Radial Immunodiffusion Protocol & Troubleshooting
Radial immunodiffusion (RID) is a type of immunodiffusion technique used to determine the amount or concentration of antigen in a sample. It is based on the principle that when the appropriate ratio of antigen to antibody is present, the antigen-antibody interaction forms a visible cross-linked precipitate producing a precipitating ring. The ring diameter is related to the concentration of antigen present in the sample.
RID is a simple and rapid immunoassay technique. Creative Biolabs offers RID laboratory techniques for exploring antigen-antibody interactions and quantification. We perform experiments according to standard protocols, and create standard curves to determine the concentration of unknown antigen samples. As well as we provide troubleshooting guides for common problems to help experiments run smoothly.
Solutions and Reagents
| Stages | Solutions and Reagents |
| Agarose Plate Preparation | Phosphate buffer (PBS), antibody solution, ionic agar or saline agar |
| Sample Preparation | Dilution buffer, standard antigen solution, sample to be tested |
Radial Immunodiffusion Procedure
RID is a technique widely used for quantitative antigen estimation. Antibodies of known specificity are uniformly distributed in an agar gel. A sample containing the target antigen is placed in a well within the gel. The antigen then diffuses radially from the wells and forms a precipitation loop at the point of antibody-antigen equilibrium. The antigen concentration is determined by measuring the diameter of the precipitation loop and extrapolating using a standard curve.
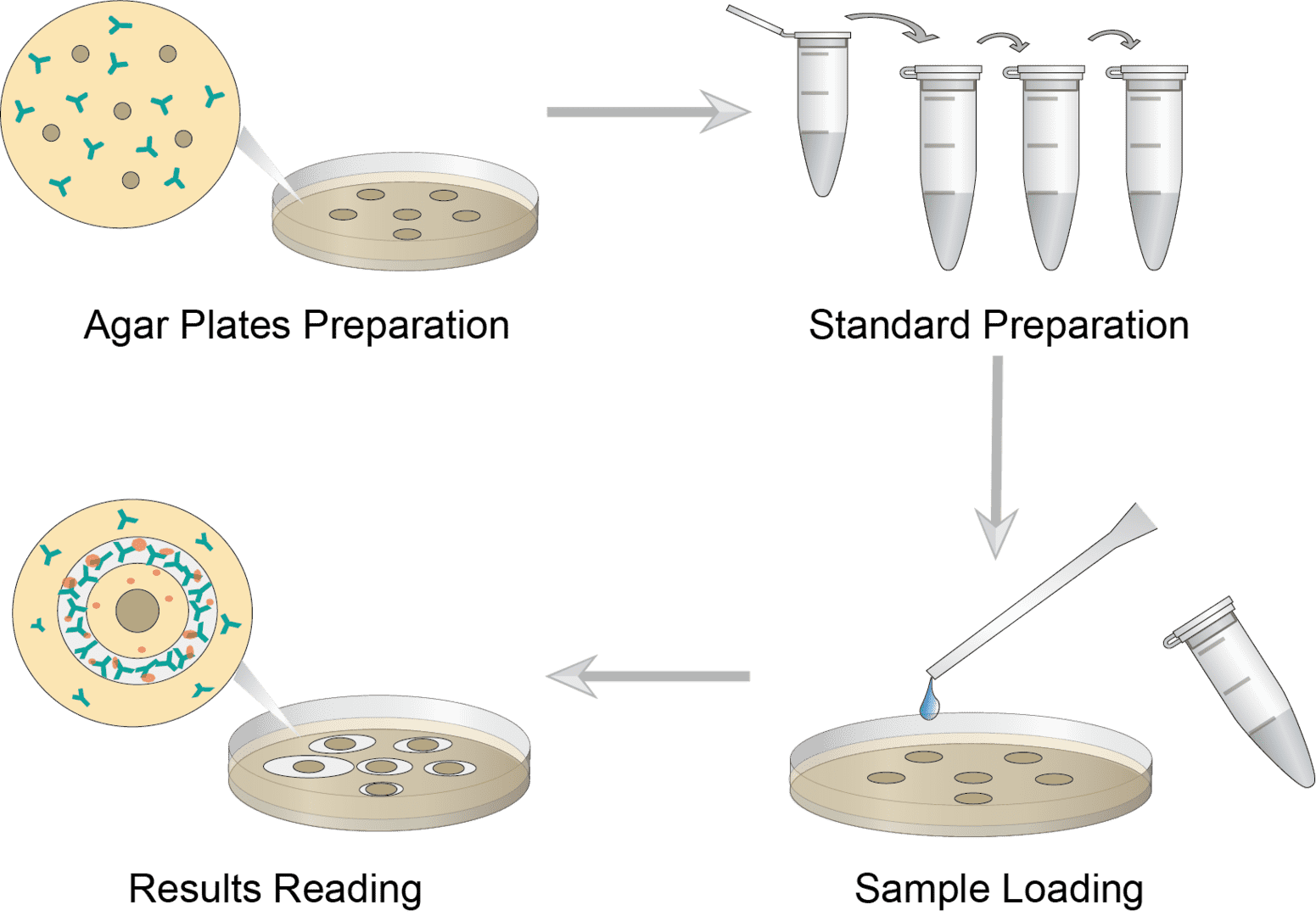
Prepare agar plates according to plate size. Dilute the known specific antibody with PBS, preheat and pour into dissolved agar solution, mix the antibody and agar well and pour on the plate. After solidification, place the agar plate on the template and use a well cutter to cut the wells in a gentle manner, then remove excess agarose.
