Tumor Tissue Targeting Antibody-coupled Liposome Development Service
Antibody-coupled liposomes for tumor tissue show promising therapeutic potential. By enabling targeted delivery and reducing side effects, Creative Biolabs offers a more precise approach to cancer treatment. We meticulously manage your project, from selecting the ideal antibodies to identifying the best conjugation chemistry, ensuring every detail is addressed with precision and care.
Antibody-coupled Liposomes Technology
As a leading Contract Research Organization (CRO) company, Creative Biolabs is committed to offering customized conjugation services to meet your specific project requirements. We specialize in antibody-liposome conjugation to fulfill your unique needs.
Antibody-coupled liposomes possess the ability to identify target cells at the molecular level, effectively destroying pathological cells. As an innovative drug delivery system, immunoliposomes combine the advantages of both liposomes and targeted antibodies, which helps to reduce drug accumulation in normal tissues, enhance therapeutic effects, and minimize toxicity. They can serve as carriers for chemotherapeutic agents, radiotherapeutic drugs, gene therapy agents, and tumor imaging diagnostics, making them widely applicable in targeted tumor treatment and detection, thereby demonstrating significant promise in clinical oncology.
Creative Biolabs provides a range of methods for preparing antibody-conjugated liposomes. Common targeting molecules include antibodies, antibody fragments, small peptides, glycoproteins, and receptor ligands. In selecting antibodies, we will consider factors such as their ability to mediate effects on adipocytes, immunogenicity, stability, and purification.
Up to now, we have developed various systems for the binding of antibodies or their fragments to liposomes, with chemical conjugation methods using reactive functional groups being the most common. For instance, antibodies can bind to lipid materials such as phospholipids through their functional groups or via crosslinking agents that contain reactive groups. At the same time, phospholipid materials can also directly bind to antibodies using functionalized phospholipid derivatives or crosslinking agents with active groups.
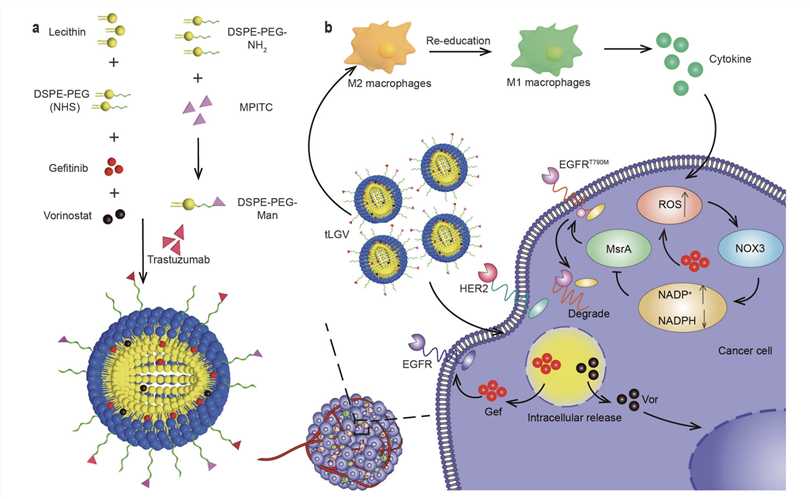 Fig.1 The Liposome Structure and Immunotherapy mechanism.1,3
Fig.1 The Liposome Structure and Immunotherapy mechanism.1,3
Tumor Tissue Targeting Antibody-coupled Liposome Solutions
Recently, the antibody-conjugated liposome platform developed by Creative Biolabs has emerged as an innovative cancer treatment strategy. This approach targets cancer cells by linking antibodies with drugs, thereby minimizing damage to normal cells. We offer a range of solutions for antibody-conjugated liposomes targeting tumor tissues:
- Targeting Mechanism
Selective Targeting: Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) specifically identify antigens on the surface of tumor cells, thereby enhancing the concentration of the drug at the tumor site.
Targeted Delivery: Antibody-conjugated liposomes effectively transport drugs directly to tumor cells while reducing systemic toxicity.
- Antibody-coupled Liposome Design
Antibody Selection: Choosing antibodies that specifically bind to tumor-associated antigens, such as HER2 or CD20 tumor markers, is crucial.
