Ertumaxomab Overview
Introduction of Ertumaxomab
Ertumaxomab, recombinant rat antibody, is a rat-murine hybrid monoclonal antibody designed to treat some types of cancer. It is a so-called trifunctional bispecific antibody (bsAb) which works by linking T-lymphocytes and macrophages to the cancer cells. BsAb combines specificities of two antibodies and simultaneously address different antigens or epitopes. BsAbs with 'two-target' functionality can interfere with multiple surface receptors or ligands associated, for example with kinds of cancers. Ertumaxomab has two antigen-recognition sites: one for CD3, an antigen expressed on mature T cells, and one for HER-2-neu, a tumor-associated antigen that promotes tumor growth.
Mechanism of Action of Ertumaxomab
The proto-oncogene HER2 codes for the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2/neu), which is overexpressed in 20% to 30% of breast cancer patients. HER2/neu overexpression is usually based on gene amplification. It is correlated with a poor prognosis, reducing progression-free outcomes and overall survival. Therefore, HER2/neu is an important target for the treatment of the breast cancers in which it is overexpressed. However, no approved anti-HER2/neu therapy is available for the majority of breast cancer patients, who express HER2/neu at low levels (with scores of 1+ or 2+/fluorescence in situ hybridization–negative). The trifunctional antibody ertumaxomab might simultaneously recruit and activate FcγRI and FcγRIII-positive accessory cells (ie, monocytes, macrophages, natural killer cells, and dendritic cells) through its unique isotype combination (mouse IgG2a and rat IgG2b), leading to the phagocytosis of the tumor cells. Ertumaxomab targets HER2/neu, CD3, and activating Fcγ receptors. The mAb attaches to CD3-expressing T cells and HER-2-neu-expressing tumor cells, selectively cross-linking tumor and immunologic cells which results in the recruitment of cytotoxic T cells to the T cell/tumor cell aggregate and forms a tri-cell complex to cause tumor cell lysis. Consequently, Ertumaxomab may give new treatment opportunities for breast cancer patients with HER2/neu expression.
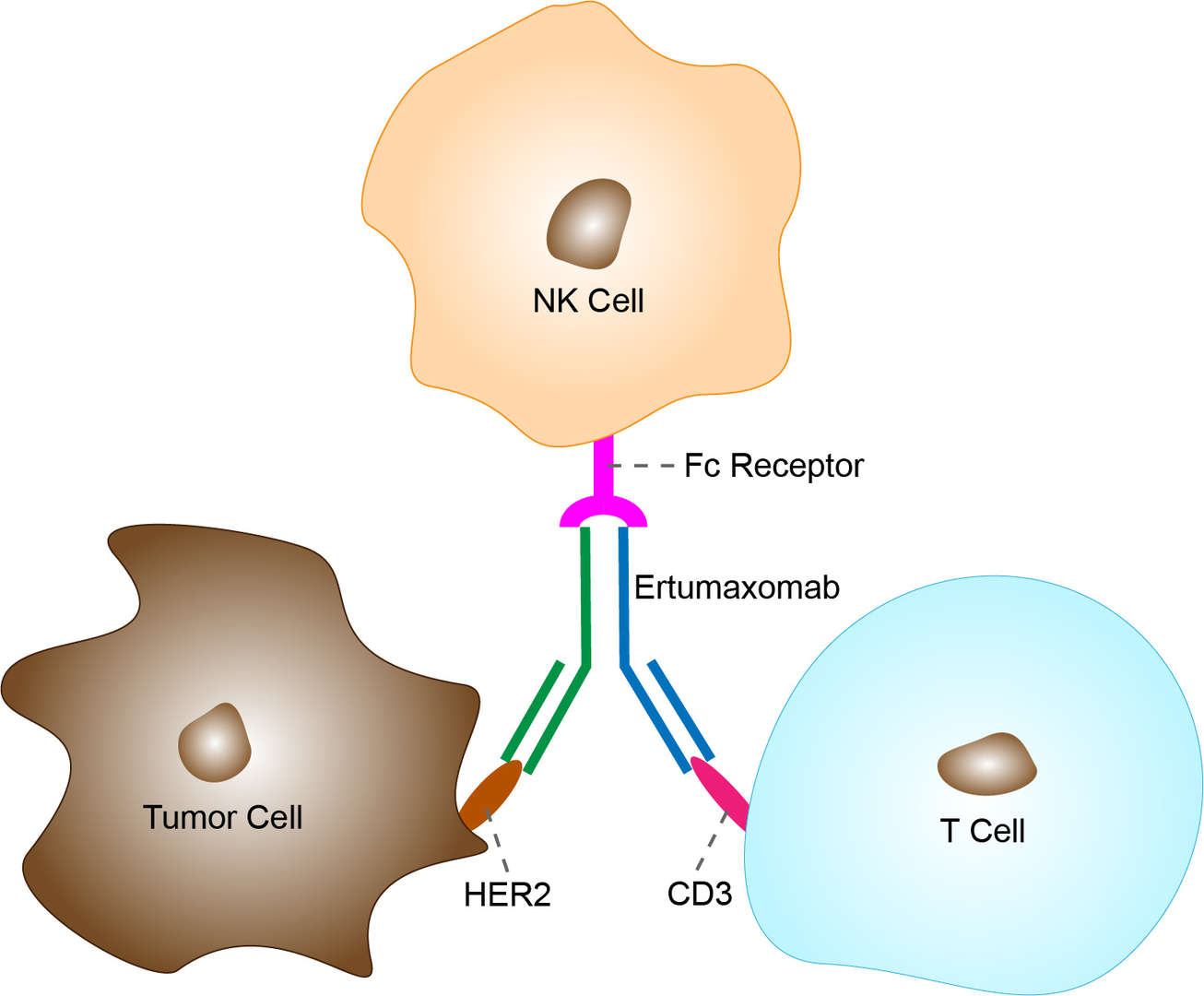 Fig 1. Mechanism of Action of Ertumaxomab
Fig 1. Mechanism of Action of Ertumaxomab
For research use only. Not intended for any clinical use.
This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

