Sulesomab Overview
Introduction of Sulesomab
Sulesomab is a Fab fragment of anti-carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 () recombinant monoclonal antibody. CEACAM6, also known as CD66c (cluster of differentiation 66c), which is a member of the carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) gene family. Technetium (99mTc) sulesomab (trade name LeukoScan) is a mouse monoclonal antibody labelled with technetium-99m, a radionuclide. It is approved for diagnostic imaging for determining the location and extent of infection/inflammation in bone in patients with suspected osteomyelitis, including patients with diabetic foot ulcers. Currently, LeukoScan has not been employed to diagnose osteomyelitis in patients with sickle cell anemia and its marketing authorization has been withdrawn at the request of the marketing authorization holder.
Mechanism of Action of Sulesomab
Receptors of the carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule (CEACAM) family are widely expressed on immune cells and epithelial cells of the respiratory and the gastrointestinal tract. CEACAM6 (CD66c, NCA), found on epithelia, expressed on epithelia and granulocytes, has glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchors. CEACAM6 is highly glycosylated and affect basic cellular functions like proliferation and apoptosis/survival and are able to regulate immune functions. In the human intestine, CEACAM6 are receptors for a variety of bacterial pathogens and mediate adhesion and internalization, e.g., of Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Neisseria meningitidis, different Escherichia coli strains, Moraxella catarrhalis, Haemophilus influenzae, Salmonella species, and Helicobacter pylori. Many of these bacteria have evolved different, structurally unrelated surface proteins that all target the human-specific extracellular immunoglobulin V (IgV)-like amino-terminal domain of CEACAM6. 99mTc-Sulesomab, the Fab fragment of anti-CEACAM6, is used as an in vivo granulocyte labeling agent for imaging inflammation. However, it is not clear to what extent it targets cells that have already migrated into the interstitial space of an inflammatory lesion as opposed to circulating cells. The suggested mechanism of action of this tracer is binding to CEACAM6 surface antigen on granulocytes, theoretically allowing in vivo labeling of granulocytes after intravenous injection. The antibody fragment is radiolabeled with 99mTc in a simple 5-min procedure, avoiding the time-consuming and potentially dangerous technique of in vitro leukocyte labeling, which, insofar as it is the technique against which new inflammation-targeting agents are generally compared, would be regarded as the gold standard for imaging acute inflammation. Although some of the injected tracer may bind to circulating granulocytes, other mechanisms of localization in areas of inflammation are also possible. It is known, for instance, that capillary permeability increases in inflamed tissues, allowing increased diffusion of proteins into the interstitial space. It has also been suggested that the antibody may preferentially bind to extravascular granulocytes that have migrated and become activated.
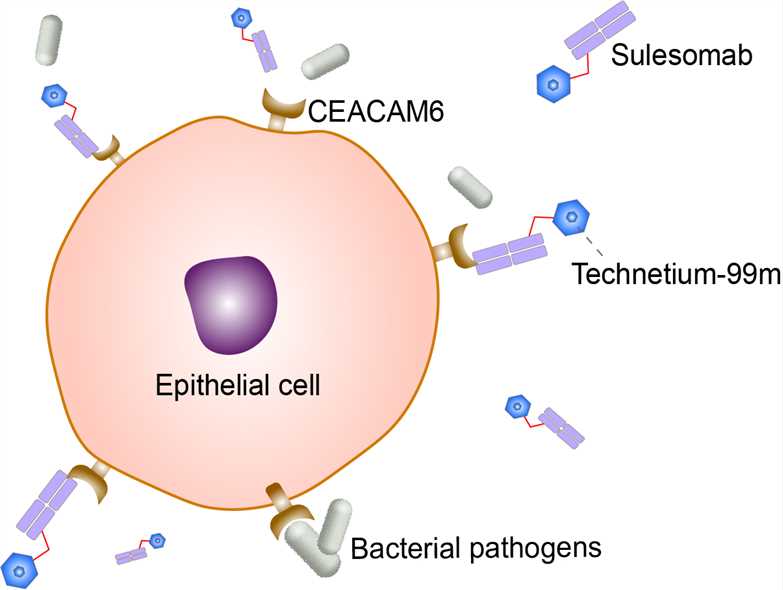 Fig 1. Mechanism of Action of Sulesomab
Fig 1. Mechanism of Action of Sulesomab
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

