Blontuvetmab Overview
Introduction of Blontuvetmab
Blontuvetmab is a recombinant monoclonal antibody specific to the canine MS4A1 protein (CD20) encoded by the MS4A1 gene. According to the researches, CD20 is primarily expressed on the surface of B cells and is acknowledged as a crucial component of the adaptive immune system. Blontuvetmab is designed to bind to this protein and effectively reduce abnormal B cell activity, making it a promising therapeutic treatment for conditions involving abnormal B cell activity, such as B-cell lymphomas and autoimmune diseases in dogs. Aratana Therapeutics Inc. released blontuvetmab with documented clinical efficacy in dogs suffering from B cell lymphoma in the United States in 2015. However, peer-reviewed studies supporting its efficacy are limited. One of the challenges in the research and development of blontuvetmab was the lack of cross-reactivity between human anti-CD20 antibodies and canine CD20, necessitating the development of a canine-specific antibody. Ongoing clinical research is investigating its efficacy and safety, with promising early results.
The Mechanism of Blontuvetmab Action
Blontuvetmab works by attaching itself to the CD20, a surface marker mostly expressed on B cells. This highly selective mode of action guarantees precision intervention by specifically targeting this non-glycosylated phosphoprotein. The CD20 antigen plays a significant role in the modulation of B cell activation and proliferation, making it a valuable target in immunotherapy. The drug successfully depletes pathogenic B cells through this binding, potentially providing therapeutic effects in conditions like B-cell lymphomas and autoimmune disorders characterized by abnormal B cell activity. Here is a detailed breakdown of its mechanism:
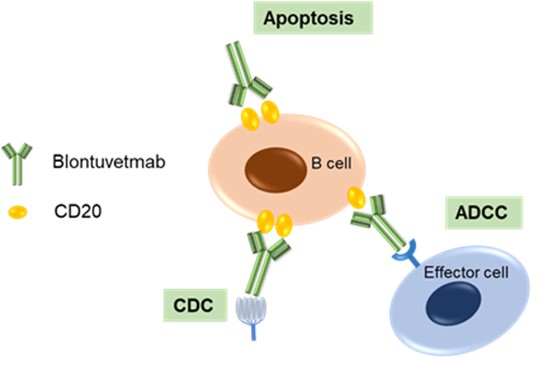 Figure 1. The Mechanism of Blontuvetmab Action (Creative Biolabs Original)
Figure 1. The Mechanism of Blontuvetmab Action (Creative Biolabs Original)
Target Recognition and Binding
Blontuvetmab has been engineered to recognize a specific epitope unique to the CD20 protein in canines. This specificity ensures that blontuvetmab selectively targets B lymphocytes in dogs, thereby minimizing off-target effects and enhancing therapeutic efficacy. The ability of blontuvetmab to precisely engage this canine-specific epitope underscores its potential as a targeted treatment modality in veterinary medicine.
B Cell Depletion
Upon binding to CD20, blontuvetmab can induce B cell depletion through several mechanisms:
- Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity (ADCC): Blontuvetmab's precise targeting and binding to the MS4A1 (CD20) protein on the surface of B cells facilitates the recruitment of immune effector cells, including natural killer (NK) cells, which recognize and eliminate the antibody-coated B cells. This targeted approach enhances the immune system's capability to specifically identify and eradicate pathogenic B cells, offering potential therapeutic benefits in treating canine cancers and autoimmune disorders.
- Complement-Dependent Cytotoxicity (CDC): The activation of the complement system culminates in the formation of the membrane attack complex (MAC), resulting in the lysis and subsequent destruction of B cells.
- Direct Apoptosis: Apoptosis, also known as programmed cell death, can be directly triggered by the cross-linking of CD20 molecules on the surface of B cells. This process activates intrinsic pathways within the B cells, leading to their methodical and controlled removal. By inducing apoptosis, this mechanism significantly contributes to the therapeutic effectiveness of blontuvetmab in targeting and reducing pathological B cell populations.
Therapeutic Outcomes
The strategic depletion of B lymphocytes has a crucial function in mitigating pathogenic B cell activity, which is particularly advantageous in the therapeutic management of B-cell lymphomas. These malignancies are characterized by the unrestrained proliferation of B cells, leading to deleterious clinical outcomes. The targeted elimination of these cells can, therefore, effectively curb the progression of such neoplastic disorders.
Moreover, the aberrant activation of B lymphocytes is a hallmark of various autoimmune diseases, where the immune system erroneously targets the body's own tissues. In these contexts, the depletion of B cells serves to attenuate inappropriate immune responses, thereby ameliorating the clinical manifestations of the disease. This intervention ultimately aids in the restoration of immune homeostasis and tolerance, providing significant therapeutic benefits in managing autoimmune conditions.
The Clinical Application of Blontuvetmab
Blontuvetmab shows promise as a therapeutic innovation in veterinary medicine, especially for autoimmune and neoplastic disorders in dogs. Preliminary clinical investigations and experimental trials have focused on its effectiveness and safety in these areas.
- Renal Transplantation: Blontuvetmab is routinely used to prevent acute organ rejection in adult and pediatric patients undergoing renal transplantation. It is administered as part of an immunosuppressive regimen that typically includes corticosteroids, cyclosporine, and other immunosuppressive medications.
- Liver Transplantation: Although primarily used for renal transplantation, blontuvetmab has also been investigated and used off-label in liver transplantation to prevent acute rejection episodes.
- Other Organ Transplantation: Studies and clinical trials have explored its utility in other organ transplants, including heart and lung, although to a lesser extent compared to renal transplants.
- B-cell Lymphomas: Dogs with B-cell lymphomas have demonstrated improved survival rates and decreased tumor burdens when treated with blontuvetmab. Clinical trials have shown its safety and potential as a monotherapy or as part of combination therapies.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Additionally, blontuvetmab is being investigated as a possible treatment for immune-mediated hemolytic anemia (IMHA) and immune-mediated thrombocytopenia (ITP) in dogs, conditions where B cells are pathologically involved. Initial results indicate a significant decrease in disease severity and improved clinical outcomes. Due to its ability to regulate the immune system by specifically targeting activated T cells, blontuvetmab has sparked interest for its possible application in managing autoimmune diseases. Nevertheless, its principal clinical application remains in transplantation medicine.
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

