Dot Blot Protocol & Troubleshooting
Dot blot is a simple and rapid technique for the detection of proteins. It is similar to western blotting, but does not require separation by electrophoresis. It is a procedure in which the sample is applied directly to a spot on the membrane and then the blotting procedure is performed. This saves significant time but does not provide information on the size of the target protein.
If your goal is to simply detect the presence of the target protein and you have purified samples of the target protein and specific antibodies. Then you can use dot blot as the technique of choice. Creative Biolabs provides a good general protocol. As well as on this page we share with you some experimental troubleshooting tips on dot blot.
For a quick and comprehensive selection of antibodies, check out our product list.
Solutions and Reagents
| Stages | Solutions and Reagents |
| Membrane Preparation | Blocking buffer, dilution buffer, membrane washing buffer |
| Blotting | Primary antibody, secondary antibody, antibody dilution buffer, membrane washing buffer, substrate |
Dot Blot Procedure
Dot blot is a simplified method that is also based on the principle of antibody recognition and binding to antigen. It can be used to determine the presence of a target protein in a sample or whether an antibody is effective. The following protocol is a good general method for each researcher to build their own experimental protocol.
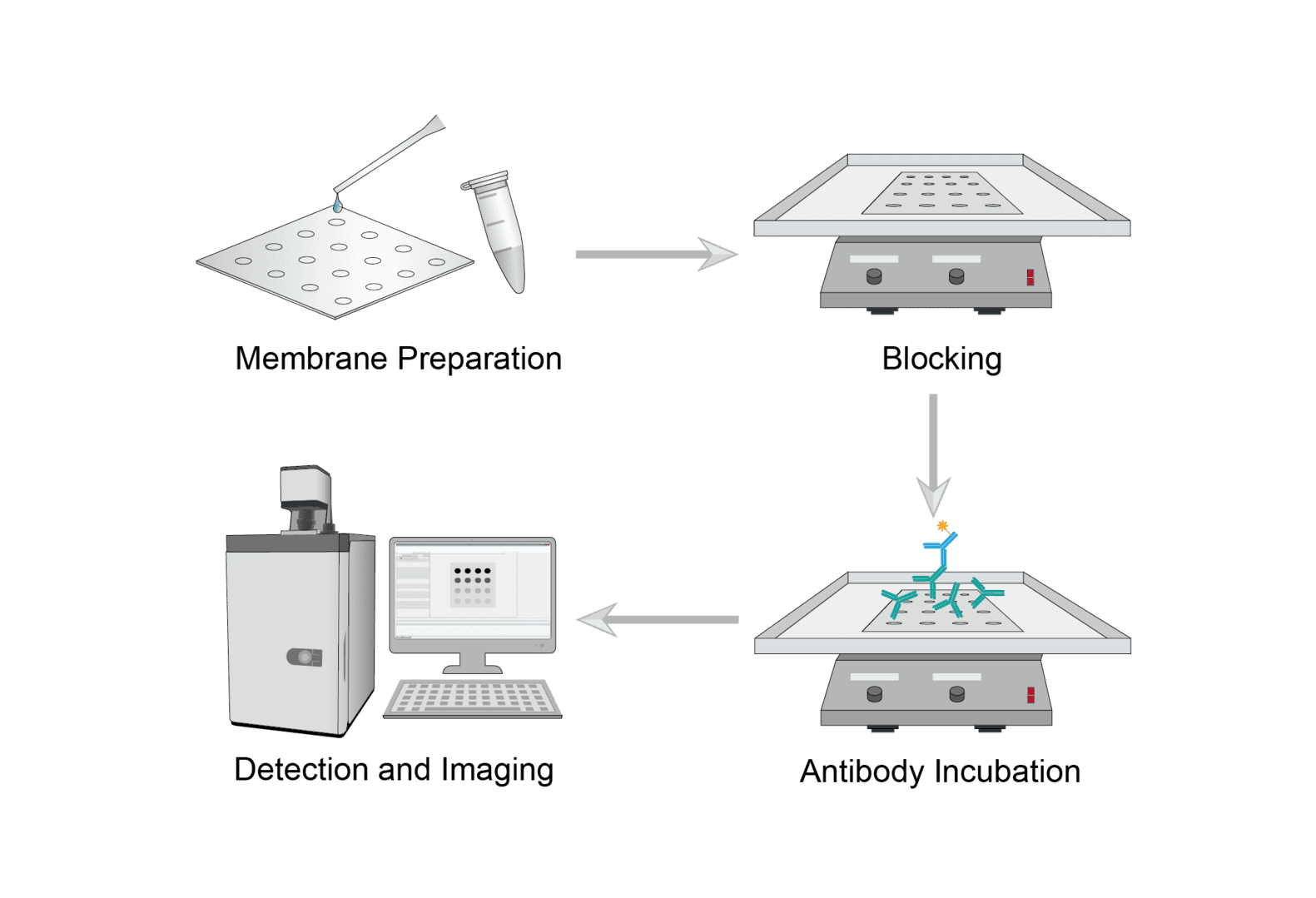
Cut a suitable piece of nitrocellulose membrane according to the sample size. Mark the membrane so that you can track the blotted samples. Secure the blotting membrane to prevent curling. Slowly aspirate the prepared sample onto the membrane at a defined location. Allow the membrane to dry.
Select the appropriate blocking buffer. Use an excess amount of blocking buffer to completely cover the membrane. Shake for blocking at room temperature. Decant the blocking solution and rinse the membrane several times with wash buffer.
Dilute the antibody with dilution buffer. Cover the membrane with sufficient diluted primary antibody solution and incubate on a rotary shaker. Discard the diluted primary antibody and wash several times with wash buffer. After washing, incubate the membrane with diluted secondary antibody. After incubation is complete, discard the diluted antibody solution and repeat the wash.
Select the appropriate substrate for incubation. Pick up the blotting membrane to drain excess reagent for chemiluminescence/fluorescence detection.
Troubleshooting
In this section, we will discuss the problems that can arise when performing dot blot techniques. In particular, how to avoid low signal, high background and non-specific binding.
Weak signal
- Sample causes. One reason for seeing a lack of signal could be a lack of protein. This may come from improper sample preparation. When homogenizing samples, be sure to do so on ice, as well as using an appropriate ice-cold buffer. If you know that your protein is located in a specific compartment, be sure to use lysis conditions that enrich the protein in that compartment.
