Mass Cytometry Protocol & Troubleshooting
Mass cytometry is a variant of flow cytometry. It is capable of interrogating multiple markers on millions of individual cells at the same time. The antibodies in it are labeled using heavy metal ion tags rather than fluorescent dyes. This allows more antibody specificities to be combined in a single sample. As well as detection is performed by time-of-flight mass spectrometry, so there is no spectral overlap of signals, which allows analysis of a larger number of target proteins.
Creative Biolabs describes an optimized protocol that primarily covers the manipulation of cell samples for mass cytometry analysis. We describe methods and troubleshooting tips that will help users avoid common pitfalls and obtain consistent results by minimizing variability. Please see our protocols page below for details.
Solutions and Reagents
| Stages | Solutions and Reagents |
| Sample Preparation | Phosphate buffer (PBS), serum-free medium, fixative solution, washing buffer |
| Antibody Staining | Antibody, dilution buffer, permeabilization solution, washing buffer |
Mass Cytometry Procedure
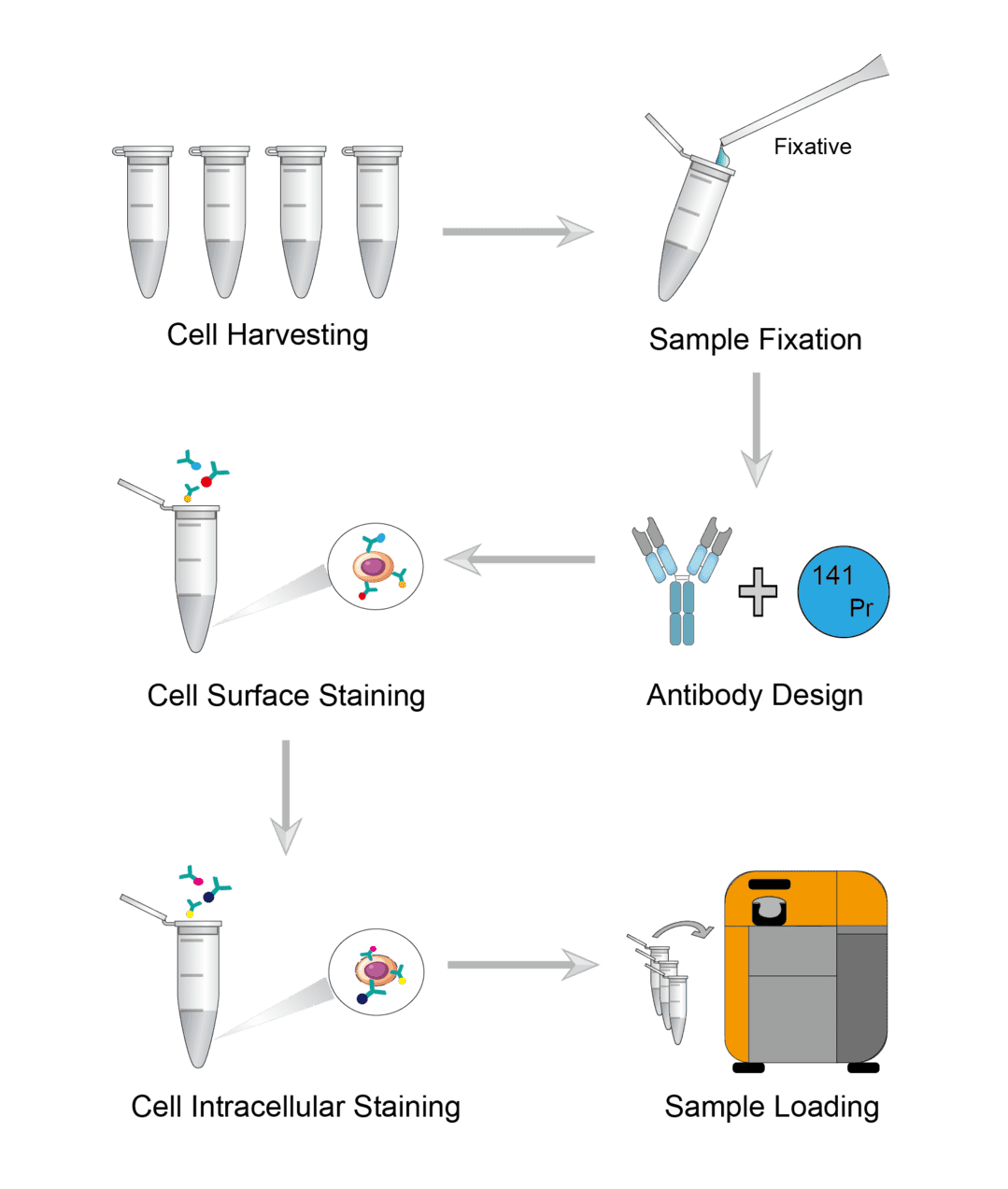
Wash the plate or flask with walled cells. And add enzymatic digestion reagent to the walled cells to obtain a single cell suspension. Then incubate for a few minutes to isolate the cells. Centrifuge the completely isolated cells and carefully aspirate the supernatant. Finally, add serum-free medium to resuspend the cells, and transfer a quantitative cell suspension to a microcentrifuge tube to count cells.