Prepare the standard solution using the serial dilution method. Prepare several microtubes labeled with concentrations. Add an equal amount of buffer to each tube and perform the serial dilution operation. Mix well the existing antigen samples for the standard curve.
Number the surrounding wells at the bottom of the plate, leaving the center well unmarked. First load the standard dilution according to the number and load the sample to be tested in the center well. Cover the plate without inverting the petri dish and place it in the incubation chamber for incubation.
The precipitate rings will be visible after incubation. Lift the plate to see the opaque circles around each well. Measure the diameter of the precipitate with a ruler. Plot a standard curve through known concentrations and calculate the value of the unknown antigen.
Troubleshooting
No precipitate ring
- Agar causes. Check the quality of the agar gel for damage or expired product, which can be replaced promptly. And the agarose gel may dry out during incubation, you should ensure that the chamber is filled with water to prevent the gel from drying out.
- Antibody causes. First check the quality of the antibody and test the antibody to select the appropriate concentration. High temperature of the agar solution during gel preparation can lead to inactivation of the antibodies. You should add antibody solution to the agar gel as soon as the appropriate temperature is reached.
- Sample causes. Check each sample well to see if a test sample has been missed. Sample loading should be done directly into the wells without spilling over to the sides to avoid underfilling of the sample. And make sure the sample concentration is not too high or too low.
- Poor lighting causes. Poor lighting during reading can cause the precipitation ring to not be observed. You need to ensure bright side lighting and a dark background when observing measurements.
Blurred precipitation ring
- Agar causes. Uneven distribution of the gel can cause this problem. First mix the antibody and agar well, then place it on a flat surface for pouring and make sure the plate is not moved until the gel is poured.
- Antibody causes. High temperature at the time of antibody addition may result in inactivation or reduced activity of the antibody.
Oversized or undersized precipitation ring
Too large or too small a precipitation ring can result in inaccurate ring diameter measurements.
- Sample causes. Incorrect test sample volume and too high/low concentration can cause this to occur.
- Temperature causes. Increases/decreases in temperature during incubation can cause over- or under-sizing of the precipitate ring. Therefore, a consistent temperature should be maintained throughout the experiment.
- Instrument causes. You should check the pipette for incorrect calibration and ensure that the correct volume of sample is being aspirated. And check the measuring instrument for accuracy to ensure that the measurements are correct.
Multi-ring
- Sample causes. Sample spoilage may result in multiple precipitation rings, please check sample quality. If it is the presence of heterotypes in the sample, a distinct ring can be read.
- Gel causes. Due to PEG gels, non-specific precipitations that interfere with the results may be produced. The gel material can be changed.
Non-circular ring
- Local antibody depletion causes. A non-circular ring is formed due to localized antibody depletion caused by high concentrations of adjacent test samples. You can dilute the sample and repeat the test.
Poor calibration curve
- Incomplete diffusion causes. Incubate for further 24 hours and re-measure the rings.
- Calibrator rings under/oversize causes. As explained above.
- Construction causes. Check calibration curve construction.
If you would like to become familiar with RID and how to use it to determine the concentration of a specific antigen, please read our protocol and troubleshooting or contact us for detailed information.
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