- Blocking causes. The initial blocking of the membrane is very important. Excessive blockage can lead to poor binding and problems in detecting antigens. We typically block for 1 hour. Or you can use a proprietary blocking solution.
- Antibody causes. If an unsuitable antibody is used, either primary or secondary antibody, the signals will not show up. Low concentrations of antibodies may result in weak signals, and increase the exposure time to help make clearer.
- Incubation causes. When incubating antibodies, BSA or skim milk is typically used. This may mask the antigen, so should be used in reduced amounts when this occurs.
- Reagent and solution causes. Check the quality of the reagents and solutions used and make sure that the buffer solution is not contaminated.
- Washing causes. Long wash times can also lead to weakening of the signal. We recommend that you take the correct washing procedure.
High background
- Antibody concentration causes. Due to the high antibody concentration, the antibody will bind to the PVDF membrane. We recommend that you preferably serial dilution of your samples and antibodies. This can help you determine the optimal antibody and sample concentrations for dot blot and reduce background.
- Blocking causes. The initial blocking of the membrane is very important. Insufficient closure (too short a time in the closure buffer) can lead to non-specific binding of primary and secondary antibodies and result in very high background.
- Washing causes. A high background may be due to the presence of excess antibodies still present. To ensure that the signal you observe is due to the binding of your target antigen and antibody and not excess antibody, you can add a proper washing step as appropriate.
Dot blot is basically a simplified approach to western blotting, so the troubleshooting that applies to western blotting also applies to dot blot. The time you can spend trying various conditions can help you avoid some headaches. In addition, it can save you the trouble of repeating the experiment unnecessarily.
We provide a general workflow for the simple capture of proteins onto membranes by dot blotting techniques. The method described is a simple and fast process. We hope that we have provided relevant support and resources to help you understand the dot blotting technique.
Antibodies play a crucial role in this technique, so you can check our related products and choose the right antibody for your experiment.
Products with Tested Data
At Creative Biolabs, we are dedicated to providing high-quality antibodies for various research applications. Each product in our extensive range has been rigorously tested to ensure superior reliability and efficacy. To showcase the performance of our antibodies, we have conducted numerous experiments using the Dot Blot assay. Below, you will find a table listing a selection of our antibody products along with images from these experiments, demonstrating their proven reliability.
| Product Name | Catalog Number | Target | Image | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Recombinant Human Anti-SARS-CoV Antibody (HuMAb 03-014) | HPAB-0297CQ | SARS-CoV |

