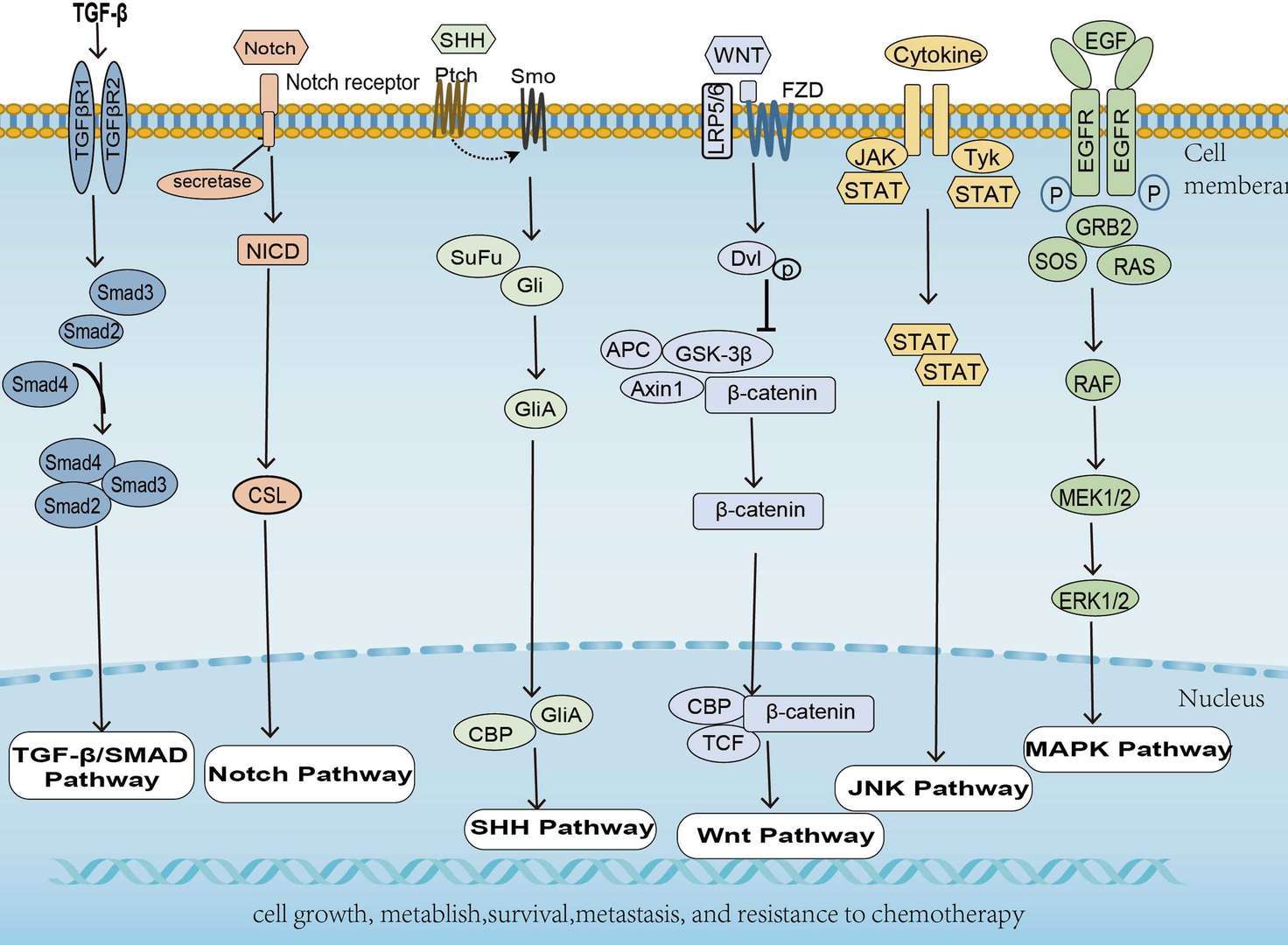 Pancreatic Cancer
Pancreatic Cancer

