SDS-PAGE Protocol & Troubleshooting
Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) is a fundamental technique used to separate proteins based on their molecular weight. This method is essential for protein analysis, providing information about protein size, purity, and relative abundance in complex biological samples.
Here we go over the SDS-PAGE protocols, including the reagents, solutions, procedures, and troubleshooting advice for typical issues. Our aim is to help you understand and explain the protocol processes and take full advantage of the detailed protocols for western blot.
Solutions and Reagents
| Stages | Solutions and Reagents |
| Preparation | Sample buffer, SDS solution, reducing agent (DTT or β-mercaptoethanol) |
| Gel Preparation | Acrylamide/bis-acrylamide solution, stacking gel buffer, resolving gel buffer, APS, TEMED |
| Electrophoresis | Running buffer, molecular weight markers |
| Visualization | Staining solution (Coomassie or silver stain), destaining solution |
Workflow
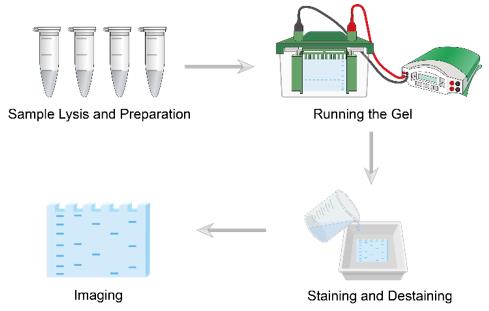 Workflow of SDS-PAGE
Workflow of SDS-PAGE
Prepare the resolving gel solution with appropriate acrylamide concentration based on protein size range. Add APS and TEMED to initiate polymerization. Once set, prepare and pour the stacking gel on top. Insert the comb immediately and allow to polymerize completely.
Mix protein samples with sample buffer containing SDS and reducing agent. Heat samples at 95-100°C for 3-5 minutes to denature proteins. Centrifuge briefly to remove any precipitates. Load samples and molecular weight markers into gel wells.
Fill the electrophoresis chamber with running buffer. Connect to power supply and run at appropriate voltage. Monitor the dye front and stop when it reaches the bottom of the gel.
Remove gel from glass plates carefully. Stain with Coomassie Brilliant Blue or silver stain. Destain until protein bands are clearly visible against a clear background. Document and analyze results.
Troubleshooting
Despite the simplicity of the SDS-PAGE, problems may still arise such as poor band resolution. For some of the problems that may occur, we provide the following troubleshooting guide.
- Poor Band Resolution
Common causes include incorrect acrylamide concentration for target protein size - select appropriate percentage based on molecular weight range; running the gel at too high voltage causing heat generation - reduce voltage or use cooling system; buffer depletion during long runs - replace with fresh buffer periodically; old or improperly stored acrylamide solutions affecting polymerization - use fresh reagents stored properly; inadequate sample denaturation - ensure complete heating and SDS binding.
- Smeared or Distorted Bands
Sample overloading can overwhelm gel capacity - reduce protein amount loaded; presence of nucleic acids or lipids in samples - perform additional purification steps; incomplete protein solubilization - optimize sample buffer composition or add solubilizing agents; high salt concentration interferes with migration - desalt or dilute samples; trapped air bubbles affect protein migration - degas solutions and pour carefully.
- Vertical Streaking
Protein precipitation in sample wells often results from insufficient SDS or high salt content - adjust buffer composition accordingly; inadequate sample heating causes incomplete denaturation - ensure proper heating time and temperature; protein aggregation may occur - consider adding urea or other solubilizing agents; contamination of wells with polyacrylamide fragments - clean wells thoroughly before loading; improper loading technique causes spillover - use proper loading tips and technique.
- Uneven Migration Across Gel
Uneven polymerization results from improper mixing of gel solution - mix thoroughly before pouring; temperature gradients during electrophoresis - ensure consistent temperature or use cooling; uneven buffer levels between chambers - check and adjust buffer volumes; electrical field distortion from buffer leaks - check apparatus for leaks; warped gel plates create uneven thickness - use properly leveled casting stand.