|
Dot Blot analysis of HPAB-0297CQ was performed by coating with Human SARS Coronavirus Spike Protein (S1 Subunit, His Tag). HPAB-0297CQ incubation concentration: 2ng/μL. The secondary antibody: HRP-Anti-Human IgG (H+L) |
| Human Anti-TNFRSF17 Recombinant Antibody (TAB-1219CL) | TAB-1219CL | TNFRSF17 |

|
Antigen: Recombinant human TNFRSF17 protein Antibody incubation concentration: 2ng/μL. The secondary antibody: HRP-conjugated goat anti-human IgG |
| Recombinant Human Anti-IAV HA Antibody (PABC-393) | PABC-393 | IAV HA |

|
Dot Blot analysis of PABC-393 was performed by coating with Antigen Influenza A H3N2 (A/Perth/16/2009) Hemagglutinin / HA Protein (His Tag). PABC-393 incubation concentration: 2 ng/μL. The secondary antibody: HRP-Goat Anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) |
| Human Anti-IAV HA Recombinant Antibody (PABJ-0204) | PABJ-0204 | IAV HA |

|
Dot Blot analysis of PABJ-0204 was performed by coating with Influenza A H1N1 (A/Brevig Mission/1/1918) Hemagglutinin Protein (HA1 Subunit) (His Tag). PABJ-0204 incubation concentration: 2 ng/μL. The secondary antibody: HRP-Anti-Human IgG (H+L) |
| Anti-IAV HA Recombinant Antibody (TAB-027ML) | TAB-027ML | IAV HA |

|
Dot Blot analysis of TAB-027ML was performed by coating with Influenza A H3N2 (A/Perth/16/2009) Hemagglutinin / HA Protein (His Tag). TAB-027ML incubation concentration: 2 μg/mL. HRP-conjugated goat anti-Human IgG as a secondary antibody (1: 2000) |
| Recombinant Human Anti-IAV HA Antibody (FI6V3) | PABL-214 | HA |

|
Dot Blot analysis of PABL-214 was performed by coating with Influenza A H2N2 (A/Japan/305/1957) Hemagglutinin / HA Protein (His Tag). PABL-214 incubation concentration: 2 μg/mL. HRP-conjugated goat anti-human IgG as a secondary antibody (1: 2000) |
| Anti-Human NGF Recombinant Antibody (TAB-111) | TAB-111 | NGF |

|
DB analysis of TAB-111 was performed with recombinant human NGF protein. NC: Negative control PC: Positive control |
| Mouse Anti-C5 Recombinant Antibody (clone BB5.1) | HPAB-0128CQ | C5 |

|
Dot blot analysis of HPAB-0128CQ was performed with with Mouse C5 protein (His Tag). HPAB-0128CQ incubation concentration: 2 ng/μL. The secondary antibody: HRP-IgG (H+L) NC : Negative control PC : Positive control |
| Rat Anti-IL18 Recombinant Antibody (clone 2C10); scFv Fragment | HPAB-0067-YC-S(P) | IL18 |
-1.jpg)
|
Dot Blot analysis of HPAB-0067-YC-S(P) was performed by coating with human IL18 protein (His tag). HPAB-0067-YC-S(P) incubation concentration: 2 μg/mL. HRP-conjugated goat anti-His tag as a secondary antibody (1: 2000) |
| Human Anti-IL13RA2 Recombinant Antibody (TAB-0158CL) | TAB-0158CL | IL13RA2 |

