Roledumab Overview
Introduction of Roledumab
Roledumab (LFB-R593) is a human IgG1 anti-rhesus (Rh)D monoclonal antibody (mAb) being evaluated for the prevention of hemolytic disease of the fetus or newborn, which can occur when maternal anti-RhD antibodies are produced and pass through the placenta during pregnancy. The ability of the mAb to eliminate RhD-positive red blood cells (RBCs) is being evaluated in clinical studies. During pregnancy, the difference in RhD status between an RhD-negative mother and an RhD-positive fetus can lead to proliferation of RhD-reactive B cells in the mother. In a subsequent pregnancy with an RhD-positive fetus, these B cells may then produce anti-RhD antibodies that cross the placenta and cause hemolytic disease of the fetus or newborn, which is potentially fatal. In a Phase 1 study, roledumab was safe and well tolerated in doses up to 3000 μg administered IV and at 300 μg administered intramuscularly (IM) to healthy RhD-negative volunteers and the terminal elimination half-life was 18-22 d. Roledumab was evaluated in a Phase 2 study (NCT00952575) that compared the efficacy (in terms of clearance of RhD-positive RBCs) and safety of the mAb vs a polyclonal anti-RhD immunoglobulin in 78 healthy RhD-negative volunteers. In this study, the RhD-positive RBCs were exogenously-administered to the volunteers. The aim of the on-going open label Phase 2/3 study (NCT02287896) is to assess the PK profile, safety and the efficacy to prevent RhD alloimmunization of 300 μg roledumab administered IM / IV in RhD-negative pregnant women carrying an RhD-positive fetus. Immunogenicity will also be assessed. The safety, efficacy and immunogenicity of roledumab (300 μg intramuscular (IM) / IV) are being evaluated in the Phase 2/3 NCT02287896 study, which has an estimated enrollment of 60 women and primary completion date in November 2017.
Mechanism of Action of Roledumab
Rh-negative mothers carrying a Rh-positive fetus may produce anti-D antibodies (anti-D) following small feto-maternal hemorrhages at birth. The production of anti-D antibodies occurs in response to the presence of fetal red blood cells in the maternal circulation; this maternal immune response towards the fetal Rhesus antigen is known as ‘sensitization’ or immunization. It is believed to take between five and 15 weeks for such antibodies to appear in the maternal circulation following a sensitizing event such as birth. Sensitization is believed to have no adverse health effects for the mother, and the first baby is usually not harmed, as the pregnancy is generally complete by the time that sensitization has occurred. These maternal antibodies (directed against antigens inherited from the father) may, however cause hemolytic disease in subsequent pregnancies with Rh-positive fetuses. In addition to feto-maternal hemorrhage at birth, events during pregnancy may lead to the production of maternal anti-D antibodies, and thus sensitization may also occur during the antenatal period. As there is a direct, proportional relationship between the volume of fetal Rh-positive red blood cells to which a Rh-negative mother is exposed and the incidence of immunization, sensitizing events (in addition to birth) may include termination of pregnancy, miscarriage, and some invasive investigative procedures. Roledumab thus is designed to bind any RhD-positive RBCs entering the maternal circulation and eliminate them before they can stimulate proliferation of RhD-reactive B cells.
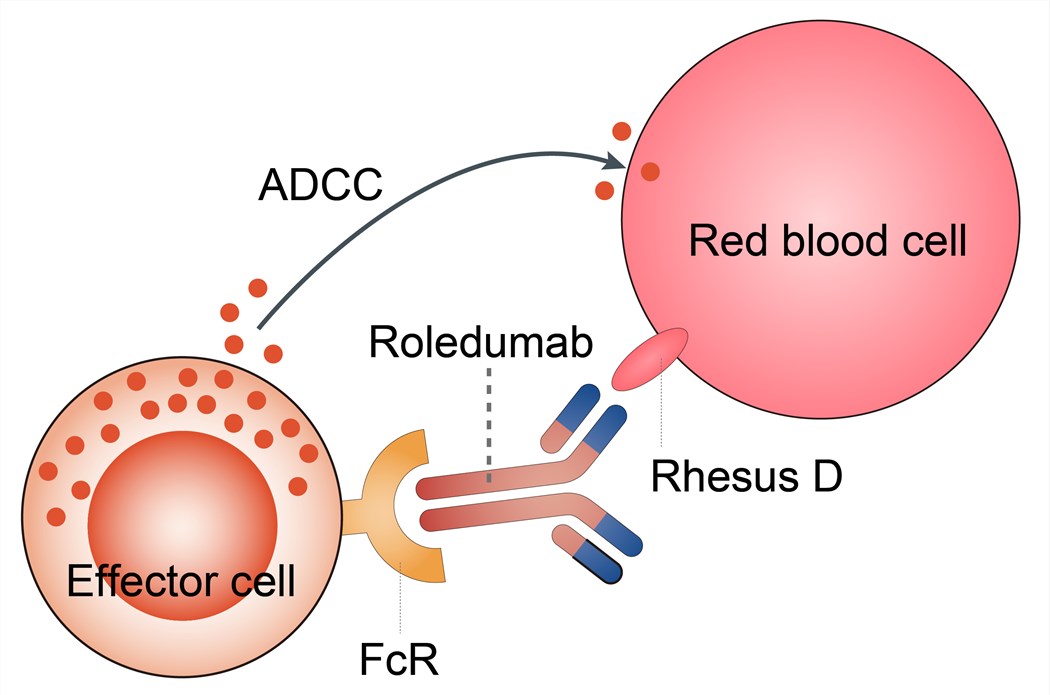
Fig.1 Mechanism of action of Roledumab
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