- No Bands Visible
Insufficient protein loading requires concentration adjustment - increase sample volume or concentrate proteins; proteins not retained during staining - check staining protocol and timing; expired or improperly prepared staining reagents - use fresh solutions; protein degradation from protease activity - add protease inhibitors during sample preparation; proteins running off gel - select appropriate gel percentage for target molecular weight.
- Ghost Bands
Carry-over contamination from previous samples requires thorough cleaning between runs; degradation products indicate proteolysis - add protease inhibitors and work quickly; non-specific staining of gel impurities - filter gel solutions before casting; artifacts from improper gel handling - use clean equipment and handle carefully; contaminated reagents or buffers - prepare fresh solutions under clean conditions.
- Wavy Band Patterns
Trapped air bubbles during gel casting create uneven patterns - degas solutions and pour carefully; uneven polymerization from temperature variations - ensure consistent room temperature; electrical field disturbances from buffer discontinuities - check buffer composition and pH; mechanical vibration during run - place apparatus on stable surface; improper comb insertion causes gel distortion - insert comb straight and level.
- Poor Staining
Insufficient staining time or incorrect concentration requires protocol optimization; SDS interference with dye binding - include destaining step to remove excess SDS; over-destaining removes protein-bound dye - monitor destaining process carefully; incompatibility between protein type and staining method - try alternative staining protocols; expired or improperly prepared staining solutions - use fresh reagents stored properly. Insufficient staining time or incorrect concentration requires protocol optimization; SDS interference with dye binding - include destaining step to remove excess SDS; over-destaining removes protein-bound dye - monitor destaining process carefully; incompatibility between protein type and staining method - try alternative staining protocols; expired or improperly prepared staining solutions - use fresh reagents stored properly.
Products with Tested Data
At Creative Biolabs, we are dedicated to providing high-quality antibodies for various research applications. Each product in our extensive range has been rigorously tested to ensure superior reliability and efficacy. To showcase the performance of our antibodies, we have conducted numerous experiments using SDS-PAGE. Below, you will find a table listing a selection of our antibody products along with images from these SDS-PAGE experiments, demonstrating their proven reliability.
| Product Name | Catalog Number | Target | Image | Description |
| Mouse Anti-Psa Recombinant Antibody; Fab Fragment (HPAB-3383LY-F(E)) | HSP90AB1 | Psa |
-1.png)
|
SDS-PAGE analysis of HPAB-3383LY-F(E) in non-reduced (Lane 1) and reduced (Lane 2) conditions. Gel stained for 30 minutes with Coomassie Blue. As a result of different β-mercaptoethanol-reduced proteins migrate as about 25 kDa. And non-reduced protein migrates as 50 kDa. |
| Human Anti-PCSK9 Recombinant Antibody (HPAB-667-FY) | IκB β | PCSK9 |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of HPAB-667-FY in non-reduced (Lane 2) and reduced (Lane 1) conditions. |
| Human Anti-CD4 Recombinant Antibody (HPAB-J0050-YC) | H3F3A (Tri Methyl Lys79) | CD4 |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of HPAB-J0050-YC in reduced (Lane 1) and non-reduced (Lane 2) conditions. |
