Enoblituzumab Overview
Introduction of Enoblituzumab
Enoblituzumab (also referred to as MGA271) is an Fc optimized humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody that binds to B7-H3 (CD276), a member of the B7 family. Enoblituzumab is Fc-engineered with 5 amino acid substitutions to enhance binding to the activating FcγR and decrease binding to the inhibitory FcγR. Pre-clinical studies show that, in human CD16A-bearing transgenic mice, MGA271 exhibited potent antitumor activity in B7-H3–expressing xenograft models of renal cell and bladder carcinoma. To date, approximately 180 patients have received enoblituzumab monotherapy in a phase I study, with good tolerability.
Mechanism of Action of Enoblituzumab
During an immune response, naive T cells engage their T-cell receptor (TCR) to interact with a complex of MHC and peptide expressed by antigen-presenting cells (APC). Interactions between members of the B7 ligand family and the CD28 receptor family provide T-cell co-stimulation and co-inhibition, regulating T-cell activation and tolerance, exhaustion and effector function, differentiation, and memory generation. B7-H3, also known as CD276, is an immune checkpoint molecule belonging to the B7-CD28 pathways. B7-H3 has limited expression in normal tissue but high expression in many cancers including melanoma (M), squamous cell cancer of the head and neck (SCCHN) and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and its overexpression correlates with poor prognosis in a broad range of cancers suggesting a potential role in enabling tumor immune escape. The B7-H3 pathway has a dual role in contributing to the regulation of innate immune responses. One study found that neuroblastoma cells express B7-H3 on their cell surface, which protect them from NK cell-mediated lysis. Another group argues that B7-H3 co-stimulates innate immunity by augmenting proinflammatory cytokines release from LPS-stimulated monocytes/macrophages, in both a Toll-like receptor 4- and 2-dependent manner. A larger body of literature suggests that B7-H3 plays an important role in T cell–mediated adaptive immunity. Enoblituzumab is an Fc-domain optimized, humanized monoclonal antibody directed against cancer stem cells (CSCs), with potential immunomodulating and antineoplastic activities. After binding of enoblituzumab to an as of yet not elucidated target expressed on CSCs and differentiated tumor cells, this agent may induce an antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) against CSCs. In mice, weekly doses of MGA271 in both renal and bladder carcinoma xenografts resulted in sustained tumor growth inhibition, effects that were Fc mediated.
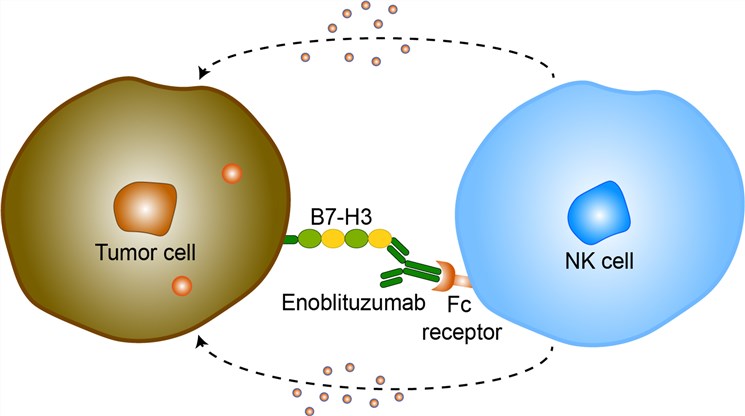 Fig 1. Mechanism of Action of Enoblituzumab
Fig 1. Mechanism of Action of Enoblituzumab
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