|
Dot Blot analysis of TAB-0158CL was performed by coating with human IL13RA2 protein (His tag). TAB-0158CL incubation concentration: 2 μg/mL. HRP-conjugated goat anti-Human IgG was used as a secondary antibody (1: 2000) |
| Mouse Anti-MUC1 Recombinant Antibody (TAB-418MZ) | TAB-418MZ | MUC1 |

|
Dot Blot analysis of TAB-418MZ was performed by coating with human MUC1 protein (His tag). TAB-418MZ incubation concentration: 2 μg/mL. HRP-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG was used as a secondary antibody (1: 2000) |
| Afuco™ Anti-KIT Recombinant Antibody (AFC-450CL), ADCC Enhanced | AFC-450CL | KIT |

|
Dot Blot analysis of AFC-450CL was performed by coating with c-Kit Protein, Human, Recombinant (His Tag). The secondary antibody: HRP Goat Anti-Human IgG (H+L) |
| Mouse Anti-IL17RB Recombinant Antibody (HPAB-AP684-YC) | HPAB-AP684-YC | IL17RB |

|
Dot Blot analysis of HPAB-AP684-YC was performed by coating with human IL17RB protein (His tag). HPAB-AP684-YC incubation concentration: 2 μg/mL. HRP conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG as a secondary antibody (1: 2000) |
| Mouse Anti-IL17RB Recombinant Antibody; Fab Fragment (HPAB-AP684-YC-F(E)) | HPAB-AP684-YC-F(E) | IL17RB |
-1.jpg)
|
Dot Blot analysis of HPAB-AP684-YC-F(E) was performed by coating with human IL17RB protein (His tag). HPAB-AP684-YC-F(E) incubation concentration: 2 μg/mL. HRP conjugated Anti-His tag as a secondary antibody (1: 2000) |
| Recombinant Human Anti-HA Antibody (S9-1-10/5-1) | HPAB-N0125-YC | HA |

|
Dot Blot analysis of HPAB-N0125-YC was performed by coating with HA protein (His tag). HPAB-N0125-YC incubation concentration: 2 μg/mL. HRP conjugated Anti-human IgG as a secondary antibody (1: 2000) |
| Anti-Human FLT3 Recombinant Antibody (IMC-EB10) | TAB-291CL | FLT3 |

|
Dot Blot analysis of TAB-291CL was performed by coating with human FLT3 protein (His tag). TAB-291CL incubation concentration: 2 μg/mL. HRP-conjugated goat anti-Human IgG was used as a secondary antibody (1: 6000) |
| Anti-Human CLEC2D Recombinant Antibody | TAB-173CL | CLEC2D |

|
Dot Blot analysis of TAB-173CL-Fc silenced was performed by coating with human CLEC2D protein (CLD-H5253, acrobiosystems). TAB-173CL-Fc silenced incubation concentration: 2 μg/mL. HRP-conjugated goat anti-Human IgG as a secondary antibody (1: 2000) |
| Human Anti-AGR2 Recombinant Antibody (TAB-0708CLV) | TAB-0708CLV | AGR2 |

|
Dot Blot analysis of TAB-0708CLV was performed by coating with human AGR2 protein (His tag). TAB-0708CLV incubation concentration: 2 μg/mL. HRP-conjugated goat anti-Human IgG as a secondary antibody (1: 2000) |
| Anti-Human CD3 Recombinant Antibody (TAB-019) | TAB-019 | CD3E |

|
Dot Blot analysis of TAB-019 was performed by coating with human CD3 protein (His tag). TAB-019 incubation concentration: 2 μg/mL. HRP-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG was used as a secondary antibody (1: 2000) |
| Human Anti-NECTIN4 Recombinant Antibody (TAB-H25) | TAB-H25 | NECTIN4 |

|
Dot Blot analysis of TAB-H25 was performed by coating with human NECTIN4 protein (His tag). TAB-H25 incubation concentration: 2 μg/mL. HRP-conjugated goat anti-Human IgG was used as a secondary antibody (1: 8000) |
| Mouse Anti-MSLN Recombinant Antibody (HPAB-0886-FY) | HPAB-0886-FY | MSLN |