| Mouse Anti-FSTL3 Recombinant Antibody (HPAB-N0094-YC) | HSP70 | FSTL3 |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of HPAB-N0094-YC in non-reduced (Lane 1) and reduced (Lane 2) conditions. |
| Human Anti-GPIb Recombinant Antibody (clone HIb-6) | H3F3A | GPIb |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of HPAB-S0057-YC in non-reduced (Lane 2) and reduced (Lane 1) conditions. |
| Human Anti-HLA-A2-Mart-1 Complex Recombinant Antibody (clone CLA12) | CASP3 | HLA-A2-Mart-1 Complex |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of HPAB-N0135-YC in non-reduced (Lane 2) and reduced (Lane 1) conditions. |
| Recombinant Human Anti-DENV E proteins Antibody (PABL-065) | LC3A | DENV E proteins |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of PABL-065 in non-reduced (Lane 1) and β-mercaptoethanol-reduced (Lane 2) conditions. |
| Mouse Anti-DOTA Recombinant Antibody (HPAB-1251WJ) | LTF | DOTA |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of HPAB-1251WJ in non-reduced (Lane1) and β-mercaptoethanol-reduced conditions (Lane2). |
| Mouse Anti-SEZ6 Recombinant Antibody (HPAB-AP167-YC) | Kif 7 | SEZ6 |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of HPAB-AP167-YC in non-reduced (Lane 2) and reduced (Lane 1) conditions. Gel stained for 30 minutes with Coomassie Blue. As a result of different β-mercaptoethanol-reduced proteins (Heavy chain and Light chain) migrate as about 50 kDa and 25 kDa, respectively. |
| Human Anti-TPO Recombinant Antibody (clone TR1.9) | MKI67 | TPO |

|
Lane M: Protein Marker Lane 1: Reducing mAb |
| Recombinant Mouse Anti-HBV preS2 Antibody (F124) | LMNB1 | HBV preS2 |

|
Lane 1: Non-reduced Lane 2: Reduced |
| Recombinant Human Anti-DENV E proteins Antibody (5J7) | DDX5 | DENV E proteins |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of PABL-067 in non-reduced (Lane 1) and β-mercaptoethanol-reduced (Lane 2) conditions. |
| Rabbit Anti-Hypusine Recombinant Antibody (PABL-202) | TP53 | Hypusine |

|
Lane 1: Reducing mAb Lane 2: Non-Reducing mAb |
| Recombinant Human Anti-IAV HA Antibody (CT149) | PRKDC | IAV HA |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of PABL-213 in non-reduced (Lane 1, 2 μg) and β-mercaptoethanol-reduced (Lane 2, 2 μg) conditions. |
| Mouse Anti-Human CD22 Recombinant Antibody | RAF1 | CD22 (Cluster of differentiation 22) |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of TAB-003LC in non-reduced and β-mercaptoethanol-reduced conditions. |
| Anti-Human CD44 Recombinant Antibody (RG7356) | Luciferase | CD44 |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of TAB-128CL in non-reduced and β-mercaptoethanol-reduced conditions. |
| Human Anti-GPC3 Recombinant Antibody; Fab Fragment (TAB-157CT-F(E)) | MICU1 | GPC3 |
-1.png)
|
SDS-PAGE analysis of TAB-157CT-F(E) in non-reduced and β-mercaptoethanol-reduced conditions. |
| Mouse Anti-Tau Recombinant Antibody (TAB-522CT) | ERBB3 | Tau |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of TAB-522CT in non-reduced and β-mercaptoethanol-reduced conditions. |
| Mouse Anti-FCRL5 Recombinant Antibody (HPAB-AP650-YC) | RPS27 | FCRL5 |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of HPAB-AP650-YC in non-reduced (lane 2) and β-mercaptoethanol-reduced (lane 1) conditions. |
| Mouse Anti-SEZ6 Recombinant Antibody (HPAB-AP163-YC) | ATG5 | SEZ6 |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of HPAB-AP163-YC in non-reduced (Lane 2) and reduced (Lane 1) conditions. Gel stained for 30 minutes with Coomassie Blue. As a result of different β-mercaptoethanol-reduced proteins (Heavy chain and Light chain) migrate as about 50 kDa and 25 kDa, respectively. |
