 Loading...
Loading...

BRAF
 Loading...
Loading...Anti-BRAF Products
- Mouse Anti-BRAF Recombinant Antibody (clone F1-F4-E10) (MRO-0189-CN)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Mouse IgG2b
- Application: WB, IHC, IF
- Rabbit Anti-BRAF Recombinant Antibody (clone CBACN-057) (MRO-0148-CN)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IHC, IP, FC
- Rabbit Anti-BRAF Recombinant Antibody (clone CBACN-596) (MRO-2303-CN)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IF, IP
- PE-B*27:05/Human BRAF (GRFGLATEK) MHC Tetramer (MHC-CN0457)
-
- Class: Class I
- Antigen: BRAF
- Antigen Species: Human
- Peptide: GRFGLATEK
- Conjugate: PE
- APC-B*27:05/Human BRAF (GRFGLATEK) MHC Tetramer (MHC-CN0458)
-
- Class: Class I
- Antigen: BRAF
- Antigen Species: Human
- Peptide: GRFGLATEK
- Conjugate: APC
- FITC-B*27:05/Human BRAF (GRFGLATEK) MHC Tetramer (MHC-CN0459)
-
- Class: Class I
- Antigen: BRAF
- Antigen Species: Human
- Peptide: GRFGLATEK
- Conjugate: FITC
- B*27:05/Human BRAF (GRFGLATEK) MHC Tetramer (MHC-CN0460)
-
- Class: Class I
- Antigen: BRAF
- Antigen Species: Human
- Peptide: GRFGLATEK
- Conjugate: Unconjugated
- PE-B*27:05/Human BRAF (GRFGLATVK) MHC Tetramer (MHC-CN0461)
-
- Class: Class I
- Antigen: BRAF
- Antigen Species: Human
- Peptide: GRFGLATVK
- Conjugate: PE
- APC-B*27:05/Human BRAF (GRFGLATVK) MHC Tetramer (MHC-CN0462)
-
- Class: Class I
- Antigen: BRAF
- Antigen Species: Human
- Peptide: GRFGLATVK
- Conjugate: APC
- FITC-B*27:05/Human BRAF (GRFGLATVK) MHC Tetramer (MHC-CN0463)
-
- Class: Class I
- Antigen: BRAF
- Antigen Species: Human
- Peptide: GRFGLATVK
- Conjugate: FITC
- B*27:05/Human BRAF (GRFGLATVK) MHC Tetramer (MHC-CN0464)
-
- Class: Class I
- Antigen: BRAF
- Antigen Species: Human
- Peptide: GRFGLATVK
- Conjugate: Unconjugated
- Human Anti-BRAF Antibody, mRNA (TAB-072CL-mRNA)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: WB
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: WB, ELISA, IHC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: WB, ELISA, IHC, IF
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA, WB, IF
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: ELISA, IHC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: IHC-P
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Type: Mouse IgG2a
- Application: WB
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: WB, ICC
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: WB, IHC, ICC, FC, ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IHC, IP, FC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, ICC, IP
-
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: ELISA, WB, IHC, FC
-
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: ELISA, WB, IHC, ICC, FC
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IP
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1, κ
- Application: ELISA
- AbPlus™ Anti-BRAF Magnetic Beads (CBACN-057) (VS-0424-XY32)
-
- Target: BRAF
- Target Species: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Application: IP, Protein Purification
- Recombinant Anti-human BRAF Antibody (MOB-122)
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: IgG
- Application: ELISA, WB, Dot, FuncS
-
- Derivation: Human
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: IgG
- Application: IP, FuncS
- Anti-Human BRAF Recombinant Antibody (TAB-072CL)
-
- Derivation: Humanized
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Antibody
-
- Derivation: Humanized
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: ADCC enhanced antibody
- Mouse Anti-BRAF Recombinant Antibody (clone 2I23) (MOB-0876MZ)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: ELISA, IHC-P, WB
-
- Application: IB, IF
- Anti-Human BRAF Recombinant Antibody scFv Fragment (CCTCC C2012122) (TAB-1284CL-S(P))
-
- Application: IB, IF
