Sonepcizumab Overview
Introduction of Sonepcizumab
Sonepcizumab (also known as LT1009) is a humanized monoclonal antibody from mouse directed against sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P), the extracellular ligand for the G protein-coupled lysophospholipid receptor EDG-1 (endothelial differentiation gene-1), with potential antiangiogenic and antineoplastic activities. Sphingomab can absorb S1P from the extracellular fluid, thereby lowering the effective concentration of S1P. Upon administration, sonepcizumab binds S1P, which may result in the inhibition of tumor angiogenesis. For the treatment of several diseases. Sonepcizumab is an experimental anti-S1P monoclonal antibody that has had a phase II clinical trial for renal cell carcinoma.
Mechanism of Action of Sonepcizumab
The bioactive lysolipid signaling molecule sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) is a little-explored target for antitumor treatment. Evidence suggests that S1P may play a major regulatory role in tumor biology by having direct effects both on tumor-associated angiogenesis and on the tumor cells themselves. S1P is a mediator of tumor cell proliferation and protects tumor cells from apoptosis through the activation of survival pathways. The balance between S1P and ceramide/sphingosine (CER/SPH) levels, the upstream precursors of S1P, is believed to provide a rheostat mechanism that determines whether a cell proliferates or undergoes apoptosis. The key regulatory enzyme of the rheostat mechanism is sphingosine kinase (SPHK), whose role is to convert the death-promoting sphingolipids (CER/SPH) into the growth-promoting S1P. S1P contributes to angiogenesis by stimulating DNA synthesis, chemotactic motility, and capillary tube formation of endothelial cells (ECs) and bone marrow-derived EC precursors, processes that contribute to early blood vessel formation. The capillary tube formation induced by S1P is comparable to that of the well-known proangiogenic mediators basic fibroblastic growth factor (bFGF) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). Furthermore, S1P elicits synergistic effects with these growth factors to promote development of vascular networks in vivo. Recently, crosstalk between S1P and other proangiogenic growth factors such as VEGF, EGF, PDGF, bFGF, and IL-8 has been reported. Since S1P is required for the optimal activity of multiple proangiogenic factors, S1P is a promising target for novel therapeutic approaches. Sonepcizumab is a humanized anti-S1P monoclonal antibody that can bind to S1P, thereby limiting the amount of free S1P molecules in tissues and reducing fibrotic activity. Sonepcizumab has high affinity for S1P and acts as a molecular sponge to reduce S1P signaling in nonclinical models. Lowering the interstitial concentration of S1P in tumors could provide a less favorable growth environment for cancer cells by decreasing angiogenesis, while decreasing proliferation and metastatic potential and increasing sensitivity to apoptosis.
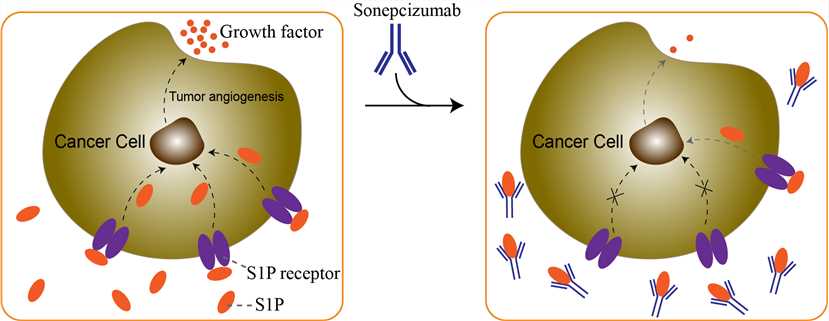
Fig.1 Mechanism of action of Sonepcizumab
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.



