Adecatumumab Overview
Introduction of Adecatumumab
Adecatumumab, also known as MT201, is a recombinant human IgG1 monoclonal antibody that targets at epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM). EpCAM (CD326) is a kind of cell surface protein, which is considered to be the cell proliferation marker of many cancers, such as gastric cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, prostate cancer, breast cancer, colon cancer and so on. Adecatumumab was generated by using EpCAM-specific VH and VL domains from a human B-cell repertoire. This drug was designed as an anticancer drug for prostate and breast cancer, and has been investigated in the clinical treatment of colorectal cancer. As early as 2006, adecatumumab had been conducted a phase I study of prostate cancer treatment to investigate its safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics. The results support the effective role of adecatumumab in EpCAM-expressing neoplasia. In 2007, it was found that the exchange of adecatumumab variable region Fcγ1 with mouse Fcγ2a enhanced the antitumor activity of adecatumumab. Subsequently, adecatumumab was studied in phase II clinical studies of metastatic breast cancer, uterine serous papillary carcinoma and prostate cancer. The results showed that adecatumumab had a good research prospect. In 2012, researchers conducted a study of adecatumumab in combination with docetaxel in the treatment of EpCAM-positive relapsed or refractory advanced-stage breast cancer. The results showed that the combination therapy was safe, feasible and promising.
Mechanism of Action of Adecatumumab
Adecatumumab is a monoclonal antibody that can directly target EpCAM, with potential anti-tumor activity. EpCAM is a transmembrane glycoprotein mediated Ca+-independent adhesion to epithelial cells that involved in cell signal transduction such as migration proliferation and differentiation. In addition, EpCAM has carcinogenic potential by upregulating the ability of c-myc, e-fabp and cyclin A and E, since EpCAM is expressed only in epithelial cells and epithelium-derived tumors. EpCAM can be used as a diagnostic marker for various cancers. It seems to play a role in carcinogenesis and metastasis, so it can also be a potential prognostic marker and a potential target for immunotherapy strategies. Adecatumumab is one of the monoclonal drugs designed to target EpCAM. When it binds to EpCAM, the drug can kill the tumor cells expressing EpCAM by the action of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). The effect of ADCC is mainly dependent on the binding of antibody Fc fragments to FcR on immune effector cells, which causes effector cells to release toxic substances and kill tumor cells directly.
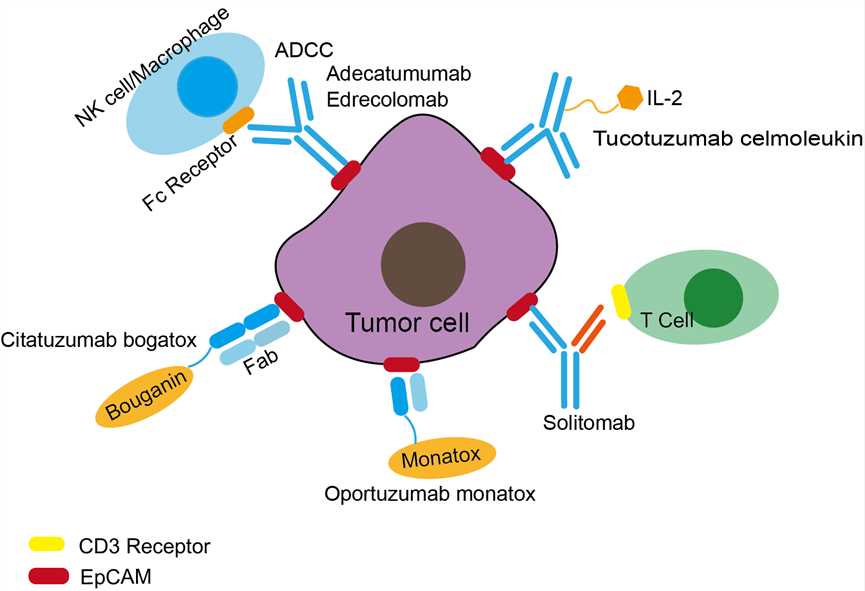
Fig 1. Mechanism of Action of Adecatumumab
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.