- Anti-Human BRAF Recombinant Antibody Fab Fragment (CCTCC C2012122) (TAB-1284CL-F(E))
-
- Application: IB, IF
- Recombinant Human Anti-human BRAF Antibody Fab Fragment (MHH-122-F(E))
-
- Derivation: Human
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Fab
- Application: ELISA, WB, Neut, FuncS
- Recombinant Human Anti-human BRAF Antibody scFv Fragment (MHH-122-S(P))
-
- Derivation: Human
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: scFv
- Application: WB, Neut, FuncS
- Recombinant Anti-human BRAF Antibody Fab Fragment (MOB-122-F(E))
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Fab
- Application: IF, Neut, FuncS
- Recombinant Anti-human BRAF Antibody scFv Fragment (MOB-122-S(P))
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: scFv
- Application: ELISA, IF, FuncS
- Rabbit Anti-NHP BRAF Recombinant Antibody (VS-1024-XY56) (VS-1024-XY56)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Non-human primate, Rat
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB
-
- Antibody Host: Mouse
- Antibody Reactivity: Human
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Type: Mouse IgG1
- Application: WB, IHC, ICC
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: WB, IHC-p, IF, ICC, ELISA
-
- Derivation: Mouse
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Mouse IgG
- Application: WB, IHC-p, IF, ELISA
- Anti-BRAF Immunohistochemistry Kit (VS-0525-XY821)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Target: BRAF
- Application: IHC
- Anti-Mouse BRAF Immunohistochemistry Kit (VS-0525-XY822)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat
- Target: BRAF
- Application: IHC
- Anti-Monkey BRAF Immunohistochemistry Kit (VS-0525-XY823)
-
- Species Reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat, Monkey
- Target: BRAF
- Application: IHC
-
- Derivation: Humanized
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Human IgG
- Application: ELISA
-
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Host Animal: Human
- Target: BRAF
- Application: ISZ, Cyt, FuncS
-
- Derivation: Phage display library screening
- Species Reactivity: Human
- Type: Rabbit IgG
- Application: WB, IHC
Can't find the products you're looking for? Try to filter in the left sidebar.Filter By Tag
Our customer service representatives are available 24 hours a day, from Monday to Sunday. Contact Us
For Research Use Only. Not For Clinical Use.
Background
Cancer-related genes, Disease related genes, Enzymes, FDA approved drug targets, Human disease related genes, Metabolic proteins
Intracellular
Cell type enhanced (Excitatory neurons, Inhibitory neurons, Oligodendrocyte precursor cells, Oligodendrocytes)
Low immune cell specificity
Low cell line specificity
Monomer. Homodimer. Heterodimerizes with RAF1, and the heterodimer possesses a highly increased kinase activity compared to the respective homodimers or monomers. Heterodimerization is mitogen-regulated and enhanced by 14-3-3 proteins. MAPK1/ERK2 activation can induce a negative feedback that promotes the dissociation of the heterodimer by phosphorylating BRAF at Thr-753. Heterodimerizes (via N-terminus) with KSR1 (via N-terminus) or KSR2 (via N-terminus) in a MAP2K1-dependent manner (PubMed:29433126). Interacts with MAP2K1 and MAP2K2 (PubMed:29433126). Found in a complex with at least BRAF, HRAS, MAP2K1, MAPK3 and RGS14. Interacts with RIT1. Interacts (via N-terminus) with RGS14 (via RBD domains); the interaction mediates the formation of a ternary complex with RAF1, a ternary complex inhibited by GNAI1 (By similarity). Interacts with DGKH (PubMed:19710016). Interacts with PRMT5 (PubMed:21917714). Interacts with KSR2 (PubMed:21441910). Interacts with AKAP13, MAP2K1 and KSR1. Identified in a complex with AKAP13, MAP2K1 and KSR1 (PubMed:21102438). Interacts with FNIP1 and FNIP2 (PubMed:27353360).