Resuspend the cell samples with PBS and add fixative. Incubate on an orbital shaker at room temperature. Wait until incubation is complete for centrifugation and carefully aspirate the supernatant. Finally, wash the sample with PBS to remove the fixative solution.
Proper pairing of antibodies to metal isotopes is critical. Design the antibody to metal isotope pairing to ensure optimal signal intensity and ideally no signal overlap. Key considerations include, isotope sensitivity range of the detection instrument, intensity of surface marker expression, background, etc.
First determine the working dilution of each antibody by titration experiments prior to the experiment. To ensure consistent antibody labeling across multiple samples, it is necessary to carefully control sample volume and antibody concentration. Add antibody dilutions to the samples and gently blow to resuspend the samples in the liquid. Incubate the samples on an orbital shaker at room temperature. After the incubation is complete, wash the sample several times with wash buffer to ensure that all free antibodies are washed away.
First you need cell permeabilization. Add the permeabilizing agent to the cells and mix gently with a pipette. Then incubate the sample for permeabilization. After incubation is complete, centrifuge the cells and carefully aspirate the supernatant. Then add washing buffer and gently resuspend the cell precipitate for washing. Finally, the same steps as for cell surface staining are followed. Use antibodies with heavy metal ion labels to stain intracellular antigens.
Resuspend the cells in buffer solution and take a quantitative cell suspension for counting. Run samples using the mass cytometry autosampler, add calibration beads to each well of the sample plate, and then add the desired number of cells to be analyzed.
Troubleshooting
Mass cytometry is a modern technique that takes advantage of the power of traditional cytometry techniques as well as the sensitivity and specificity of mass spectrometry. In order to prevent and minimize most common problems that may be encountered in mass cytometry, we list some key steps in the protocol and troubleshooting strategies for reference.
High background signal
- Sample causes. The original sample produces isotopic background noise of iodine and platinum.
- Metal isotope causes. Certain metal isotopes have strong oxides, such as lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium and neodymium. They can produce a background signal in the mass channel. This background noise cannot be avoided, but can be reduced by optimizing the plasma temperature. On the other hand, isotopic impurities can cause signal overlap in the mass channel. This is often the case with the isotopes Nd-144, Nd-145, and Nd-146. This signal overlap can be reduced or prevented by using markers of mutually exclusive lineages or dumping the channels that contain the most contaminated isotopes.
- Blocking causes. In sample staining, if cells have high levels of receptor expression, this will result in non-specific antibody binding. This can be prevented by adding blocker incubation prior to surface marker staining.
- Reagent causes. The impurities in the fixed, transmissive reagents may cause background noise from samarium isotopes. Contamination of washing agents and other buffers may produce background noise for barium and lead isotopes. Reagent contamination can be avoided by using different batches of products.
No or weak marker signal
- Cell causes. For mass cytometry assays, staining of fresh live cells with 95% viability is always ideal. If frozen cells are used, they should be resuscitated to prevent cell aggregation and death. And count the resuscitated cells to determine the viability and number of cells before performing the experiment. During sample preparation, some washing and handling steps can lead to loss of cell numbers. You can reduce cell loss by increasing centrifuge speed and centrifugation time or by reducing the number of washing steps.
- Fixation and permeabilization causes. The concentration of fixation and permeabilization reagents depends on the surface and intracellular molecules detected in the cells. When these reagents are not at the right concentration and dosage, certain molecules are disrupted or undetected. Therefore, once the antibody panel has been selected, it is necessary to titrate the concentration of the fixation and permeabilization solution. The optimized concentration is effective for staining intracellular molecules with minimal damage to cell surface epitopes.
- Antibody causes. The optimal staining concentration for each antibody should be determined in a titration experiment along with appropriate positive and negative controls. If the marker of interest is still not detected, it may mean that the isotope conjugation may have failed and you can repeat the ligation.
Antibody staining variance
- Cell causes. You need to check the cell counts to bring the total number of cells in each well to a reasonable value.
- Antibody causes. Test for technical errors in the preparation of antibody master mixes and check antibody shelf life. We recommend that you collect the batch times of all antibodies and run them in a barcoded batch to minimize variation. Alternatively, you can use the same fresh antibody master mix, as well as re-titrate the relevant antibodies.
We offer a full range of services that can assist you in all aspects of your mass cytometry application. Here you will also find more guides and resources to help you get your project up and running.
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

