Multiplex Bead based Assay Protocol & Troubleshooting
A multiplex assay is an immunoassay, and it is a derivative of ELISA. It uses beads bound to a capture antibody for the assay, where each bead is specifically recognizable. This method allows multiple analyses to be measured simultaneously in a single experiment.
Creative Biolabs offers bead-based multiplex assay services that can detect and quantify multiple biomarker proteins in the provided samples. We describe protocols for optimal bead-based multiplex analysis and various troubleshooting techniques during the assay to ensure actionable and high-quality results.
Solutions and Reagents
| Stages | Solutions and Reagents |
| Sample Preparation | Samples, standards, wash buffer, and dilution buffer |
| Assay Procedure | Antibody-coupled beads, dilution buffer, wash buffer, biotinylated antibody, SA-PE solution, and assay buffer |
Multiplex Bead-Based Assay Procedure
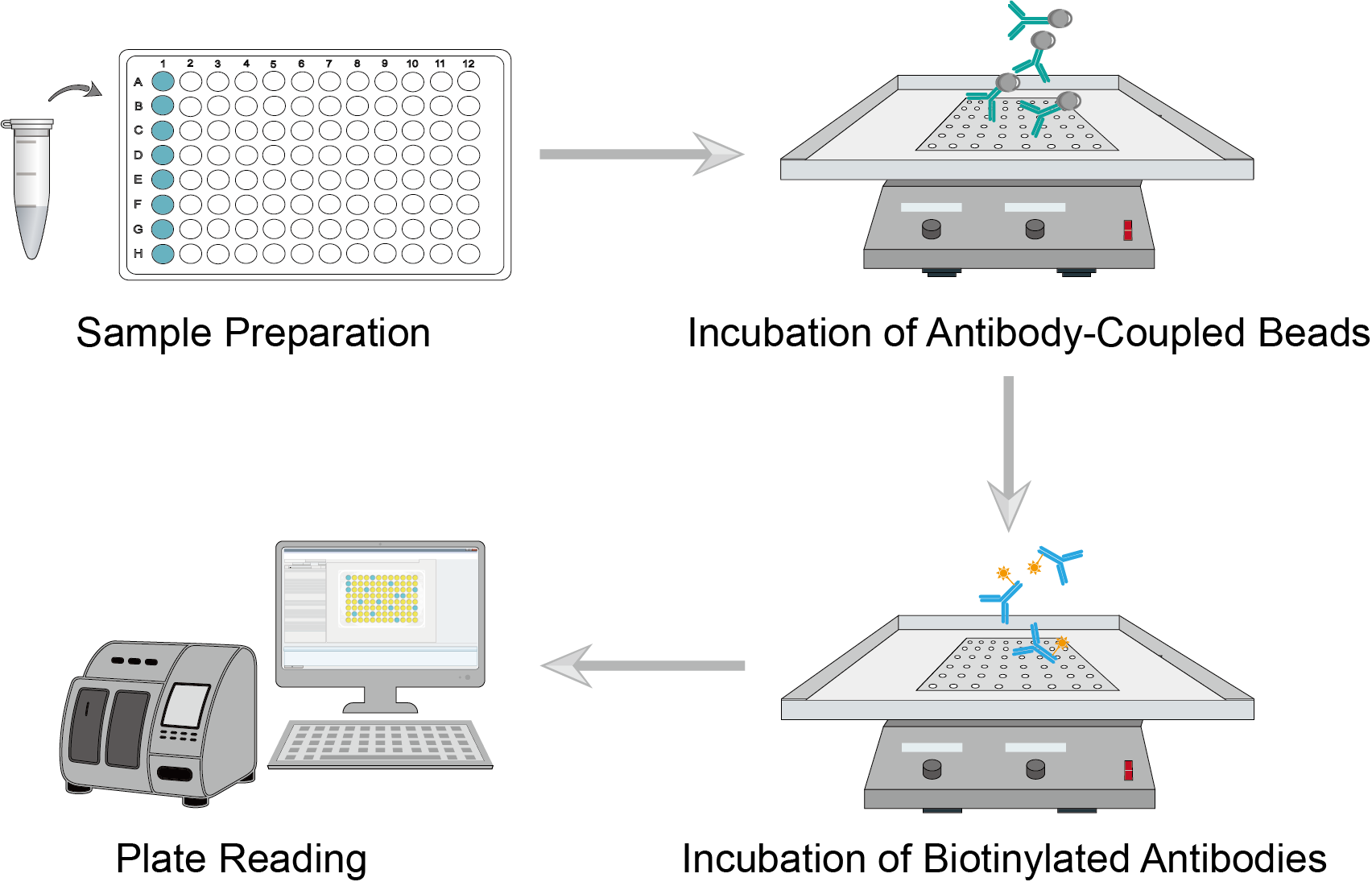 Figure 1: Live Cell Imaging Procedure
Figure 1: Live Cell Imaging Procedure
A multiplex assay can analyze a variety of biological samples, including serum, plasma, tissue, cell lysates, etc. Collect samples and analyze them shortly thereafter. When taking samples from frozen conditions, thaw the sample to avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles. Dilute the sample appropriately with buffer and vortex the sample for a few seconds to mix the sample well. Prepare standards and dilute, and then vortex for a few seconds to mix well.