Allosteric enzyme, Kinase, Serine/threonine-protein kinase, Transferase


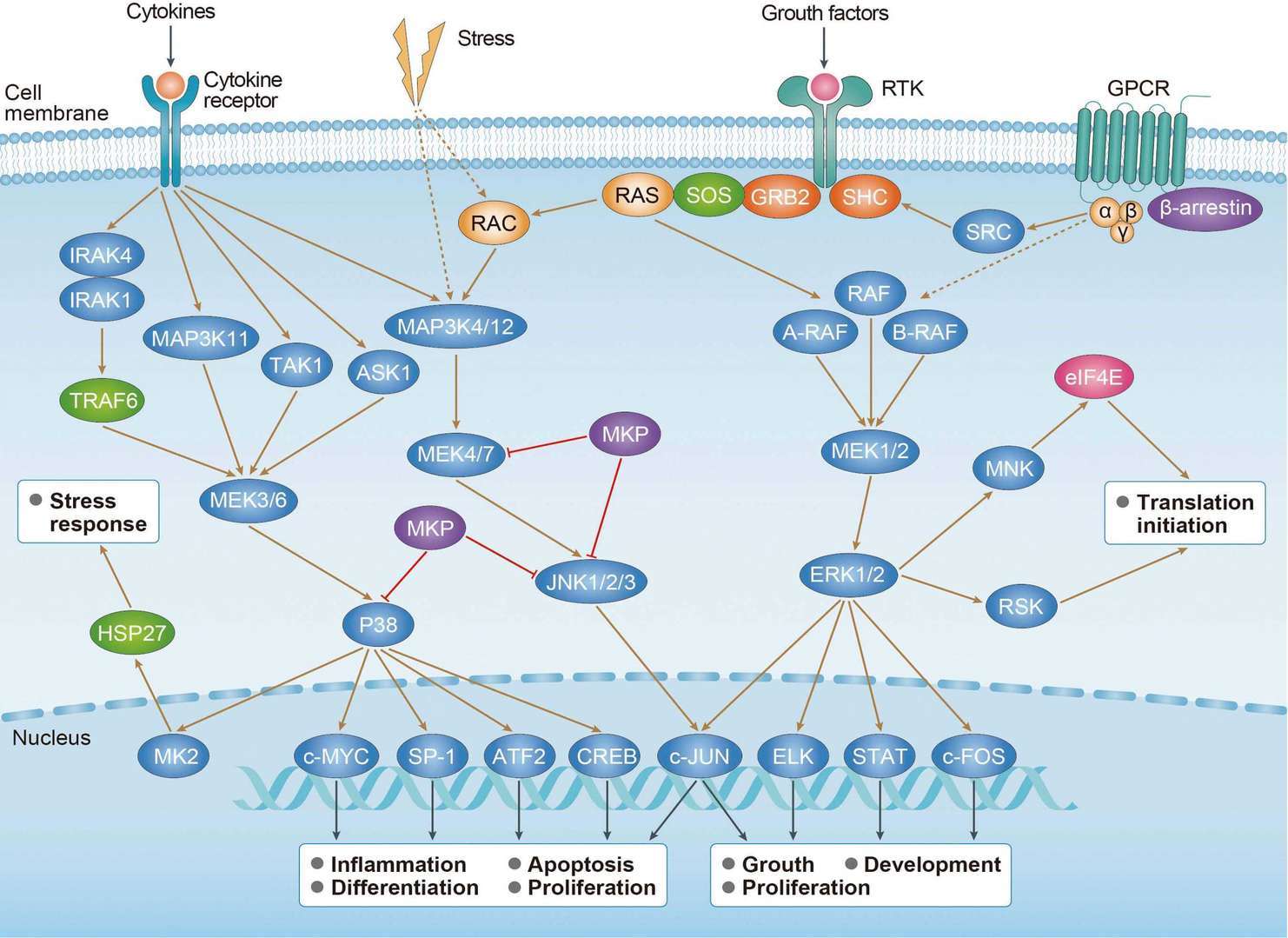