| Anti-Human CD276 Recombinant Antibody (TAB-117CL) | ATG7 | CD276 |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of TAB-117CL in non-reduced (Lane 1) and β-mercaptoethanol-reduced (Lane 2) conditions. |
| Recombinant Human Anti-IAV HA Antibody (5J8) | RTN3 | IAV HA |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of PABL-207 in non-reduced and reduced conditions. |
| Human Anti-MS4A1 Recombinant Antibody (clone 2F2) | RTN1 | MS4A1 |

|
Lane 1: Non-reduced Lane 2: Reduced |
| Human Anti-GREM1 Recombinant Antibody (TAB-007CT) | NEFM | GREM1 |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of TAB-007CT in non-reduced (Lane 1) and β-mercaptoethanol-reduced (Lane 2) conditions. |
| Human Anti-CD3E Recombinant Antibody (TAB-124CL) | VIM | CD3E |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of TAB-124CL in non-reduced and β-mercaptoethanol-reduced conditions. |
| Mouse Anti-SNCA Recombinant Antibody (TAB-0750CLV) | ACTA2 | Alpha-synuclein |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of TAB-0750CLV in non-reduced (Lane 1) and reduced (Lane 2) conditions. Gel stained for 30 minutes with Coomassie Blue. As a result of different β-mercaptoethanol-reduced proteins (Heavy chain and Light chain) migrate as about 50 kDa and 25 kDa, respectively. |
| Anti-Human IL5RA Recombinant Antibody (TAB-222) | ENO2 | IL5RA |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of TAB-222 in non-reduced (Lane 1) and reduced (Lane 2) conditions. Gel stained for 30 minutes with Coomassie Blue. As a result of different β-mercaptoethanol-reduced proteins (Heavy chain and Light chain) migrate as about 50 kDa and 25 kDa, respectively. |
| Mouse Anti-KIT Recombinant Antibody (clone 79D) | MAP2 | KIT |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of PABL-642 in non-reduced (Lane 1) and reduced (Lane 2) conditions. |
| Human Anti-TMEM30A Recombinant Antibody (PABL-712CQ) | α skeletal muscle actin | TMEM30A |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of PABL-712CQ in non-reduced and β-mercaptoethanol-reduced conditions. |
| Rabbit Anti-SNCA Recombinant Antibody (TAB-0740CLV) | CASP8 | Alpha-synuclein |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of TAB-0740CLV in non-reduced and β-mercaptoethanol-reduced conditions. |
| Anti-Human PERP Recombinant Antibody (KM3411) | KRT8 | PERP (p53 apoptosis effector related to PMP-22) |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of TAB-1017CL in non-reduced (Lane 1) and reduced (Lane 2) conditions. Gel stained for 30 minutes with Coomassie Blue. As a result of different β-mercaptoethanol-reduced proteins (Heavy chain and Light chain) migrate as about 50 kDa and 25 kDa, respectively. |
| Human Anti-TSHR Recombinant Antibody (clone K1-70) | XRCC4 | TSHR |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of PABL-737 in non-reduced (Lane 1) and β-mercaptoethanol-reduced (Lane 2) conditions. Gel stained for 30 minutes with Coomassie Blue. As a result of different β-mercaptoethanol-reduced proteins (Heavy chain and Light chain) migrate as about 50 kDa and 25 kDa, respectively. And non-reduced protein migrates as about 180-245 kDa. |
| Human Anti-IL20 Recombinant Antibody (TAB-0009CL) | α-SMA | IL20 |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of TAB-0009CL in non-reduced (Lane 1) and reduced (Lane 2) conditions. |
| Human Anti-GPC3 Recombinant Antibody; Fab Fragment (TAB-158CT-F(E)) | MyHCs | GPC3 |
-1.png)
|
SDS-PAGE analysis of TAB-158CT-F(E) in non-reduced and β-mercaptoethanol-reduced conditions. |
| Human Anti-TREM1 Recombinant Antibody; scFv Fragment (TAB-167CQ-S(P)) | EGFR | Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 |
-L-1.png)
|
SDS-PAGE analysis of TAB-167CQ-S(P) in reduced (Lane 1) and non-reduced (Lane 2) conditions. |
