Denintuzumab Mafodotin Overview
Introduction of Denintuzumab mafodotin
Denintuzumab mafodotin, also known as SGN-CD19A, is an antineoplastic agent composed of a monoclonal antibody against CD19 conjugated with tubulin inhibitor monomethyl auristatin F (MMAF). CD19 is widely expressed on the surface of most B-cell malignant tumors. MMAF is a derivative of auristatin, which can target the tubulin of cells and inhibit the polymerization of tubulin so that the cell cycle arrest and cell growth stop. Denintuzumab mafodotin has been investigated in the clinical treatment of B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), invasive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, lymphocytic leukemia, and follicular lymphoma.
Mechanism of Action of Denintuzumab mafodotin
Denintuzumab mafodotin is an antibody-drug conjugate, which is obtained by conjugation of IgG1-kappa type monoclonal antibody targeting CD19 with synthetic cytotoxin MMAF by a linker. The human CD19 antigen, a 95kd typeⅠ transmembrane glycoprotein, belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily. CD19 has a transmembrane region, a cytoplasmic C-terminal and an extracellular N-terminal, which enables it to transmit signals from the outside of the cell to the inside of the cell. It has been found that CD19 is essential for B cell differentiation, including in the formation of B -1 germinal center. CD19 deficient B cells show selective growth disadvantage, therefore, there is little lack of CD19 antigen in tumor B cells. Because CD19 is expressed in almost all B-cell and B-cell-derived tumors, it is considered to be a biomarker of B cells and an immunotherapeutic target for tumor lymphocytes. MMAF is a synthetic cytotoxic drug with certain antitumor activity. Although it has a well-killing effect on tumor cells, the lack of specificity will cause systemic toxicity, so it cannot be used as an anti-tumor drug alone. In general, MMAF is conjugated with certain monoclonal antibodies that specifically recognize antigens on the surface of tumor cells to form anti-drug conjugates. This method can not only reduce the toxicity of MMAF to non-target cells but also make MMAF accumulate in tumor cells and increase the anti-tumor effect. The anti-tumor mechanism of denintuzumab mafodotin depends on an anti-CD19 monoclonal antibody and toxin MMAF. Upon administration, the monoclonal part recognizes and binds to the CD19 antigen on the surface of the tumor cell. When antigen and antibody are combined, internalization occurs and the whole drug enters the cytoplasm. The linker between the antibody and the drug is hydrolyzed by proteases in the cell, resulting in the release of MMAF into the cell. MMAF binds to tubulin and inhibits its polymerization, resulting in cell cycle arrest in the G2/M phase and apoptosis of tumor cells.
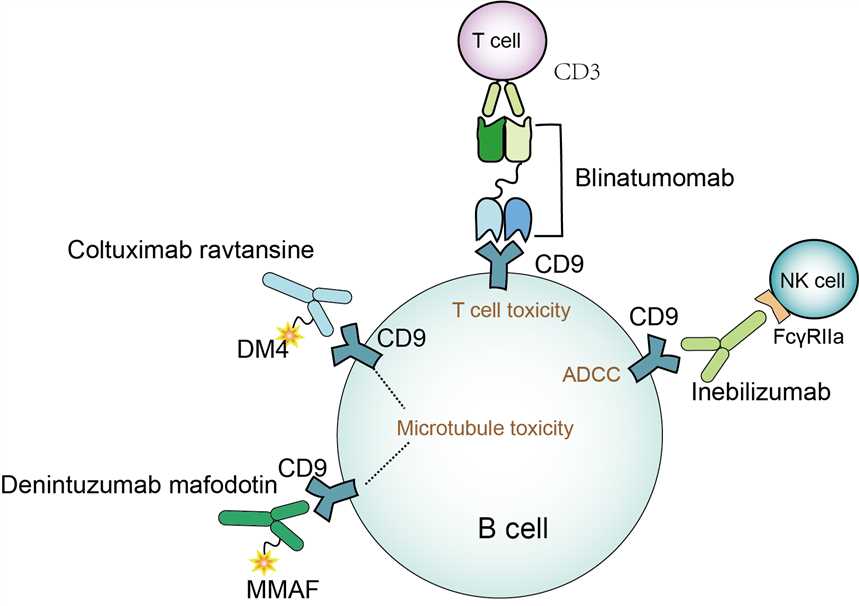
Fig 1. Mechanism of Action of Denintuzumab mafodotin
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