 cAMP Signaling Pathway
cAMP Signaling Pathway
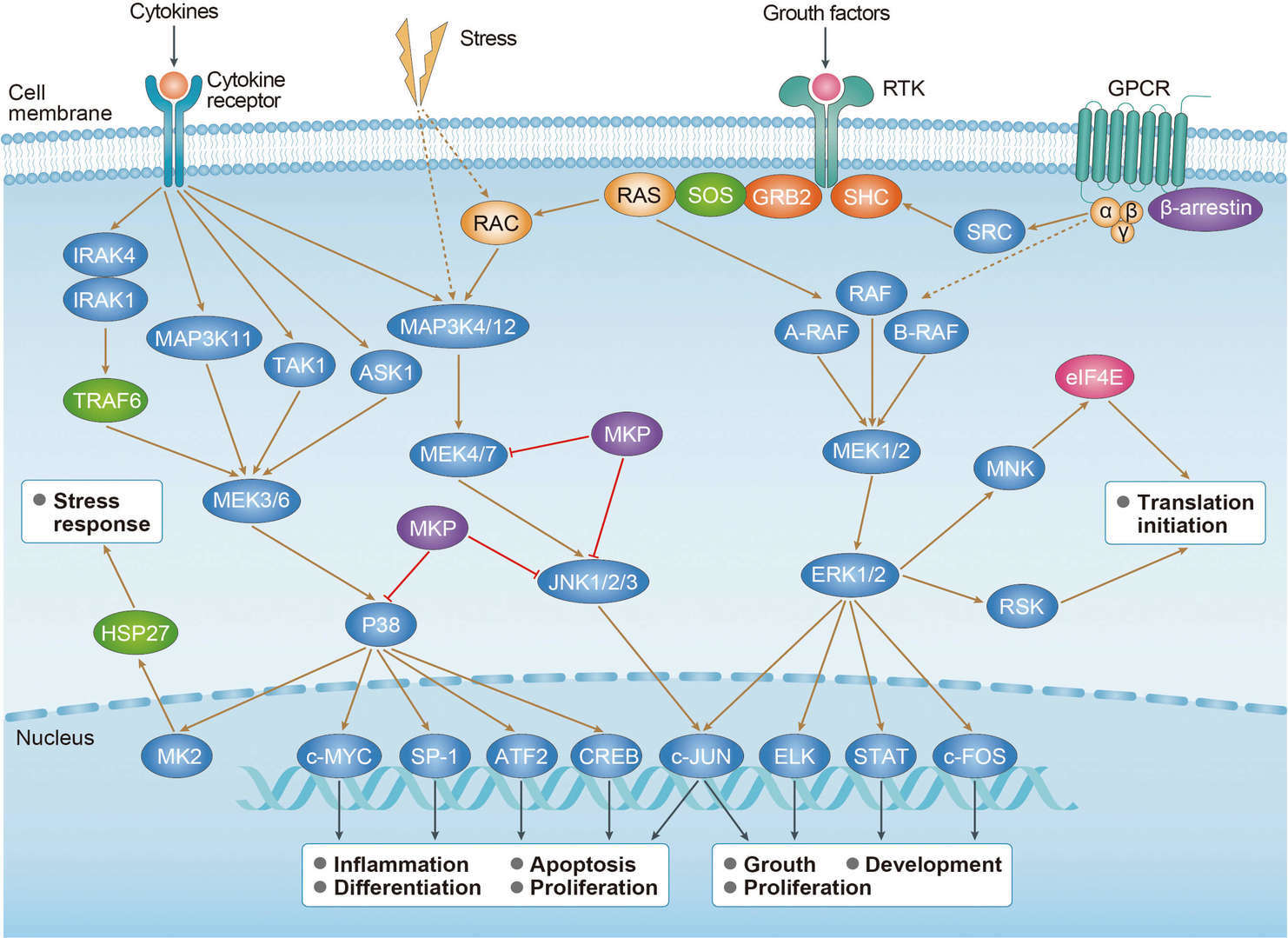 