|
Dot Blot analysis of HPAB-0886-FY was performed by coating with Human MSLN Protein (His Tag). HPAB-0886-FY incubation concentration: 2 μg/mL. HRP-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG as a secondary antibody (1: 2000) |
| Anti-Human NRP1 Recombinant Antibody (Vesencumab) | TAB-264 | NRP1 |

|
Dot Blot analysis of TAB-264 was performed by coating with human NRP1 protein (His tag). TAB-264 incubation concentration: 2 μg/mL. HRP-conjugated goat anti-Human IgG was used as a secondary antibody (1: 6000) |
| Rat Anti-IL18 Recombinant Antibody (clone 2C10); Fab Fragment | HPAB-0067-YC-F(E) | IL18 |
-1.jpg)
|
Dot Blot analysis of HPAB-0067-YC-F(E) was performed by coating with human IL18 protein (His tag). HPAB-0067-YC-F(E) incubation concentration: 2 μg/mL. HRP conjugated Anti-Rat IgG (H+L) as a secondary antibody (1: 3000) |
| Mouse Anti-MAPT Recombinant Antibody (NS-090CN) | NS-090CN | MAPT |

|
Dot Blot analysis of NS-090CN was performed by coating with human MAPT protein (His tag). NS-090CN incubation concentration: 2 μg/mL. HRP conjugated Anti-Mouse IgG as a secondary antibody (1: 2000) |
| Mouse Anti-CCR4 Recombinant Antibody (HPAB-1268WJ) | HPAB-1268WJ | CCR4 |

|
Dot Blot analysis of HPAB-1268WJ was performed by coating with human CCR4 protein (His tag). HPAB-1268WJ incubation concentration: 2 μg/mL. HRP-conjugated goat anti-Mouse IgG was used as a secondary antibody (1: 2000) |
| Humanized Anti-NCAM1 Recombinant Antibody (clone Lorvotuzumab) | TAB-188 | NCAM1 |

|
Dot Blot analysis of TAB-188 was performed by coating with human NCAM1 protein (His tag). TAB-188 incubation concentration: 2 μg/mL. HRP-conjugated goat anti-Human IgG was used as a secondary antibody (1: 6000) |
| Anti-ANGPT2 Recombinant Antibody | TAB-769 | ANGPT2 |

|
Dot Blot analysis of TAB-769 was performed by coating with human ANGPT2 protein (His tag). TAB-769 incubation concentration: 2 μg/mL. HRP-conjugated goat anti-Human IgG was used as a secondary antibody (1: 6000) |
| Mouse Anti-SIGLEC15 Recombinant Antibody (HPAB-N0240-YC) | HPAB-N0240-YC | SIGLEC15 |

|
Dot blot analysis of HPAB-N0240-YC was performed with Recombinant human SIGLEC15 Protein (ECD, His Tag). HPAB-N0240-YC incubation concentration: 2 ng/μL. The secondary antibody: HRP-Goat Anti-Mouse IgG (H+L) Antigen: 10 ng - 60 ng |
| Rat Anti-IL18 Recombinant Antibody (clone 2C10) | HPAB-0067-YC | IL18 |

|
Dot Blot analysis of HPAB-0067-YC was performed by coating with human IL18 protein (His tag). HPAB-0067-YC incubation concentration: 2 μg/mL. HRP-conjugated goat anti-Rat IgG as a secondary antibody (1: 2000) |
| Anti-Human DKK1 Recombinant Antibody (BHQ880) | TAB-214CL | DKK1 |

|
Dot Blot analysis of TAB-214CL was performed by coating with human DKK1 protein (His tag). TAB-214CL incubation concentration: 2 μg/mL. HRP-conjugated goat anti-Human IgG was used as a secondary antibody (1: 2000) |
| Anti-Human selectin P Recombinant Antibody (Inclacumab) | TAB-246 | SELP |

|
Dot Blot analysis of TAB-246 was performed by coating with human Selectin P antigen. TAB-246 incubation concentration: 2 ng/μL. The secondary antibody: HRP-Anti-Human IgG (H+L) |
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