Prepare antibody-coupled beads and dilute them using assay buffer. Vortex the diluted beads for a few tens of seconds and add an equal amount of the solution to each well. Gently vortex the prepared standards, blanks, samples, and controls, and add equal amounts of samples to the corresponding wells. Seal the plate and incubate it on a microplate shaker. After incubation, wash the plate and repeat several times.
Prepare a biotinylated detection antibody and dilute it using an antibody diluent. Add equal dilutions of the biotinylated detection antibody to each well. Seal the plate and incubate it on an oscillator. Wash and repeat several times after the incubation is complete. Add an equal amount of streptavidin (SA-PE) solution to each well. Seal the plate, cover it with aluminum foil, and incubate it on an oscillator.
Centrifuge or apply a magnetic field to precipitate the complex. Aspirate the contents of each well, then add wash buffer to each well, leave to wash, and aspirate the contents again. Repeat the wash again. Add quantitative assay buffer to each well and mix on a shaker to resuspend the antibody beads. Read the plate immediately using the bead-based multiplex assay plate reader.
Troubleshooting
As with any technique, generating accurate and reproducible data requires adequate experimental planning, optimization, and attention to detail. We provide you with some troubleshooting tips and hints for multiplex analysis experiments. This information will put you on the right path to produce accurate, efficient, and biologically relevant results.
High signals
- Incubation causes. The incubation time of the samples on the plate is too long. We recommend a shorter appropriate incubation time.
- Instrument causes. Instrument calibration target values set too high may result in a high signal. For some instruments, the default target setting for the calibrator is a high target value. You should calibrate with a low target value and reanalyze the plate.
Signals are out of range
- Sample causes. This may be an analyte that is absent or below the detectable level in the sample.
High signal variation
- Well contamination causes. Cross-well contamination causes variance. When reusing the plate sealer, check that no reagents are touching the plate sealer. When using the same pipette tips as for adding reagents, you should take care that the pipette tips do not touch the reagents in the plate.
- Incubation causes. Inadequate mixing during plate incubation causes. The plates should be agitated during all incubation steps using a vertical plate shaker. The speed should be such that the beads are in constant motion without causing spattering.
- Plate washing causes. The sample may have high levels of particulate matter or other interfering substances. You should confirm that all reagents are completely removed during all washing steps.
High background
- Background well contamination causes. We recommend the appropriate use of a well sealer to avoid cross-well contamination. And use a multichannel pipette to pipette without touching the reagents in the plate.
- Washing causes. It may be the cause of insufficient washing. You need to increase the number of washes.
Insufficient bead count
- Sample causes. This may be due to sample particulate matter or viscosity. It should be sonicated and vortexed appropriately.
- Bead mixture causes. The bead mixture was improperly prepared. According to the protocol, the beads are sonicated and vortexed prior to the addition of the bead mixture. The bead mixture should also be intermittently agitated when transferred to the plate.
You can follow the tips and guidance we provide, which will enable you to better optimize your multiplex analysis. Creative Biolabs offers bead-based multiplex analysis services, including a wide range of optimized protocol solutions, instruments, and analysis software. We aim to provide you with high-quality analytical data quickly and efficiently.
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