MAPK Signaling Pathway
MAPK Signaling Pathway
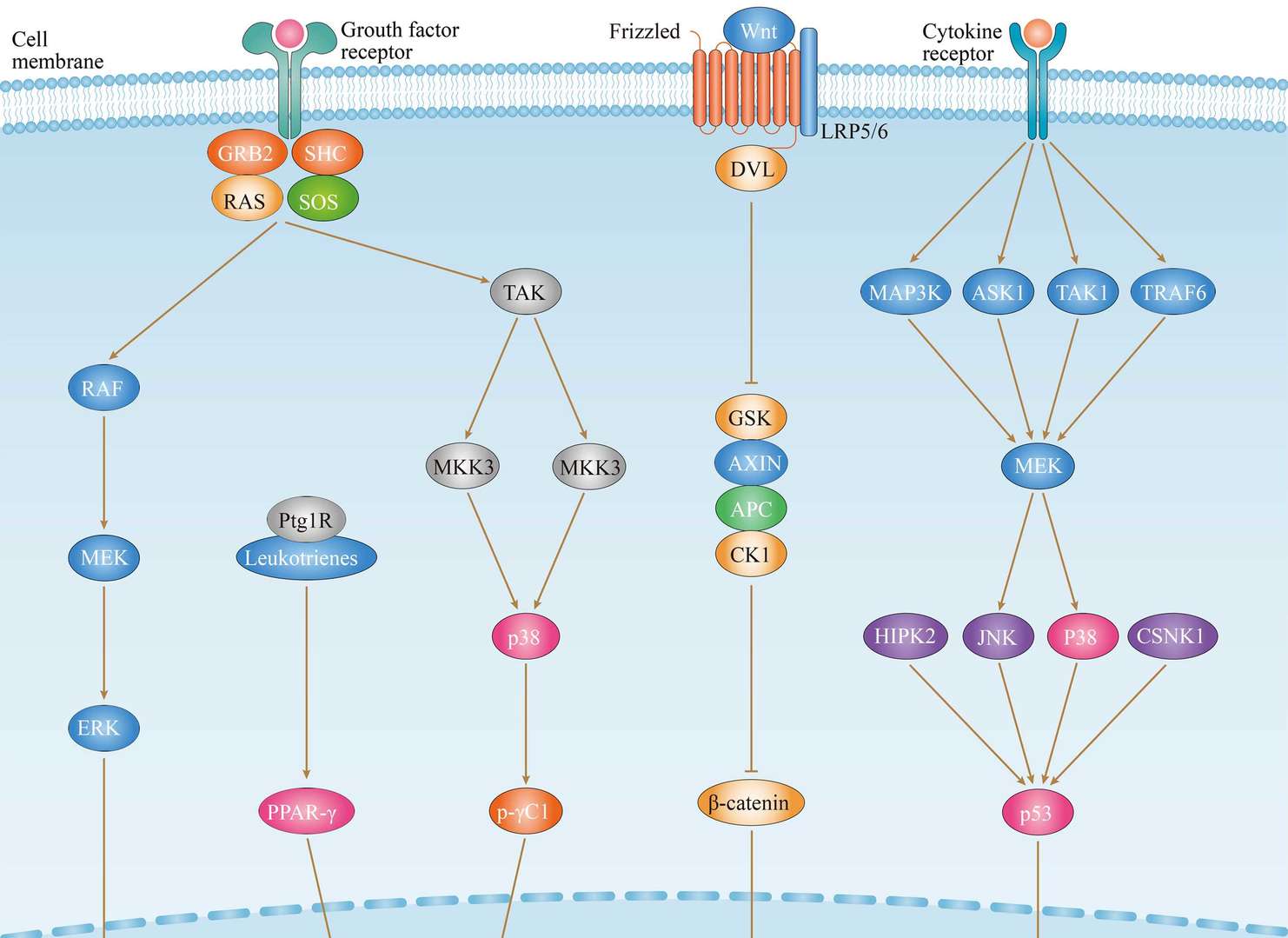 Throid Cancer