Drug Selection: Commonly used drugs include chemotherapy agents, cytotoxic drugs, or small molecule targeted therapies, ensuring stable covalent binding with the antibodies.
Liposome Preparation: Liposomes are prepared through methods such as sonication or self-assembly to ensure effective drug encapsulation and controlled release. Optimize the liposome particle size to enhance targeting and permeability, with an ideal range typically between 100-200 nm.
- Antibody-coupled Liposome Development
Coupling Assays: Common techniques include disulfide bond coupling and amine coupling, ensuring the appropriate ratio of antibody to drug to achieve optimal therapeutic efficacy.
Stability studies: Conduct long-term stability studies, including storage conditions and freeze-thaw cycles, to evaluate the stability of liposomes after antibody coupling.
Quality Control System: Monitoring coupling efficiency, fluorescence, and drug release characteristics is essential to optimize the preparation process.
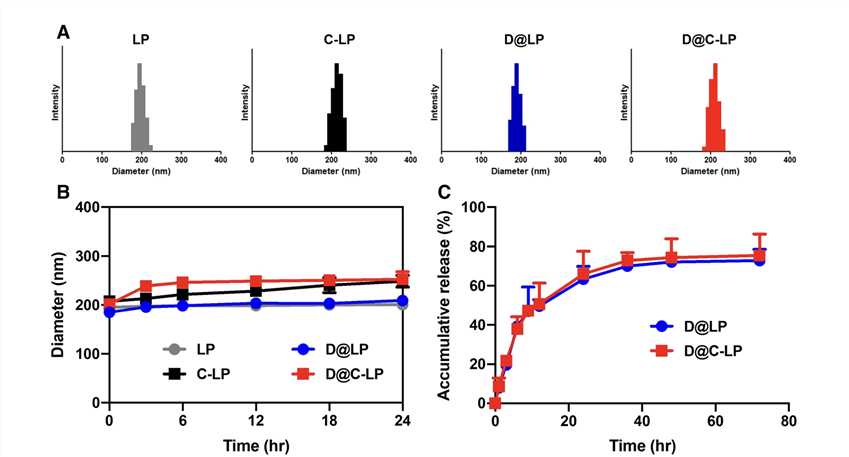 Fig.2 Liposomes Characterization.2,3
Fig.2 Liposomes Characterization.2,3
Case Study
In our labs, we typically prepare liposomes using methods such as film hydration and sonication, followed by ultrafiltration to remove any unencapsulated drugs. We then activate the antibodies using chemical methods, such as the EDC/NHS method, to enable their binding to the surface of the liposomes. Once activated, the antibodies are coupled with the liposomes under specific conditions to form stable antibody-conjugated liposomes.
We assess the drug release rate and its cytotoxic effects on target cells under simulated physiological conditions. Moreover, we validate the selective binding and internalization of the antibody-conjugated liposomes in tumor cells using techniques such as flow cytometry. So far, we have assisted our clients in developing an anti-HER2 antibody-conjugated liposome for the treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer. Our data from mouse models indicate that this conjugated liposome effectively targets tumor cells while significantly reducing toxicity to normal cells.
- Enables the selective recognition and binding of tumor cells;
- Enhances the solubility and stability of drugs to prevent premature release within the body;
- Reduces toxicity to non-target cells;
- Facilitates imaging and monitoring of tumor tissues;
- Overcomes drug resistance in traditional chemotherapy.
Creative Biolabs leverages advanced technologies to develop antibody-coupled liposomes that improve efficacy while reducing side effects. By merging the precision of antibodies with the strength of liposomes, we create powerful therapeutic agents aimed at precisely targeting and eliminating cancer cells. Regardless of your needs, we have the technology and expertise to deliver exceptional products. If you have any questions, feel free to contact us.
- Gao, Ang, et al. "Overview of recent advances in liposomal nanoparticle-based cancer immunotherapy." Acta Pharmacologica Sinica 40.9 (2019): 1129-1137.
- Bang, Chaeeun, et al. "Liposomes targeting the cancer cell-exposed receptor, claudin-4, for pancreatic cancer chemotherapy." Biomaterials Research 27.1 (2023): 53.
- Distributed under Open Access license CC BY 4.0, without modification.
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