| Anti-Human IL17RA Recombinant Antibody (TAB-217) | DES | IL17RA |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of TAB-217 in non-reduced (Lane 1, 2.5ug) and reduced (Lane 2, 2.5ug) conditions. |
| Mouse Anti-FCRL5 Recombinant Antibody (MOB-056CQ) | HAO1 | FCRL5 |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of MOB-056CQ in non-reduced (lane 2) and β-mercaptoethanol-reduced (lane 1) conditions. |
| Anti-Human Abeta Recombinant Antibody (Solanezumab) | TUBE1 | Abeta |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of TAB-228 in non-reduced (lane 1) and β-mercaptoethanol-reduced (lane 2) conditions. |
| Mouse Anti-GDF15 Recombinant Antibody (HPAB-0344-CN) | MAPK3 | GDF15 |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of HPAB-0344-CN in non-reduced (Lane 1) and reduced (Lane 2) conditions. |
| Recombinant Human Anti-HSV Antibody (AC8) | LGALS3 | HSV |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of HPAB-J0123-YC in non-reduced (Lane 2) and reduced (Lane 1) conditions. |
| Human Anti-SA Recombinant Antibody (HPAB-2545LY) | NBR1 | serum albumin |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of HPAB-2545LY in non-reduced (lane 2) and reduced (lane 1) conditions. Gel stained for 30 minutes with Coomassie Blue. As a result of different β-mercaptoethanol-reduced proteins (Heavy chain and Light chain) migrate as about 50 kDa and 25 kDa, respectively. |
| Mouse Anti-MRC2 Recombinant Antibody (HPAB-M0694-YC) | GAPDH | MRC2 |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of HPAB-M0694-YC in reduced (Lane 1) and non-reduced (Lane 2) conditions. |
| Mouse Anti-EREG Recombinant Antibody (clone 9E5) | HIST1H2BB | EREG |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of PABL-084 in non-reduced (Lane 1, 2 μg) and reduced (Lane 2, 2 μg) conditions. |
| Recombinant Mouse Anti-B. burgdorferi OspA Antibody ( LA-2) | RELA | B. burgdorferi OspA |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of PABZ-012 in reduced (Lane 1) and non-reduced (Lane 2) conditions. |
| Human Anti-MERS-CoV S Recombinant Antibody (MRO-887LC) | ERBB2 | S protein |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of MRO-887LC in non-reduced (Lane 2) and reduced (Lane 1) conditions. |
| Human Anti-PIV3 Prefusion Recombinant Antibody Fab Fragment (PABJ-0161-F(E)) | LacZ | PIV3 Prefusion |
-1.png)
|
SDS-PAGE analysis of PABJ-0161-F(E) in non-reduced (Lane 2) and reduced (Lane 1) conditions. |
| Anti-Human IFNG Recombinant Antibody (Fontolizumab) | LAMC1 | IFNG |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of TAB-041 in non-reduced (Lane 2) and reduced (Lane 1) conditions. |
| Anti-Human CD22 Recombinant Antibody (TAB-183-F(E)) | Cardiotin | CD22 |
-1.png)
|
SDS-PAGE analysis of TAB-183-F(E) in non-reduced (Lane 1). Gel stained for 30 minutes with Coomassie Blue. And non-reduced protein migrates as 70 kDa. |
| Anti-Influenza A Virus (H1N1/H2N2) HA Recombinant Antibody (C179) | RPA2 | HA |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of MRO-248LC in non-reduced (Lane 1) and reduced (Lane 2) conditions. |
| Mouse Anti-gB glycoprotein Recombinant Antibody (MRO-960LC) | SKP2 | gB glycoprotein |

|
SDS-PAGE analysis of MRO-960LC in reduced (Lane 1) and non-reduced (Lane 2) conditions. |
- Bhatt, Mukesh, et al. "SDS-PAGE and Western blotting: Basic principles and protocol." Protocols for the Diagnosis of Pig Viral Diseases. New York, NY: Springer US, 2022. 313-328.
- Gallagher, Sean R. "SDS‐polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS‐PAGE)." Current protocols essential laboratory techniques 1 (2008): 7-3.
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