Throid Cancer
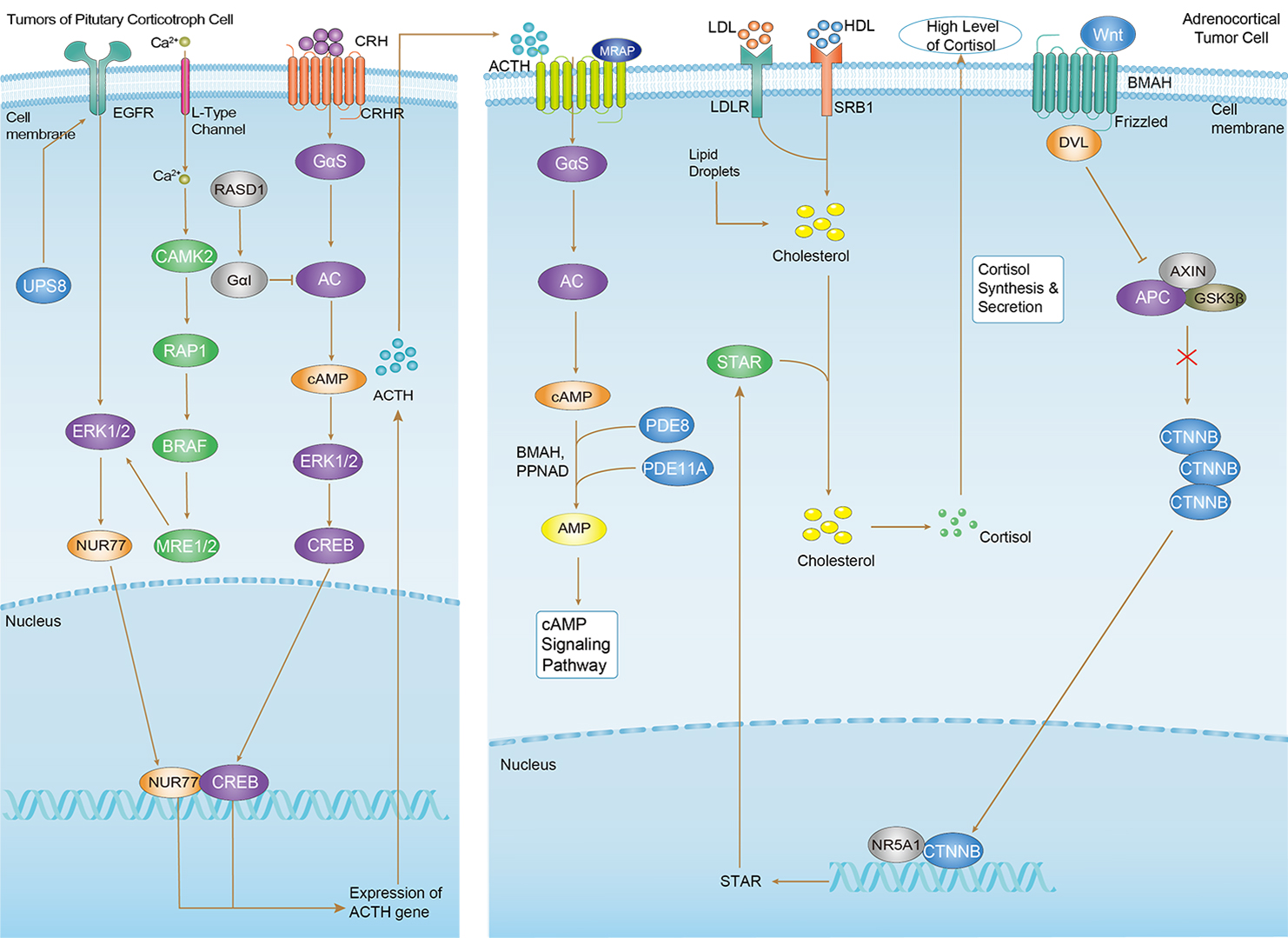 Cushing Syndrome
Cushing Syndrome

